Qcom_Sensor(九)--- 之 aDSP端Sensor Driver流程
- MAIN
- SMGR INIT
- 1. HAL层数据处理
- 2. aDSP层数据处理
- Sensor Probe过程:
- push配置文件
- 获取init log
- 方法一
- 方法二
- 命令行获取sensor数据
- config 文件解析代码
- bug --- sleep 模式下capsensor无效
- bug --- SSI auto detect下允许初始化的sensor个数
- bug --- auto detect every boottime
- bug --- add product keyword to match different sensor configurations
Sensor在最初的时候都是直接挂在处理器上处理的, 其驱动都是和linux或android标准的驱动一样,都是生成对应的设备节点给上层提供数据。
但是,由于sensor可能需要一直处于工作状态,产生了功耗的问题,故而各个芯片厂商才推出了自己的解决方案。
而高通则将sensor的处理放到了application digital signal processor(aDSP)中,这样待机时主处理器休眠以降低功耗,
由这个aDSP在处理音频数据的间隙捎带着就能把sensor的数据处理了,
真是高明。
今天我们就开始窥探一下高通是怎样具体实现的,先看一下高通给出的架构图。
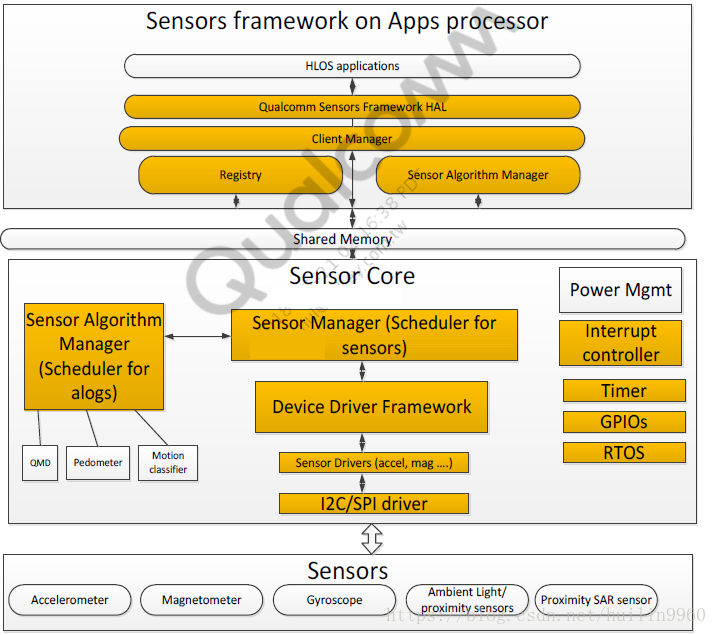
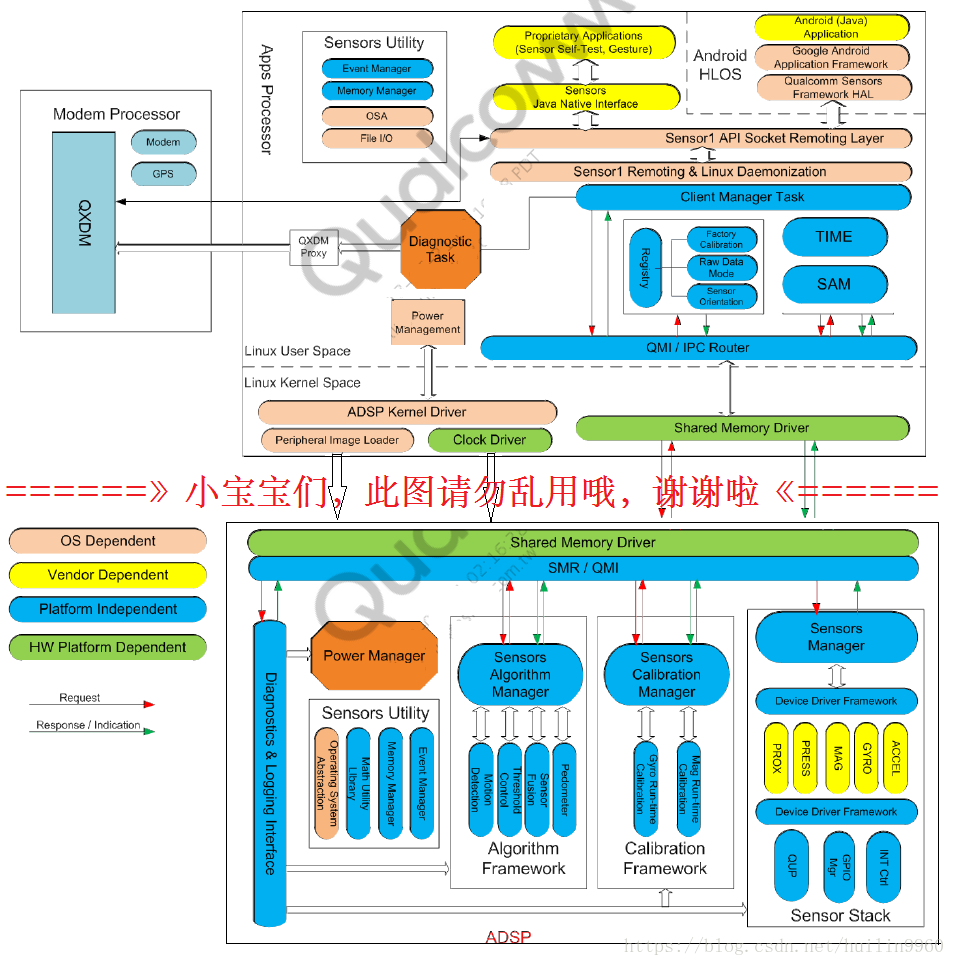
上面两张图完整的展示了高通SSC的架构,其中上半部分为AP,下半部分则是aDSP,
下半部分图我们在之前的dsps架构分析中已经列举了各个组成模块以及相应的功能特点。
我们之前的文章已经分析到SMR/QMI发送消息的流程,接下来我们就要进入Sensor Manager(SMGR),深入驱动程序了。
MAIN
aDSP模块的启动从main函数开始执行,该函数定义在sns_pd.c中,路径为adsp_proc/Sensors/dsps/src/common/。
int main (void)
{
/* Core Init for user PD */
coremain_main();
printf("Core Init for sensors image donen");
/* Sensors Initialization */
sns_init();
return 0; /* never reaches, no user exit handling yet */
}
这里的coremain_main方法是定义在modem端的,在modem_proc/中,我们暂不关注,
而sns_init则是对sensor的初始化过程,其方法主体就是调用sns_init_once方法执行one-time的初始化过程,它会调用各个模块的初始化方法。
static void sns_init_once( void )
{
int i;
INT8U err;
OS_FLAGS flags = 0;
const sns_init_fcn init_ptrs[] = SNS_INIT_FUNCTIONS;
if ( SNS_SUCCESS != sns_heap_init()) {
MSG(MSG_SSID_SNS, DBG_ERROR_PRIO, "Sensors Heap Init failed, using Default heap ID");
sns_heap_id = QURT_ELITE_HEAP_DEFAULT;
}
sns_init_flag_grp = sns_os_sigs_create( SNS_INIT_FLAG_DONE, &err );
SNS_ASSERT(NULL != sns_init_flag_grp);
for( i = 0; NULL != init_ptrs[i]; i++ ) {
//MSG_1(MSG_SSID_QDSP6, DBG_HIGH_PRIO, "Sensors Init : %d", i);
if( SNS_SUCCESS != init_ptrs[i]() ) {
/* Handle error */
//MSG_1(MSG_SSID_QDSP6, DBG_HIGH_PRIO, "Sensors Init FAIL: %d", i);
sns_init_done();
}
while( !(SNS_INIT_FLAG_DONE & flags) ) {
/* Continue polling for the flag until module init is done */
flags = sns_os_sigs_pend( sns_init_flag_grp,
SNS_INIT_FLAG_DONE,
OS_FLAG_WAIT_SET_ANY,
0,
&err );
MSG_1(MSG_SSID_QDSP6, DBG_HIGH_PRIO, "Sensors Init : waiting(%x)", flags);
}
flags = 0;
}
MSG(MSG_SSID_QDSP6, DBG_HIGH_PRIO, "Sensors Init : ///init once completed///");
}
我们又看到了类似的场景了,通过定义的全局SNS_INIT_FUNCTIONS函数指针,依次进行调用。当所有init方法执行完成,发送init done的信号。
我们这里以MSM8960板子的初始化函数定义列表为例,来分析aDSP的初始化流程,如下:
#ifdef FEATURE_MSM8960
# define SNS_INIT_FUNCTIONS
{ sns_memmgr_init, // 内存管理器
sns_init_dsps, // 各种dsps服务的初始化
sns_em_init, // 事件管理器
sns_smr_init, // Message Router用于传递消息(resp/ind)
sns_dl_init, // Dynamic Loading service
sns_smgr_init, // Sensor Manager(核心部分)
sns_scm_init, // 检验管理器
sns_sam_init, // 算法管理器
sns_pm_test_task_init, //
dog_init,
NULL }
其中最重要的当属SMGR的初始化了。
SMGR INIT
SMGR的init方法是直接启动了一个sns_smgr_task,所有的任务都放在task中完成的。
SNS_SMGR_UIMAGE_CODE sns_err_code_e sns_smgr_init(void)
{
sns_os_task_create_ext(sns_smgr_task, NULL,
(OS_STK *)&sns_smgr_task_stack[SNS_MODULE_STK_SIZE_DSPS_SMGR-1],
SNS_MODULE_PRI_DSPS_SMGR,
SNS_MODULE_PRI_DSPS_SMGR,
(OS_STK *)&sns_smgr_task_stack[0],
SNS_MODULE_STK_SIZE_DSPS_SMGR,
(void *)0,
OS_TASK_OPT_STK_CHK | OS_TASK_OPT_STK_CLR |
OS_TASK_OPT_ISLAND,
(uint8_t *)"SNS_SMGR");
return SNS_SUCCESS;
}
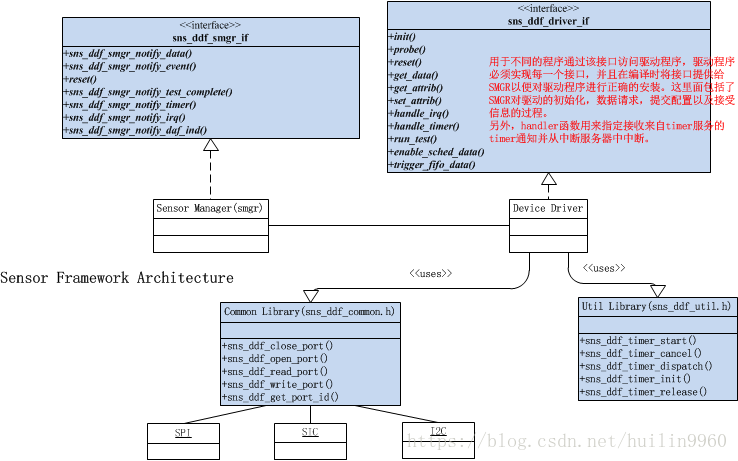
这里我直接给出大致的流程图:

上图中,Communication Library通过I2C以及GPIO,SPI等,直接和sensor device通信了,通过下面的图可以了解这个流程:
I2C挂载图:
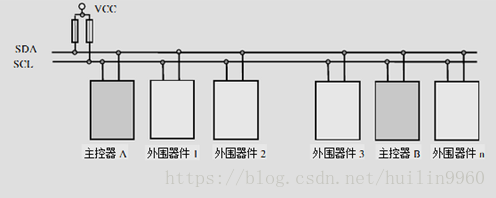
图中,外围期间1,2等便可以是我们的sensor设备或其他可使用I2C通信的电子器件了。
ddf打开的过程如下:
sns_ddf_status_e sns_ddf_open_port( sns_ddf_handle_t* handle, const sns_ddf_port_config_s* cfg )
{
sns_ddf_status_e status = SNS_DDF_SUCCESS;
if ( cfg == NULL || handle == NULL )
{
return SNS_DDF_EINVALID_PARAM;
}
*handle = NULL;
status = sns_ddf_comm_malloc( (void **)handle, sizeof(sns_ddf_sensor_info_s) );
if ( SNS_DDF_SUCCESS != status )
{
SNS_PRINTF_STRING_ERROR_1( SNS_DBG_MOD_DSPS_DDF, "Malloc fail, size = %d",
sizeof(sns_ddf_sensor_info_s) );
return status;
}
switch( cfg->bus )
{
// 根据设备配置的config bus,如果是I2C,则调用sns_ddf_comm_bus_i2c_open,如果是SPI,则调用sns_ddf_comm_bus_spi_open
case SNS_DDF_BUS_I2C:
status = sns_ddf_comm_bus_i2c_open( *handle, cfg );
break;
case SNS_DDF_BUS_SPI:
status = sns_ddf_comm_bus_spi_open( *handle, cfg );
break;
default:
status = SNS_DDF_EINVALID_PARAM;
}
if ( SNS_DDF_SUCCESS != status )
{
SNS_PRINTF_STRING_ERROR_1(SNS_DBG_MOD_DSPS_DDF, "open_port, result = %d", status);
sns_ddf_comm_mfree( *handle );
*handle = NULL;
return SNS_DDF_EBUS;
}
return status;
}
// initializes and configures SPI communication bus.
static sns_ddf_status_e sns_ddf_comm_bus_spi_open
(
sns_ddf_handle_t handle,
const sns_ddf_port_config_s* cfg
)
{
#if SNS_DDF_COMM_BUS_SPI_ENABLE_DRIVER
static const spi_device_id_t spi_bus_instances[] =
{
0,
SPI_DEVICE_1,
SPI_DEVICE_2,
SPI_DEVICE_3,
SPI_DEVICE_4,
SPI_DEVICE_5,
SPI_DEVICE_6,
SPI_DEVICE_7,
SPI_DEVICE_8,
SPI_DEVICE_9,
SPI_DEVICE_10,
SPI_DEVICE_11,
SPI_DEVICE_12,
};
SPI_RESULT result; //spi_errors.h
sns_ddf_sensor_info_s* sns_info = (sns_ddf_sensor_info_s*)handle;
if ( cfg->bus_instance >= ARR_SIZE(spi_bus_instances) )
{
return SNS_DDF_EINVALID_PARAM;
}
/* Initialize member params */
sns_info->bus = SNS_DDF_BUS_SPI;
sns_info->spi_s.dev_id = spi_bus_instances[cfg->bus_instance];
sns_info->spi_s.cfg = cfg->bus_config.spi;
if ( EnableSPI == false )
{
return SNS_DDF_SUCCESS;
}
/* Open SPI port*/
result = spi_open(sns_info->spi_s.dev_id);
if ( result != SPI_SUCCESS )
{
SNS_PRINTF_STRING_ERROR_1( SNS_DBG_MOD_DSPS_DDF, "spi_open fail result=%d", result );
return SNS_DDF_EBUS;
}
//TODO: fake write switching sensor to SPI mode? ------------------------
/* Close device - this only turns the clocks off */
result = spi_close(sns_info->spi_s.dev_id);
if ( result != SPI_SUCCESS )
{
SNS_PRINTF_STRING_ERROR_1( SNS_DBG_MOD_DSPS_DDF, "spi_close fail result=%d", result );
return SNS_DDF_EBUS;
}
#endif
return SNS_DDF_SUCCESS;
}
// Initializes and configures I2C communication bus.
static sns_ddf_status_e sns_ddf_comm_bus_i2c_open
(
sns_ddf_handle_t handle,
const sns_ddf_port_config_s* cfg
)
{
//TODO: table declared twice! Check sns_smgr_hw.c I2cDrv_I2cBusId sns_i2c_bus_table[]
static const I2cDrv_I2cBusId i2c_bus_instances[] =
{
0,
I2CDRV_I2C_1,
I2CDRV_I2C_2,
I2CDRV_I2C_3,
I2CDRV_I2C_4,
I2CDRV_I2C_5,
I2CDRV_I2C_6,
I2CDRV_I2C_7,
I2CDRV_I2C_8,
I2CDRV_I2C_9,
I2CDRV_I2C_10,
I2CDRV_I2C_11,
I2CDRV_I2C_12
};
int32 result;
sns_ddf_sensor_info_s* sns_info = (sns_ddf_sensor_info_s*)handle;
if ( cfg->bus_instance >= ARR_SIZE(i2c_bus_instances) )
{
return SNS_DDF_EINVALID_PARAM;
}
/* Initialize member params */
sns_info->bus = SNS_DDF_BUS_I2C;
sns_info->i2c_s.reg_addr_type = cfg->bus_config.i2c->reg_addr_type;
sns_info->i2c_s.i2c_bus.clntCfg.uSlaveAddr = cfg->bus_config.i2c->slave_addr;
sns_info->i2c_s.i2c_bus.clntCfg.uBusFreqKhz = SNS_DDF_DEFAULT_I2C_BUS_FREQ;
sns_info->i2c_s.i2c_bus.clntCfg.uByteTransferTimeoutUs = SNS_DDF_DEFAULT_BYTE_XFER_TMO;
if ( EnableI2C == false )
{
return SNS_DDF_SUCCESS;
}
if (i2c_bus_instances[cfg->bus_instance] == I2CDRV_I2C_5)
sns_info->i2c_s.i2c_bus.clntCfg.uBusFreqKhz = 100;
/* Obtain the handle for the port. */
result = I2cDrv_Open(i2c_bus_instances[cfg->bus_instance], &sns_info->i2c_s.i2c_bus, 0);
if ( I2C_RES_SUCCESS != result )
{
SNS_PRINTF_STRING_ERROR_1( SNS_DBG_MOD_DSPS_DDF, "I2cDrv_Open, result = %d", result );
return SNS_DDF_EBUS;
}
return SNS_DDF_SUCCESS;
}
由此可见,挂载SPI上的设备终会调用spi_open打开设备,而I2C上的则用I2cDrv_Open来进行处理。
以上便是整个aDSP的流程了,结合代码,相信你会很快掌握这个过程,RTFSC,Go!
App processor 与aDSP端数据流图
AP侧从libsensor1开始的数据流走向如下图所示,其中上层到libsensor1的调用逻辑已经在之前的文章中理清了。无非是通过SensorContext的poll从Queue中读取数据,请自行查找回顾,这里只贴出HAL层的框架图及相关的API供参考。
1. HAL层数据处理
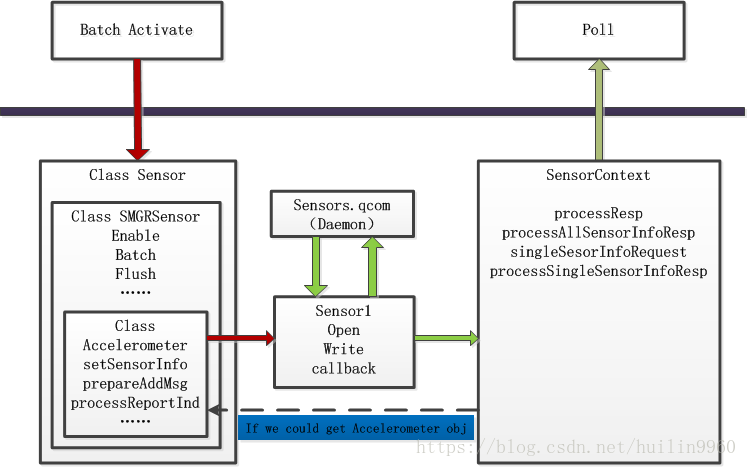
2. aDSP层数据处理

Sensor数据获取方式
Sensor上报数据的三种方式:
-
(Polling)0x00
调用一次get_data后启动timer,等到timer到时间后调用sns_ddf_driver_if_s中指定的handle_timer()函数上报一组传感器数据 -
(DRI)0x80
调用enable_sched_data()启用DRI(Data ReadyInterrupt,数据完成中断),按照set_cycle_time指定的ODR(Output Data Rate,数据输出速率)进行数据采集,采集完成后调用sns_ddf_driver_if_s中指定的handle_irq()函数上报传感器数据。 -
(FIFO)0xD0
调用trigger_fifo_data()函数启动FIFO模式,当数据量到达指定的阈值,触发sns_ddf_smgr_data_notify()函数上报一批数据。
Sensor Probe过程:
// sns_smgr_reg.c
SMGR_STATIC void sns_smgr_parse_reg_devinfo_resp( uint16_t Id, const sns_reg_ssi_devinfo_group_s* devinfo)
{
...
SNS_SMGR_PRINTF2(HIGH, "ssi: probing devinfo_idx[i]: %u[%u]", devinfo_idx, i);
SNS_SMGR_PRINTF3(HIGH, "ssi: bus_instance:%u gpio1:%u slave_addr:0x%x",
devinfo->uuid_cfg[i].i2c_bus, devinfo->uuid_cfg[i].gpio1,
devinfo->uuid_cfg[i].i2c_address );
// 调用dd sensor驱动的probe函数
status = drv_fn_ptr->probe( &dev_access, &memhandler,&num_sensors, &sensor_list );
if( status == SNS_DDF_SUCCESS && num_sensors != 0 )
{
SNS_SMGR_PRINTF2(HIGH, "zch---ssi: devinfo_idx[i]: %u[%u] probe success", devinfo_idx, i);
return;
}
else
SNS_SMGR_PRINTF3(HIGH, "ssi: devinfo_idx[i]: %u[%u] probe failed error=%d", devinfo_idx, i, status);
...
}
push配置文件
For MSM8974, MSM8x26, APQ8084 – /etc/sensor_def_.conf
For MSM8994/MSM8992, MSM8952, MSM8996 – /etc/sensors/sensor_def_.conf
adb root
adb remount
adb shell rm /system/etc/sensors/sensor_def_qcomdev.conf
adb push sensor_def_qcomdev.conf /system/etc/sensors/sensor_def_qcomdev.conf
adb shell chmod 644 /system/etc/sensors/sensor_def_qcomdev.conf
adb shell rm /persist/sensor/sns.reg
adb shell sync
adb reboot
生成的 sns.reg 文件地址
For MSM8974, MSM8x26, APQ8084 – /data/misc/sensors/sns.reg
For MSM8994/92, MSM8952, MSM8996 – /persist/sensors/sns.reg
获取init log
方法一
adb root
adb wait-for-device
adb remount
adb shell rm /persist/sensors/sns.reg
adb shell sync
adb shell stop sensors
adb shell "echo 'related' > /sys/bus/msm_subsys/devices/subsys2/restart_level"
adb shell "echo 'restart' > /sys/kernel/debug/msm_subsys/adsp";
adb shell start sensors'
方法二
adb root
adb wait-for-device
adb remount
adb shell rm /persist/sensors/sns.reg
adb shell sync
adb shell stop sensors
adb shell "echo 'related' > /sys/bus/msm_subsys/devices/subsys2/restart_level"
QXDM 中 send_data 75 37 03 48 00
send_data 75 37 03 48 00
3) adb shell start sensors
命令行获取sensor数据
-r : rate
-d: duration in secound
-s: Sensor ID
-t data_type // 几个数据
sns_cm_test -r 20 -d 1 -s 40 -t 1 测试prox
sns_cm_test -r 20 -d 1 -s 0 -t 0 测试G-sensor
sns_cm_test -r 20 -d 1 -s 10 -t 0测试GYRO
sns_cm_test -r 20 -d 1 -s 20 -t 0测试MAG
#check sensor registry configure:
sns_regedit_ssi -r
#check which sensor init success:
sns_dsps_tc0001
config 文件解析代码
vendor/qcom/proprietary/sensors/dsps/sensordaemon/reg/src/sns_reg_conf_la.c
sns_reg_write_conf_item
bug — sleep 模式下capsensor无效
—— 将数据上传模式改为wakeup
--- a/vendor/qcom/proprietary/sensors/dsps/libhalsensors/src/SAR.cpp
+++ b/vendor/qcom/proprietary/sensors/dsps/libhalsensors/src/SAR.cpp
@@ -18,6 +18,7 @@ SAR::SAR(int handle)
:SMGRSensor(handle)
{
trigger_mode = SENSOR_MODE_EVENT;
+ bWakeUp = true;
}
/*============================================================================
@@ -38,7 +39,8 @@ void SAR::setSensorInfo(sns_smgr_sensor_datatype_info_s_v01* sensor_datatype)
{
HAL_LOG_DEBUG("%s: SAR DTy: %d", __FUNCTION__, sensor_datatype->DataType);
setType(SENSOR_TYPE_SAR);
- setFlags(SENSOR_FLAG_ON_CHANGE_MODE);
+ setFlags(SENSOR_FLAG_ON_CHANGE_MODE|SENSOR_FLAG_WAKE_UP);
+ strlcat(name," -Wakeup",SNS_MAX_SENSOR_NAME_SIZE);
setResolution((float)((float)sensor_datatype->Resolution *
UNIT_CONVERT_Q16));
setMaxRange((float)((float)sensor_datatype->MaxRange *
bug — SSI auto detect下允许初始化的sensor个数
#adsp_proc/Sensors/smgr/src/sns_smgr_sensor_config.h
SNS_SMGR_NUM_SENSORS_DEFINED
bug — auto detect every boottime
diff --git a/Sensors/smgr/src/sns_smgr_reg.c b/Sensors/smgr/src/sns_smgr_reg.c
index ed725ec..65aedf6 100755
--- a/Sensors/smgr/src/sns_smgr_reg.c
+++ b/Sensors/smgr/src/sns_smgr_reg.c
@@ -1733,7 +1733,7 @@
0,
sizeof(sns_reg_ssi_smgr_cfg_group_s));
- ssi_cfg_ptr->maj_ver_no = 1;
+ ssi_cfg_ptr->maj_ver_no = 0;
ssi_cfg_ptr->min_ver_no = 1;
ssi_cfg_ptr->reserved1 = 0;
ssi_cfg_ptr->reserved2 = 0;
@@ -1990,7 +1990,7 @@
sns_smgr.all_init_state = SENSOR_ALL_INIT_CONFIGURED;
}
}
- else if ( (cfg_group_ptr->maj_ver_no != 1) && !valid_cfg )
+ else if ( !valid_cfg )
{
/* Only use the configuration if the major version is 1.
Otherwise autodetect sensors */
bug — add product keyword to match different sensor configurations
add product keyword to match different sensor configurations
Change-Id: I1afbb2b23e0758bc32378330ffba3dafe27e4130
---
diff --git a/dsps/sensordaemon/reg/src/sns_reg_conf_la.c b/dsps/sensordaemon/reg/src/sns_reg_conf_la.c
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 831a2d9..71ac549
--- a/dsps/sensordaemon/reg/src/sns_reg_conf_la.c
+++ b/dsps/sensordaemon/reg/src/sns_reg_conf_la.c
@@ -295,6 +295,7 @@
@param item_id[i]: Item ID
@param item_val[i]: Discovered item val, if any
@param hw_conf[i]: Hardware string selected in the conf file
+ @param product_conf[i]: Product string selected in the conf file
@param platform_conf[i]: Platform string selected in the conf file
@param soc_id_conf[i]: SOC ID string selected in the conf file
@param subtype_conf[i]: Platform subtype string selected in the conf file
@@ -307,6 +308,7 @@
void sns_reg_write_conf_item( int32_t item_id,
uint64_t item_val,
char (*hw_conf)[META_VAL_LEN],
+ char (*product_conf)[META_VAL_LEN],
char (*platform_conf)[META_VAL_LEN],
char (*version_conf)[META_VAL_LEN],
char (*soc_id_conf)[META_VAL_LEN],
@@ -318,6 +320,7 @@
{
int index;
static char hw_string[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX] = "";
+ static char product_string[20] = "";
static char platform_string[20] = "";
static char platform_subtype_string[20] = "";
static char platform_subtype_id_string[20] = "";
@@ -333,6 +336,25 @@
/* get the hw string from property */
property_get("ro.board.platform", hw_string, "");
+
+ /* check the motorola product */
+ fp = sns_fsa_open("/sys/devices/soc0/motorola_product", "r" );
+ if( fp == NULL )
+ {
+ SNS_PRINTF_STRING_ERROR_1( SNS_MODULE_APPS_REG,
+ "motorola_product fopen failed %i", errno );
+ strlcpy(product_string, invalid_str, sizeof(product_string));
+ }
+ else if( fgets(product_string, sizeof(product_string), fp) == NULL )
+ {
+ SNS_PRINTF_STRING_ERROR_1( SNS_MODULE_APPS_REG,
+ "product_string fgets failed %i: %i", errno );
+ strlcpy(product_string, invalid_str, sizeof(product_string));
+ }
+ if( fp != NULL )
+ {
+ sns_fsa_close( fp );
+ }
fp = sns_fsa_open("/sys/devices/soc0/hw_platform", "r" );
if( fp == NULL )
@@ -452,6 +474,12 @@
/* Configuration file set a hardware string, and it doesn't match
this hardware. Abort */
return;
+ }
+ if( ( product_conf[0][0] != 0 ) &&
+ sns_reg_match_conf_item( product_string, product_conf ) ) {
+ /* Configuration file set a product string, and it doesn't match
+ the product string. Abort */
+ return;
}
if( ( platform_conf[0][0] != 0 ) &&
sns_reg_match_conf_item( platform_string, platform_conf ) ) {
@@ -581,6 +609,7 @@
char *buf = malloc(sz);
uint32_t file_version = 0;
char hw_conf[META_MAX_KEY][META_VAL_LEN];
+ char product_conf[META_MAX_KEY][META_VAL_LEN];
char platform_conf[META_MAX_KEY][META_VAL_LEN];
char soc_id_conf[META_MAX_KEY][META_VAL_LEN];
char subtype_conf[META_MAX_KEY][META_VAL_LEN];
@@ -592,6 +621,7 @@
for( key_var = 0; key_var < META_MAX_KEY; key_var++ ) {
hw_conf[key_var][0] = 0x00;
+ product_conf[key_var][0] = 0x00;
platform_conf[key_var][0] = 0x00;
soc_id_conf[key_var][0] = 0x00;
subtype_conf[key_var][0] = 0x00;
@@ -629,7 +659,7 @@
/* Check for an item */
if( true == sns_reg_parse_conf_item( buf, &item_id, &item_val, &item_ver ) ) {
if( item_ver > conf_info->version) {
- sns_reg_write_conf_item( item_id, item_val, hw_conf,
+ sns_reg_write_conf_item( item_id, item_val, hw_conf, product_conf,
platform_conf, version_conf, soc_id_conf,
subtype_conf, subtype_id_conf, soc_rev_conf, &property_conf );
}
@@ -642,6 +672,8 @@
if( sscanf_result > 0 ) {
if( 0 == strncmp( key_meta, "hardware", META_KEY_LEN ) ) {
sns_reg_get_conf_key(buf, hw_conf);
+ } else if( 0 == strncmp( key_meta, "product", META_KEY_LEN ) ) {
+ sns_reg_get_conf_key(buf, product_conf);
} else if( 0 == strncmp( key_meta, "platform", META_KEY_LEN ) ) {
sns_reg_get_conf_key(buf, platform_conf);
} else if( 0 == strncmp( key_meta, "soc_id", META_KEY_LEN ) ) {
最后
以上就是狂野大山最近收集整理的关于Qcom_Sensor(九)--- 之 aDSP端Sensor Driver流程的全部内容,更多相关Qcom_Sensor(九)---内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复