list的使用-----深拷贝
1、问题
一次开发中,使用list的时候,对list的内容进行改变时,出现数据丢失的问题,最后排查数据找到问题的原因,是因为使用list的是浅拷贝,值引用。
2、产生的原因
List<Question> questionList = new ArrayList<>();
Question question1 = new Question();
question1.setQuestionBody("111111111");
questionList.add(question1);
List<Question> questionList= questionList.stream().filter(item -> item.getId().equals(0)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.arraycopy
使用 arrayList.addAll(); 进行数组的生成,结果还是浅拷贝,因为其使用的是System.arraycopy
源码如下:
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
System.arraycopy 就是将新的数组指向的原数组的内存地址
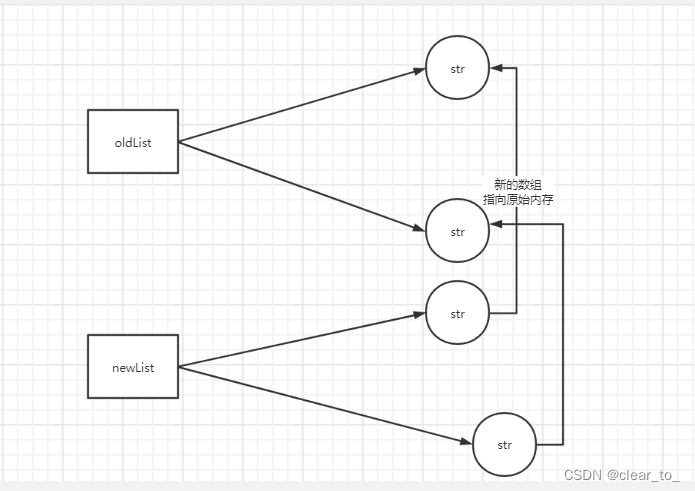
所以是无法实现深拷别,还是浅拷贝,别被别人忽悠。
Arrays.copyOf
源码
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {
return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
查看其源码还是如此的使用的是 System.arraycopy,终究还是浅拷贝。
3、解决
List<Question> newQuestionList = new ArrayList<>();
int index = 0;
for (Question question: questionList) {
Question question5= new Question();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(question,question5);
question5.setId(index);
question5.setQuestionBody(index + "");
newQuestionList.add(question5);
index++;
}
即就是需要重新new一个对象,分配一块新的内存地址,这样新的数组和原来的之间就没有关系,改变新的数组并不会影响原来的数组的内容。
结果

又或者
List<Question> list = questionList.stream().filter(doc -> doc.getQuestionBody().equals("111111111")).map(item -> {
Question question = new Question();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, question);
return question;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
所以使用map去创建一个对象,然后进行收集,生成一个全新的对象,则两个对象之间是没有任何的关系。
结果

4、总结
使用list stream,对原始list修改其中的某些值时,最好生成一个新的list这样就不会造成原数组的值发生改变影响自己的后续处理,因为自己操作的是同一块内存区域。
因此,如果原始数组只是用一次,可以不进行map收集,这样可减少内存的开销、
最后
以上就是勤奋日记本最近收集整理的关于Java list 使用的过程中出现的问题list的使用-----深拷贝的全部内容,更多相关Java内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复