集合迭代器
使用:
public class IteratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add("abc");
collection.add(123);
collection.add("def");
//调用集合的iterator()方法 生成迭代器
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
//使用迭代器遍历集合
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
hasNext()方法,判断当前指针的下一个元素是否为空
next()方法,指针先下移一个位置,下移之后返回该指针所指明的元素
错误写法一
while (iterator.next()!=null){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
结果:跳一个输出,最后一个会报异常NoSuchElementException
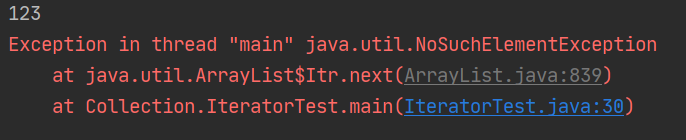
原因:next()方法会使得iterator指针往下移一个位置,所以执行一次循环下移了两次指针,所以出现这种情况
错误写法二
while (collection.iterator().hasNext()){
System.out.println(collection.iterator().next());
}
结果:程序进入死循环,并且一直输出第一个
原因:collection.iterator()方法会生成一个新的迭代器,在循环时,迭代器就一直被生成,当然只要元素不为空,代码可以一直执行。
迭代器中的方法
迭代器中共有三个方法
hasNext() 略
next() 略
remove()
该方法可以移除一个当前指针所指的集合中的元素
注意:生成iterator之后其下移一次指针位置之后不能移动回来,所以想要再次迭代需要再生成一个迭代器
foreach遍历集合
foreach 又叫增强for循环
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add("abc");
collection.add(123);
collection.add("def");
//形式如下
for (Object o : collection) {
System.out.println(o);
}

for(元素类名 元素对象名 :需要迭代的集合){
//逻辑代码
}
foreach和普通for循环的差别
String[] strings = new String[]{"a","b","c"};
for (String string : strings) {
string = "x";
}
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
System.out.println(strings[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
strings[i] = "y";
}
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
System.out.println(strings[i]);
}
结果:使用foreach遍历的,原来的String数组没有改变,而使用普通for循环的数组改变了
结果:使用foreach遍历的,原来的String数组没有改变,而使用普通for循环的数组改变了

原因:foreach迭代中是把数组中的每一个值都赋给了一个新的变量,再拿这个新的变量去修改,原来的数组不会受到影响,而普通的for循环中是拿原来的数组改变值
最后
以上就是苗条期待最近收集整理的关于Java 集合迭代器iterator foreach遍历详解 错误分析!集合迭代器的全部内容,更多相关Java内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复