ROS与底盘的通信协议:
ROS平台与小车底盘通信一般是通过串口
写入串口的内容是 左右轮的速度
从串口中读取到的是小车x,y坐标,方向角,角速度
ROS平台串口处理程序:
主要是写在base_controller.cpp中,ROS向串口发送速度
实现键盘控制小车运动
1、先学习一下这个控制原理
- 按下键盘,teleop_twist_keyboard 包会发布 /cmd_vel 主题发布速度
- 我们在 base_controller 节点订阅/cmd_vel话题,接收速度数据,转换成与底盘通信的格式,写入串口
- 我们在 base_controller 节点读取底盘向串口发送来的里程计数据,进行处理,然后再发布出去,同时更新tf
- 小车底盘接收到串口发送来的速度后,控制电机运转,实现键盘控制小车移动
2、具体操作过程参考https://www.ncnynl.com/archives/201703/1418.html
3、小车控制思想

编码器:
编码器只会告诉你改如何定位,要如何执行,是需要靠PLC之类控制器或者步进电机来实现定位的,编码器好比人的眼睛,知道电机轴或者负载处于当前某个位置,工业上用的一般是光电类型编码器,下边简单说明一下......
这样只要有仪器能读到脉冲个数,就可以知道码盘对应在什么位置了,如果把编码器安装到电机的轴上,电机轴和码盘是刚性连接,两者的位置关系会一一对应,通过读编码器脉冲,就可以知道电机的轴位置。
读取编码器的计数脉冲转成ROS的odom:
移动机器人编码器,安装在左右轮上,机器人地底盘的坐标系为base_link坐标系,里程计坐标系为odom。
文件riki_base.cpp
![]()
发布odom主题
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Odometry.h>
#include <tf/transform_broadcaster.h>
#include <riki_base.h>
RikiBase::RikiBase():
linear_velocity_x_(0),
linear_velocity_y_(0),
angular_velocity_z_(0),
last_vel_time_(0),
vel_dt_(0),
x_pos_(0),
y_pos_(0),
heading_(0)
{
ros::NodeHandle nh_private("~");
odom_publisher_ = nh_.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("raw_odom", 50);
velocity_subscriber_ = nh_.subscribe("raw_vel", 20, &RikiBase::velCallback, this);
nh_private.getParam("linear_scale", linear_scale_);
//ROS_INFO("linear_scale_: %f", linear_scale_);
//velocity 速度 Odometry 里程表
}
void RikiBase::velCallback(const riki_msgs::Velocities& vel)
{
ros::Time current_time = ros::Time::now();
linear_velocity_x_ = vel.linear_x * linear_scale_;
linear_velocity_y_ = vel.linear_y * linear_scale_;
angular_velocity_z_ = vel.angular_z;
vel_dt_ = (current_time - last_vel_time_).toSec();
last_vel_time_ = current_time;
double delta_heading = angular_velocity_z_ * vel_dt_ ; //radians
double delta_x = (linear_velocity_x_ * cos(heading_) - linear_velocity_y_ * sin(heading_)) * vel_dt_ ; //m
double delta_y = (linear_velocity_x_ * sin(heading_) + linear_velocity_y_ * cos(heading_)) * vel_dt_ ; //m
//calculate current position of the robot
x_pos_ += delta_x;
y_pos_ += delta_y;
heading_ += delta_heading;
//calculate robot's heading in quaternion angle
//ROS has a function to calculate yaw in quaternion angle
geometry_msgs::Quaternion odom_quat = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromYaw(heading_);
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped odom_trans; //创建一个tf发布需要使用的TransformStamped类型消息
odom_trans.header.frame_id = "odom";
odom_trans.child_frame_id = "base_footprint";
//robot's position in x,y, and z
odom_trans.transform.translation.x = x_pos_;
odom_trans.transform.translation.y = y_pos_;
odom_trans.transform.translation.z = 0.0;
//robot's heading in quaternion
odom_trans.transform.rotation = odom_quat;
odom_trans.header.stamp = current_time;
//publish robot's tf using odom_trans object
// odom_broadcaster_.sendTransform(odom_trans);
//创建里程计对象
nav_msgs::Odometry odom;
odom.header.stamp = current_time;
odom.header.frame_id = "odom";
odom.child_frame_id = "base_footprint";
//robot's position in x,y, and z
odom.pose.pose.position.x = x_pos_;
odom.pose.pose.position.y = y_pos_;
odom.pose.pose.position.z = 0.0;
//robot's heading in quaternion
odom.pose.pose.orientation = odom_quat;
odom.pose.covariance[0] = 0.001;
odom.pose.covariance[7] = 0.001;
odom.pose.covariance[35] = 0.001;
//linear speed from encoders
odom.twist.twist.linear.x = linear_velocity_x_;
odom.twist.twist.linear.y = linear_velocity_y_;
odom.twist.twist.linear.z = 0.0;
odom.twist.twist.angular.x = 0.0;
odom.twist.twist.angular.y = 0.0;
//angular speed from encoders
odom.twist.twist.angular.z = angular_velocity_z_;
odom.twist.covariance[0] = 0.0001;
odom.twist.covariance[7] = 0.0001;
odom.twist.covariance[35] = 0.0001;
odom_publisher_.publish(odom);
}bring.launch文件
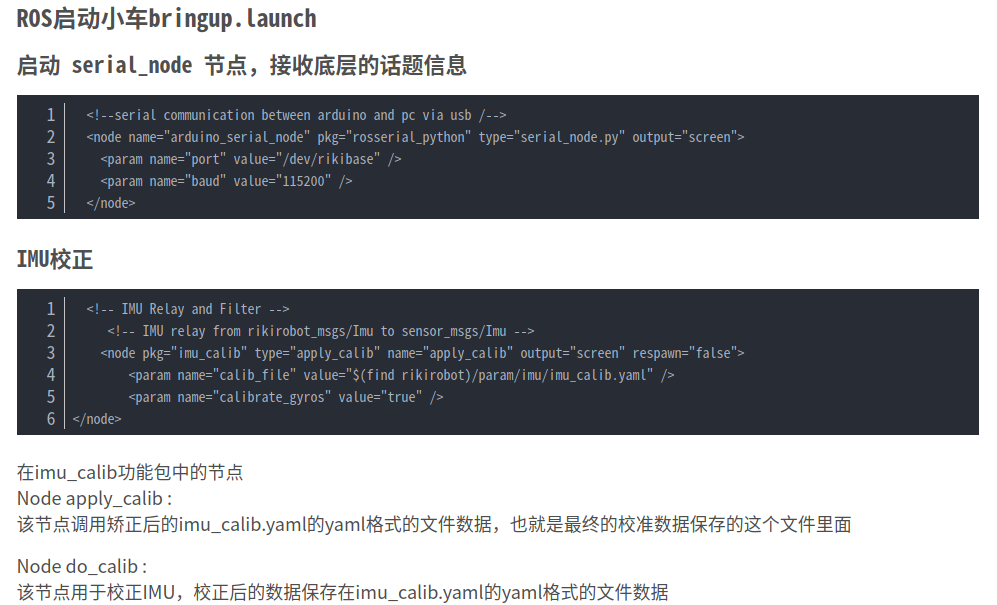



校准过程:参考文章
先校准imu,线速度、角速度
Rikirobot的线速度是通过电机转动+编码器计数+PID速度调节反馈,来完成线速度的计算
######################################分割线#######################################


base_controller节点将接收到的cmd_vel速度信息转换为自定义的结构体或union类型的数据(自定义的数据类型中可以包含校验码等其它信息),并通过串口发送控制速度信息(speed_buf)或读取机器人传回的速度信息 (speed_buf_rev)。base_controller节点正确读取到底层(比如嵌入式控制板)传回的速度后进行积分,计算出机器人的估计位置和姿态,并将里程计信息和tf变换发布出去。
最后
以上就是紧张枕头最近收集整理的关于ROSNOTE : 上下层衔接的原理,未完的全部内容,更多相关ROSNOTE内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复