location匹配顺序
示例配置代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71user root root; worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; #worker_rlimit_nofile 655350; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; client_max_body_size 1024m; #gzip on; server { listen 8090; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } location /aa-web { #root /home/abc/nginx/html; index index.html index.htm; try_files $uri $uri/ /aa-web/index.html; } location ^~ /aa-server { proxy_pass http://192.168.1.80:18081; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; chunked_transfer_encoding off; client_max_body_size 100m; # rewrite ^/aa-server/?(.*)$ /$1 break; #proxy_port off; #proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; } } }
nginx有两层指令来匹配请求 URI 。第一个层次是 server 指令,它通过域名、ip 和端口来做第一层级匹配,当找到匹配的 server 后就进入此 server 的 location 匹配。
location 的匹配并不完全按照其在配置文件中出现的顺序来匹配,请求URI 会按如下规则进行匹配:
1
2
3
4
5
6
71、先精准匹配 = ,精准匹配成功则会立即停止其他类型匹配; 2、没有精准匹配成功时,进行前缀匹配。先查找带有 ^~ 的前缀匹配,带有 ^~ 的前缀匹配成功 则立即停止其他类型匹配,普通前缀匹配(不带参数 ^~ )成功则会暂存,继续查找正则匹配; 3、= 和 ^~ 均未匹配成功前提下,查找正则匹配 ~ 和 ~* 。当同时有多个正则匹配时,按其在配置文件中出现的 先后顺序优先匹配,命中则立即停止其他类型匹配; 4、所有正则匹配均未成功时,返回步骤 2 中暂存的普通前缀匹配(不带参数 ^~ )结果
location 支持的语法 location [=||*|^~|@] pattern { … },乍一看还挺复杂的,来逐个看一下。
以上规则简单总结就是优先级从高到低依次为(序号越小优先级越高):
1
2
3
4
5
6
71. location = # 精准匹配 2. location ^~ # 带参前缀匹配 3. location ~ # 正则匹配(区分大小写) 4. location ~* # 正则匹配(不区分大小写) 5. location /a # 普通前缀匹配,优先级低于带参数前缀匹配。 6. location / # 任何没有匹配成功的,都会匹配这里处理
location修饰符类型
「=」 修饰符:要求路径完全匹配
1
2
3
4
5
6
7server { server_name website.com; location = /abcd { […] } }
- http://website.com/abcd匹配
- http://website.com/ABCD可能会匹配 ,也可以不匹配,取决于操作系统的文件系统是否大小写敏感(case-sensitive)。ps: Mac 默认是大小写不敏感的,git 使用会有大坑。
- http://website.com/abcd?param1¶m2匹配,忽略 querystring
- http://website.com/abcd/不匹配,带有结尾的/
- http://website.com/abcde不匹配
「~」修饰符:区分大小写的正则匹配
1
2
3
4
5
6
7server { server_name website.com; location ~ ^/abcd$ { […] } }
^/abcd$这个正则表达式表示字符串必须以/开始,以$结束,中间必须是abcd
- http://website.com/abcd匹配(完全匹配)
- http://website.com/ABCD不匹配,大小写敏感
- http://website.com/abcd?param1¶m2匹配
- http://website.com/abcd/不匹配,不能匹配正则表达式
- http://website.com/abcde不匹配,不能匹配正则表达式
「~*」不区分大小写的正则匹配
1
2
3
4
5
6
7server { server_name website.com; location ~* ^/abcd$ { […] } }
- http://website.com/abcd匹配 (完全匹配)
- http://website.com/ABCD匹配 (大小写不敏感)
- http://website.com/abcd?param1¶m2匹配
- http://website.com/abcd/ 不匹配,不能匹配正则表达式
- http://website.com/abcde 不匹配,不能匹配正则表达式
「^~」修饰符:前缀匹配
如果该 location 是最佳的匹配,那么对于匹配这个 location 的字符串, 该修饰符不再进行正则表达式检测。注意,这不是一个正则表达式匹配,它的目的是优先于正则表达式的匹配
查找的顺序及优先级
当有多条 location 规则时,nginx 有一套比较复杂的规则,优先级如下:
1
2
3
4
5- 精确匹配 = - 前缀匹配 ^~(立刻停止后续的正则搜索) - 按文件中顺序的正则匹配 ~或~* - 匹配不带任何修饰的前缀匹配。
这个规则大体的思路是
先精确匹配,没有则查找带有 ^~的前缀匹配,没有则进行正则匹配,最后才返回前缀匹配的结果(如果有的话)
案例分析
案例 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11server { server_name website.com; location /doc { return 701; # 用这样的方式,可以方便的知道请求到了哪里 } location ~* ^/document$ { return 702; # 用这样的方式,可以方便的知道请求到了哪里 } }
curl -I website.com:8080/document HTTP/1.1 702
按照上述的规则,第二个会有更高的优先级
案例2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10server { server_name website.com; location /document { return 701; } location ~* ^/document$ { return 702; } }
curl -I website.com:8080/document
第二个匹配了正则表达式,优先级高于第一个普通前缀匹配
案例 3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10server { server_name website.com; location ^~ /doc { return 701; } location ~* ^/document$ { return 702; } }
curl http://website.com/document HTTP/1.1 701
第一个前缀匹配^~命中以后不会再搜寻正则匹配,所以会第一个命中
案例 4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10server { server_name website.com; location /docu { return 701; } location /doc { return 702; } }
curl -I website.com:8080/document 返回 HTTP/1.1 701,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10server { server_name website.com; location /doc { return 702; } location /docu { return 701; } }
curl -I website.com:8080/document 依然返回 HTTP/1.1 701
前缀匹配下,返回最长匹配的 location,与 location 所在位置顺序无关
案例 5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13server { listen 8080; server_name website.com; location ~ ^/doc[a-z]+ { return 701; } location ~ ^/docu[a-z]+ { return 702; } }
curl -I website.com:8080/document 返回 HTTP/1.1 701
把顺序换一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13server { listen 8080; server_name website.com; location ~ ^/docu[a-z]+ { return 702; } location ~ ^/doc[a-z]+ { return 701; } }
curl -I website.com:8080/document 返回 HTTP/1.1 702
正则匹配是使用文件中的顺序,找到返回
常见问题
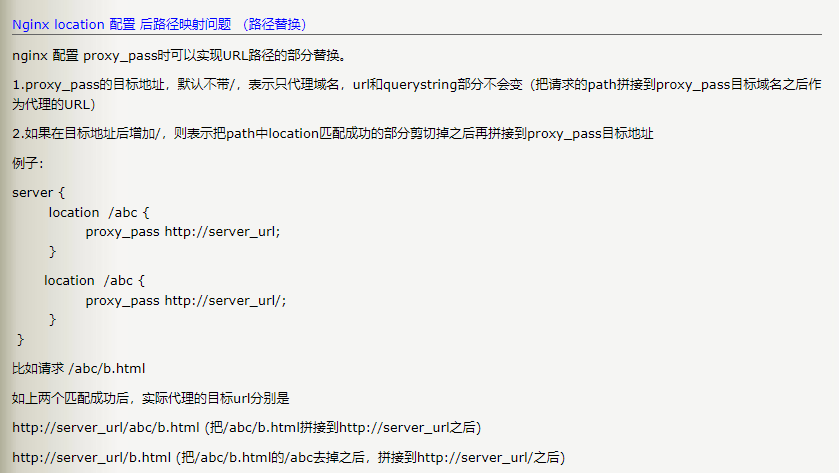
1、location 路径替换
最后
以上就是玩命小海豚最近收集整理的关于Nginx location 匹配location匹配顺序的全部内容,更多相关Nginx内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。







发表评论 取消回复