一、读写锁的工作原理是:
- 当「写锁」没有被线程持有时,多个线程能够并发地持有读锁,这大大提高了共享资源的访问效率,因为「读锁」是用于读取共享资源的场景,所以多个线程同时持有读锁也不会破坏共享资源的数据。
- 但是,一旦「写锁」被线程持有后,读线程的获取读锁的操作会被阻塞,而且其他写线程的获取写锁的操作也会被阻塞。
所以说,写锁是独占锁,因为任何时刻只能有一个线程持有写锁,类似互斥锁和自旋锁,而读锁是共享锁,因为读锁可以被多个线程同时持有。
知道了读写锁的工作原理后,我们可以发现,读写锁在读多写少的场景,能发挥出优势。
另外,根据实现的不同,读写锁可以分为「读优先锁」和「写优先锁」。
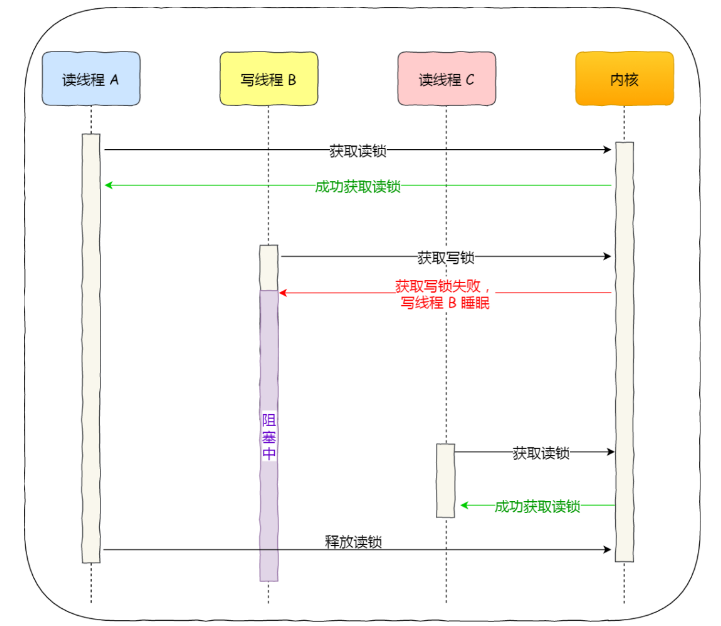
1、读优先锁期望的是,读锁能被更多的线程持有,以便提高读线程的并发性,它的工作方式是:当读线程 A 先持有了读锁,写线程 B 在获取写锁的时候,会被阻塞,并且在阻塞过程中,后续来的读线程 C 仍然可以成功获取读锁,最后直到读线程 A 和 C 释放读锁后,写线程 B 才可以成功获取读锁。如下图:
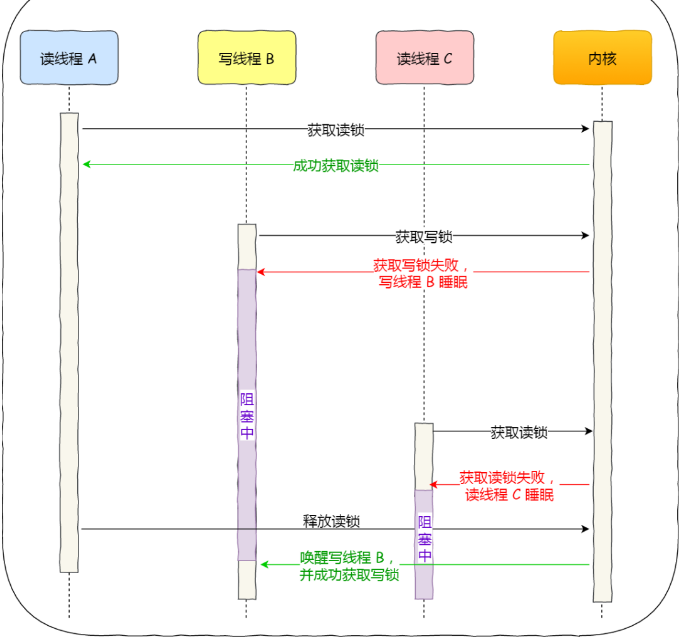
2、而写优先锁是优先服务写线程,其工作方式是:当读线程 A 先持有了读锁,写线程 B 在获取写锁的时候,会被阻塞,并且在阻塞过程中,后续来的读线程 C 获取读锁时会失败,于是读线程 C 将被阻塞在获取读锁的操作,这样只要读线程 A 释放读锁后,写线程 B 就可以成功获取读锁。如下图:
读优先锁对于读线程并发性更好,但也不是没有问题。我们试想一下,如果一直有读线程获取读锁,那么写线程将永远获取不到写锁,这就造成了写线程「饥饿」的现象。
写优先锁可以保证写线程不会饿死,但是如果一直有写线程获取写锁,读线程也会被「饿死」。
既然不管优先读锁还是写锁,对方可能会出现饿死问题,那么我们就不偏袒任何一方,搞个「公平读写锁」。
公平读写锁比较简单的一种方式是:用队列把获取锁的线程排队,不管是写线程还是读线程都按照先进先出的原则加锁即可,这样读线程仍然可以并发,也不会出现「饥饿」的现象。
转载自
二、自己实现读写锁
对于共享数据的操作无非读和写,多线程条件下,对于共享资源是否冲突,如下图:
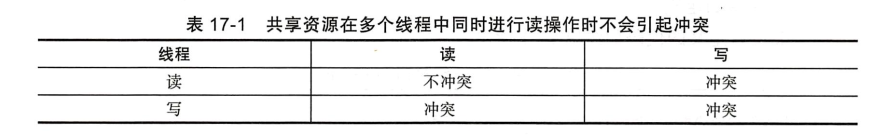
如上可以看出对于写操作是不需要加锁的,这样可以很大提升性能;写操作都需要具有排他方式的加锁。
public class ReadWriteLock {
//等待读操作线程数
private int watingReades;
//正在读得线程数,这里支持多线程同时读取
private int readeingReades;
//等待写的线程数
private int wateingWrites;
//正在写的线程数,写操作冲突所以支持单线程操作,所以数量不能大于1
private int writingWrites;
//操作偏好,true:偏向于写线程 false:偏向于读线程
private boolean preferWriter;
public ReadWriteLock() {
//默认偏向于写线程
this(true);
}
public ReadWriteLock(boolean preferWriter) {
this.preferWriter = preferWriter;
}
//读锁
public synchronized void lockReade() throws InterruptedException {
//等待写线程数量增加,使用finally保证一定执行
watingReades++;
try {
//正在写操作 或 有等待写线程并且偏向于写,则无法获取读锁,被挂起
while (writingWrites > 0 || (preferWriter && wateingWrites > 0)) {
this.wait();
}
//成功获取读锁,正在写线程数量增加
readeingReades++;
}finally {
watingReades--;
}
}
public synchronized void unlockReade(){
readeingReades--;
//为了保证读写锁获取的概率一样
this.preferWriter = true;
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void lockWrite() throws InterruptedException {
wateingWrites++;
try{
//正在读操作或正在写操作,则进入this的waiter set中而被阻塞
while (readeingReades > 0 || writingWrites > 0){
this.wait();
}
writingWrites++;
}finally {
wateingWrites--;
}
}
public synchronized void unlockWrite() {
writingWrites--;
//为了保证读写锁获取的概率一样
this.preferWriter = false;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ShareData {
private final char[] buffer;
private ReadWriteLock lock = new ReadWriteLock();
public ShareData(int size) {
buffer = new char[size];
for (int i = 0 ;i < size ; i++){
buffer[i] = 'c';
}
}
public char[] rader() throws InterruptedException {
char[] chars = new char[buffer.length];
try {
lock.lockReade();
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length; i++) {
chars[i] = buffer[i];
}
} finally {
lock.unlockReade();
}
slowly();
return chars;
}
public void write(char c) throws InterruptedException {
try{
lock.lockWrite();
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length; i++) {
buffer[i] = c;
}
slowly();
}finally {
lock.unlockWrite();
}
}
private void slowly(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class ReadeThread extends Thread {
private final ShareData data;
public ReadeThread(ShareData data){
this.data=data;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
char[] rader = data.rader();
System.out.println(currentThread()+" reade "+ String.valueOf(rader));
}
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
}
public class WriteThread extends Thread {
private final ShareData data;
private final String filler;
private int index;
public WriteThread(ShareData data,String filler){
this.data=data;
this.filler=filler;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
char c = writeChar();
System.out.println(currentThread()+" write "+ c);
}
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
private char writeChar() throws InterruptedException {
char c = filler.charAt(index);
data.write(c);
index++;
if(index >= filler.length())
index = 0;
return c;
}
}
public class ReadWriteTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareData shareData = new ShareData(10);
new ReadeThread(shareData).start();
new ReadeThread(shareData).start();
new ReadeThread(shareData).start();
new ReadeThread(shareData).start();
new ReadeThread(shareData).start();
new WriteThread(shareData,"qazwsxewdcv").start();
new WriteThread(shareData,"QAZWSXEWDCV").start();
}
}
最后
以上就是大胆心情最近收集整理的关于读写分离锁,读写锁设计模式的全部内容,更多相关读写分离锁内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复