Elastic Stack系列--ElasticSearch基础
- 1.Elastic Stack简介
- 2.ElasticSearch
- 2.1.简介
- 2.2.安装
- 2.2.1.非docker安装
- 2.2.2.docker安装
- 2.2.3.elastic-search-head安装
- 2.3.基本概念
- 2.4.Restful API
- 2.4.1.创建和删除非结构化索引
- 2.4.2.插入数据
- 2.4.2.1.指定id
- 2.4.2.2.自动生成id
- 2.4.3.更新数据
- 2.4.3.1.覆盖
- 2.4.3.2.局部更新
- 2.4.4.删除数据
- 2.4.5.搜索数据
- 2.4.5.1.根据id搜索数据
- 2.4.5.2.搜索全部数据
- 2.4.5.3.关键字搜索数据
- 2.4.6.DSL搜索
- 2.4.7.高亮显示
- 2.4.8.聚合
- 2.5.核心内容
- 2.5.1.文档
- 2.5.2.查询响应
- 2.5.2.1.pretty
- 2.5.2.2.指定响应字段
- 2.5.3.判断文档是否存在
- 2.5.4.批量操作
- 2.5.4.1.批量查询
- 2.5.4.2._bulk操作
- 2.5.4.2.1.批量插入数据
- 2.5.4.2.2.批量删除
- 2.5.5.分页
- 2.5.6.映射
- 2.5.7.结构化查询
- 2.5.7.1.term查询
- 2.5.7.2.terms查询
- 2.5.7.3.range查询
- 2.5.7.4.exists查询
- 2.5.7.5.match查询
- 2.5.7.6.bool查询
- 2.5.8.过滤查询
- 2.6.分词
- 2.6.1.分词介绍
- 2.6.2.分词API
- 2.6.3.内置分词器
- 2.6.3.1.Standard
- 2.6.3.2.Simple
- 2.6.3.3.Whitespace
- 2.6.3.4.Stop
- 2.6.3.5.Keyword
- 2.6.4.中文分词
- 2.6.4.1.自定义词汇
1.Elastic Stack简介
ELK实际上是三款软件的简称,分别是ElasticSearch,Logstash,Kibana组成.在发展的过程中,又有了新成员Beats的加入,所以就形成了Elastic Stack.所以说,ELK是旧的称呼,Elastic Stack是新的名字.

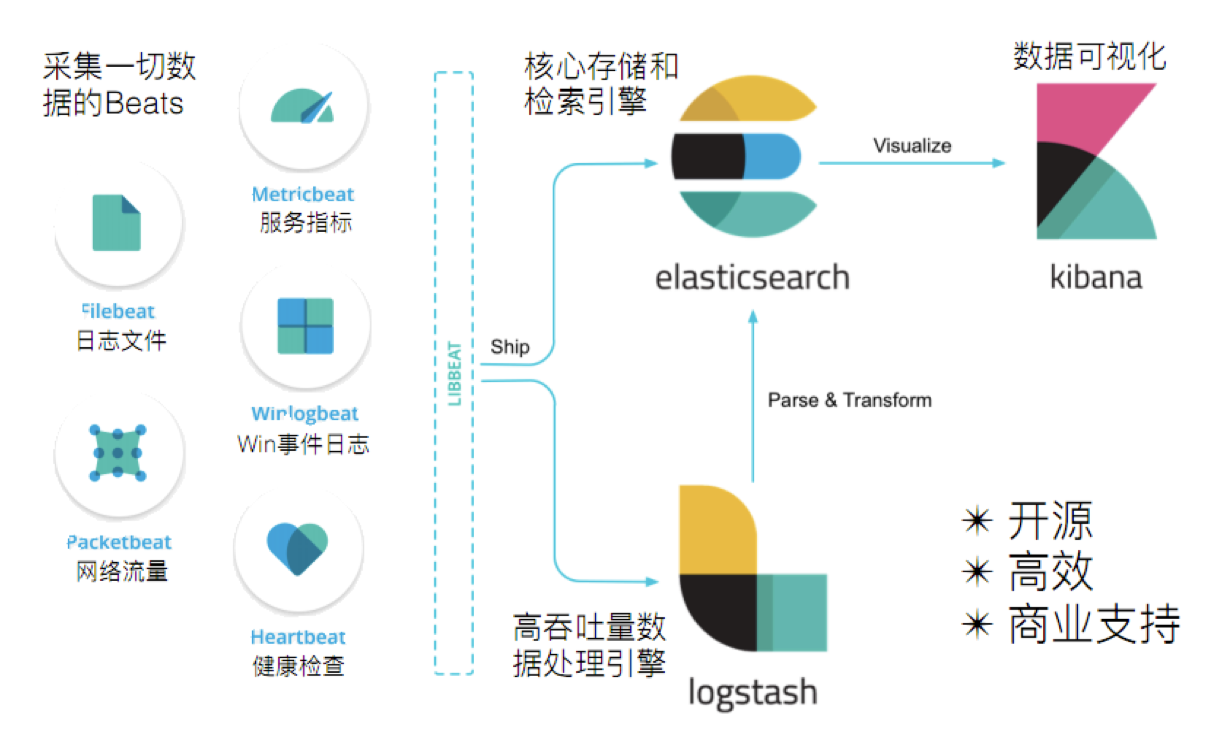
- ElasticSearch:ELasticSearch基于Java,是个开源分布式搜索引擎,它的特点有:分布式,零配置,自动发现,索引自动分片.索引自动分片,索引副本机制,Restful风格接口,多数据源,自动搜索负载等;
- Logstash:Logstash是基于Java的,是一个开源的用于收集,分析和存储日志的工具;
- Kibana:Kinbana基于Node.js,也是一个开源和免费的工具,Kibana可以为Logstash和ElasticSearch提供的日志分析友好的Web界面,可以汇总,分析和搜索重要数据日志.
- Beats:Beats是elastic公司开源的一款采集系统监控数据的代理agent,是在被监控服务器上以客户端形成运行的数据收集器的统称,可以直接把数据发送给ElasticSearch或者通过Logstash发送给ElasticSearch,然后进行后续的数据分析活动.Beats由如下组成:
- Packetbeat:是一个网络数据包分析器,用于监控,收集网络流量信息,Packetbeat嗅探服务器之间的流量,解析应用层协议,并关联到消息的处理,其支持ICMP(v4 and v6),DNS,HTTP,MySQL,PostgreSQL,Redis.MongoDB,Memcache等协议;
- Filebeat:用于监控,收集服务器日志文件,其已取代Logstash forwarder;
- Metribeat:可定期获取外部系统的监控指标信息,其可以监控,收集Apache,HAProxy,MongoDB,MySQL,Nginx,PostgreSQL,Redis,System,Zookeeper等服务;
- Winlogbeat:用于监控,收集Windows系统的日志信息;
2.ElasticSearch
2.1.简介
ELasticSearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器,它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口.ElasticSearch是用于Java开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是当前流行的企业级搜索引擎,设计用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜搜,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便;
我们建立一个网站或应用程序,并要添加搜索,但是想要完成搜索工作的创建是非常困难的.我们希望搜搜索决方案要运行速度快,我们希望能有一个完全免费的搜索模式,我们希望能够简单地使用JSON通过HTTP来索引数据,我们希望我们的搜索服务始终可用,我们希望能够从一台开始并扩展到数百台,我们要实时搜索,我们要简单的多租户,我们希望建立一个云的解决方案.因此我们利用ElasticSearch来解决所有这些问题及可能出现的更多其它问题.
2.2.安装
ElasticSearch的发展是非常快速的,所以在ES5.0之前,ELK的各个版本都不统一,出现了版本号混乱的状态.所以从5.0开始,所有Elastic Stack中的项目全部统一版本号,目前我们使用6.5.4;
2.2.1.非docker安装
2.2.2.docker安装
docker pull elasticsearch:6.5.4
docker create --name elasticsearch --net host -e "discovery.type=single-node" -e "network.host=172.16.124.131" elasticsearch:6.5.4
docker start elasticsearch
docker logs elasticsearch
需要说明的是:此docker安装是开发模式,并没有配置目录挂载等内容,集群环境后续再使用
2.2.3.elastic-search-head安装
docker pull mobz/elasticsearch-head:5
docker create --name elasticsearch-head -p 9100:9100 mobz/elasticsearch-head:5
docker start elasticsearch-head
注意:由于前后端分离开发,所以会存在跨域问题,需要在服务端做CORS的配置,如下所示,通过chrome插件安装的方式不存在该问题.
vim elasticsearch.yml
http.cors.enabled:true
http.cors.allow-origin:"*"
2.3.基本概念
- 索引
- 索引(index)是ElasticSearch对逻辑数据的逻辑存储,所以它可以分为更小的部分;
- 可以把索引看成关系型数据库的表,索引的结构是为快速有效的全文索引准备的,特别是它不存储原始值;
- ElasticSearch可以把索引存放在一台机器或者分散在多台服务器上,每个索引有一或多个分片(shard),每个分片有多个副本(replica);
- 文档
- 存储在ElasticSearch中的主要实体叫文档(document),用关系型数据库来类比的话,一个文档相当于数据库表中的一行记录;
- ElasticSearch和MongoDB中的文档类似,都可以有不同的结构,但ElasticSearch的文档中,相同字段必须有相同的类型;
- 文档由多个字段组成,每个字段可能多次出现在一个文档里,这样的字段叫做多值字段;
- 每个字段的类型,可以是文本,数值,日期等,字段类型也可以是复杂类型,一个字段包含其他子文档或者数组;
- 映射
- 所有文档写进索引之前都会先进行分析,如何将输入的文本风分割成词条,哪些词条又会被过滤,这种行为叫做映射(mapping),一般由用户自己定义规则;
- 文档类型
- 在ElasticSearch中,一个索引对象可以存储很多不同用途的对象,例如,一个博客应用可以保存文章和评论;
- 不同的文档类型不能为相同的属性设置不同的类型,例如,在同一索引中的所有文档类型中,一个叫title的字段必须具有相同的类型;
2.4.Restful API
在ElasticSearch中,提供了功能丰富的Restful API的操作,包括基本的CRUD,创建索引,删除索引等操作;
2.4.1.创建和删除非结构化索引
在Lucene中,创建索引是需要定义字段名称以及字段的类型的,在ElasticSearch中提供了非结构化的索引,就是不需要创建索引结构,即可写入数据到索引中,实际上在ElasticSearch底层会进行结构化操作,此操作对用户是透明的.
创建索引
PUT http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke
{
"settings":{
"index":{
"number_of_shards":"2",
"number_of_replicas":"0"
}
}
}
删除索引
DELETE http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke
{
"acknowledged":true
}
2.4.2.插入数据
2.4.2.1.指定id
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/(索引)/(类型)/(id)
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/1001
#请求数据
{
"id":1001,
"name":"张三",
"age":20,
"sex":"男"
}
#响应数据
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1
}
2.4.2.2.自动生成id
同样我们也可以不指定id插入数据,我们可以看出它已经自动生成id了.
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user
#请求数据
{
"id":1002,
"name":"李四",
"age":20,
"sex":"男"
}
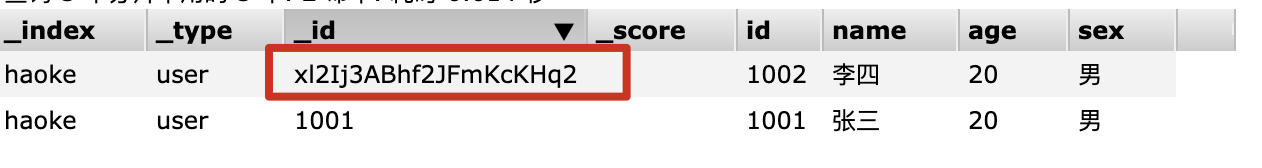
注意:1.URL后面的id是文档id,请求数据中的id是业务id,这两个id是完全不一样的.
2.非结构化的索引,不需要事先创建,直接插入数据默认创建索引.
2.4.3.更新数据
2.4.3.1.覆盖
在ElasticSearch中,文档数据是不能被修改的,但是可以通过覆盖的方式进行更新;
PUT http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/1001
{
"id":1002,
"name":"王五",
"age":20,
"sex":"男"
}
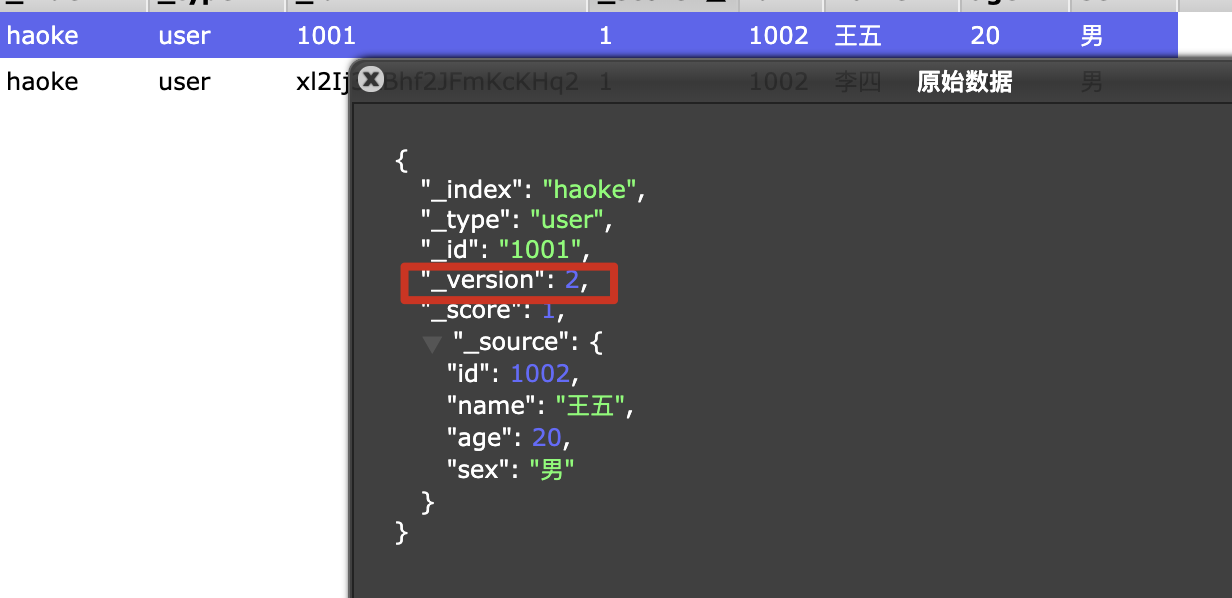
我们可以看到,数据已经更新了,并且版本进行了+1.
2.4.3.2.局部更新
问题来了,可以局部进行更新吗?答案是可以的,之前我们讲的是文档数据不能进行更新,其实是这样的:
- 第一步:从旧文档中检索出JSON;
- 第二步:修改它;
- 第三步:删除旧文档;
- 第四步:索引新文档;
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/1001/_update
#请求数据
{
"doc":{
"name":"赵柳"
}
}
#响应数据
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_version": 3,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 2,
"_primary_term": 1
}
2.4.4.删除数据
DELETE http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/1001
注意:如果删除一条不存在的数据,会响应404,删除一个文档也不会立即从磁盘上移除,它只是被标记成已删除,ElasticSearch将会在你之后添加更多索引的时候才会在后台进行删除内容的清理.
2.4.5.搜索数据
2.4.5.1.根据id搜索数据
GET http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/1001
#响应数据
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
}
2.4.5.2.搜索全部数据
GET http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search
#响应数据(默认返回10条数据)
{
"took": 7,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "xl2Ij3ABhf2JFmKcKHq2",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"id": 1002,
"name": "李四",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
}
]
}
}
2.4.5.3.关键字搜索数据
#查询姓名是张三的用户
GET http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search?q=name:张三
#响应数据
{
"took": 29,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 0.5753642,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_score": 0.5753642,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
}
]
}
}
2.4.6.DSL搜索
ElasticSearch提供丰富且灵活的查询语言叫做DSL查询,它允许你构建更加复杂,强大的查询.**DSL(Domain Specific Language特定领域语言)**以JSON请求体的形式出现.
1.查询年龄为20岁的用户
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search
#请求体
{
"query":{
"match":{
"age":20
}
}
}
#响应体
{
"took": 4,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "xl2Ij3ABhf2JFmKcKHq2",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"id": 1002,
"name": "李四",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
}
]
}
}
2.查询年龄大于15岁的男性用户
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search
#请求体
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"filter":{
"range":{
"age":{
"gt":15
}
}
},
"must":{
"match":{
"sex":"男"
}
}
}
}
}
#响应体
{
"took": 28,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 3,
"max_score": 0.6931472,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1002",
"_score": 0.6931472,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_score": 0.2876821,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "xl2Ij3ABhf2JFmKcKHq2",
"_score": 0.2876821,
"_source": {
"id": 1002,
"name": "李四",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
}
]
}
}
3.全文搜索
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search
#请求体
{
"query":{
"match":{
"name":"张三 网五"
}
}
}
#响应体
{
"took": 5,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 1.3862944,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1003",
"_score": 1.3862944,
"_source": {
"id": 1003,
"name": "网五",
"age": 10,
"sex": "女"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_score": 0.5753642,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
}
]
}
}
2.4.7.高亮显示
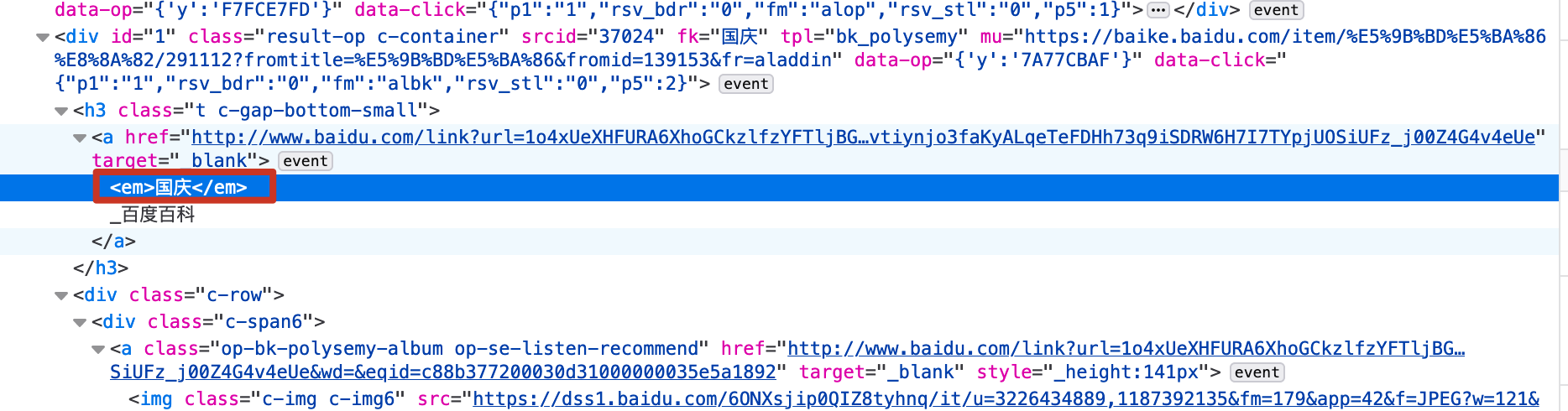
我们可以通过查看百度的前端源码,发现百度是通过加上<em>标签来实现高亮
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search
#请求体
{
"query":{
"match":{
"name":"张三 网五"
}
},
"highlight":{
"fields":{
"name":{}
}
}
}
#响应体
{
"took": 86,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 1.3862944,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1003",
"_score": 1.3862944,
"_source": {
"id": 1003,
"name": "网五",
"age": 10,
"sex": "女"
},
"highlight": {
"name": [
"<em>网</em><em>五</em>"
]
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_score": 0.5753642,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
},
"highlight": {
"name": [
"<em>张</em><em>三</em>"
]
}
}
]
}
}
2.4.8.聚合
在ElasticSearch中,支持聚合操作,类似SQL中的group by操作
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search
#请求体
{
"aggs":{
"all_interests":{
"terms":{
"field":"age"
}
}
}
}
#响应体
{
"took": 64,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 4,
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "xl2Ij3ABhf2JFmKcKHq2",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"id": 1002,
"name": "李四",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1002",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1003",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"id": 1003,
"name": "网五",
"age": 10,
"sex": "女"
}
}
]
},
"aggregations": {
"all_interests": {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
"sum_other_doc_count": 0,
"buckets": [
{
"key": 20,
"doc_count": 2
},
{
"key": 10,
"doc_count": 1
},
{
"key": 22,
"doc_count": 1
}
]
}
}
}
2.5.核心内容
2.5.1.文档
在ElasticSearch中,文档以JSON格式进行存储,可以是复杂结构.如下图所示:Card是一个复杂对象,嵌套的Card对象

一个文档不只有数据,它还包含了元数据(metedata),关于文档的信息,三个必须的元数据节点是:
| 节点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| _index | 文档存储的地方 |
| _type | 文档代表的对象的类 |
| _id | 文档的唯一标识 |
1.index(索引)
索引类似于关系型数据库里的"数据库"–它是我们存储和索引关联数据的地方.事实上,我们的数据被存储和索引在分片(shards)中,索引只是一个把一个或多个分片分组在一起的逻辑空间.然而,这只是一些内容细节,我们的程序完全不用关心分片.对于我们的程序而言,文档存储在索引中.剩下的细节ElasticSearch关心即可.
2.type(类型)
在应用中,我们使用对象表示一些"事物",例如一个用户,一片博客,一个评论,或者一封邮件,每个对象都属于一个类,这个类定义了属性或与对象关联的数据,在关系型数据库中,我们经常将相同的类的对象存储在一个表里,因为它们有着相同的结构.同理,在ElasticSearch中,我们使用相同类型(type)的文档表示相同的事物,因为他们的数据结构也是相同的.
每个类型都有自己的**映射(mapping)**或者结构定义,就像传统数据库表中的列一样.所有类型下的文档被存储在同一个索引下,但是类型的映射(mapping)会告诉ElasticSearch不同的文档如何被索引.
type的名字可以是大写或消息,不能包含下划线或逗号
3.id
id仅仅是一个字符串,它与index和type组合时,就可以在ElasticSearch中唯一标识一个文档.当创建一个文档,你可以自定义id,也可以让ElasticSearch帮你自动生成(32位长度)
2.5.2.查询响应
2.5.2.1.pretty
我们可以在查询url后面添加pretty参数,使得返回json更易查看例如:GET http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search?pretty
2.5.2.2.指定响应字段
在响应数据中,如果我们不需要全部字段,可以指定某些需要的字段进行返回.
GET http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search?_source=id,name
#响应体
{
"took": 8,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 4,
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "张三",
"id": 1001
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "xl2Ij3ABhf2JFmKcKHq2",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "李四",
"id": 1002
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1003",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "网五",
"id": 1003
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1002",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "呵呵",
"id": 1005
}
}
]
}
}
如果不需要返回元数据,仅仅返回原始数据,可以这样
GET http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/1003/_source
#响应体
{
"id": 1003,
"name": "网五",
"age": 10,
"sex": "女"
}
我们还可以返回原始数据并指定需要的字段
GET http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/1003/_source?_source=id,name
#响应体
{
"name": "网五",
"id": 1003
}
2.5.3.判断文档是否存在
如果我们只需要判断文档是否存在,而不是查询文档的内容,可以这样
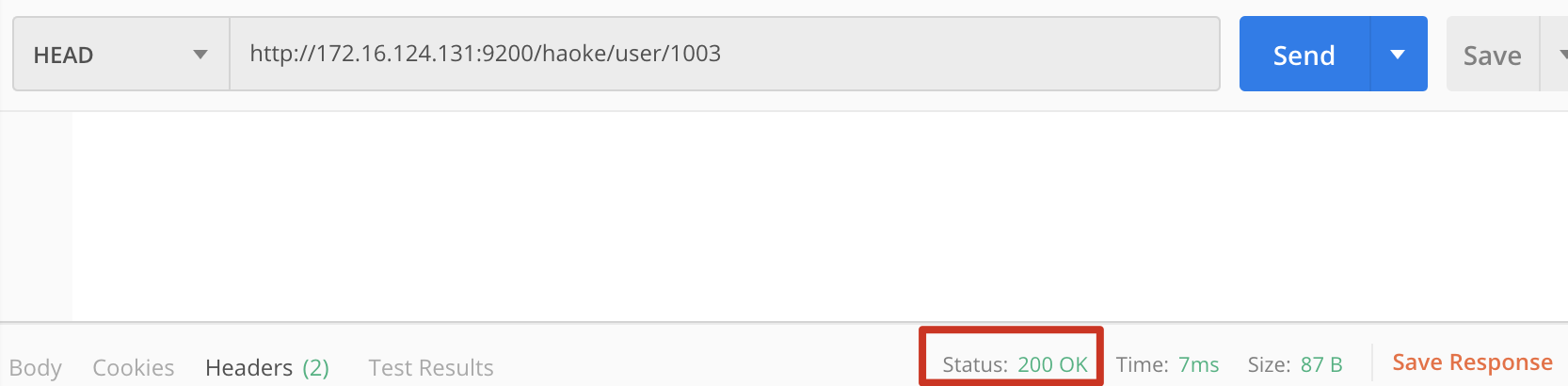
HEAD http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/1003
下图是文档内容存在的结果为200OK
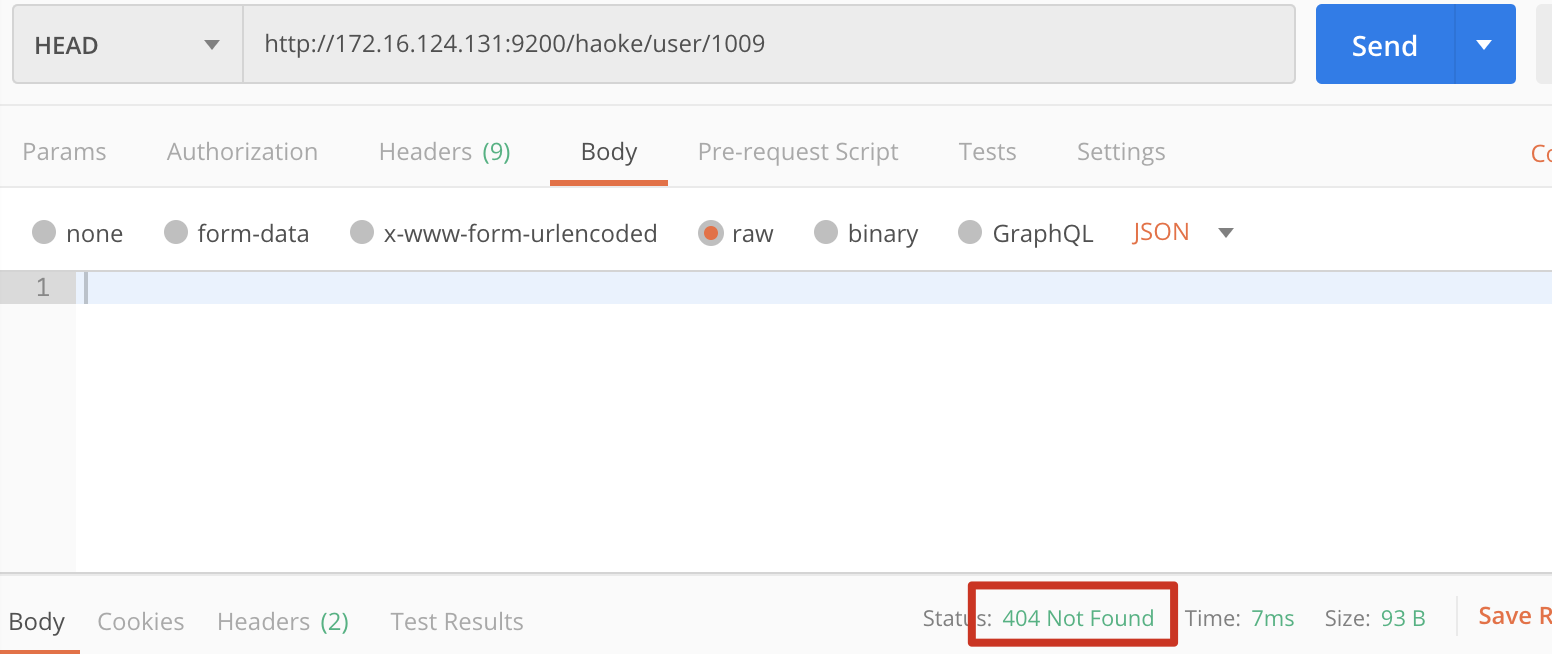
下图是文档内容不存在的结果为404NOT FOUND
2.5.4.批量操作
有些情况下可以通过批量操作来减少网络请求,如批量查询,批量插入数据.
2.5.4.1.批量查询
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_mget
#请求体
{
"ids":[1001,1002]
}
#响应体
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1002",
"_version": 3,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 1005,
"name": "呵呵",
"age": 22,
"sex": "男",
"card": {
"card_number": "123456"
}
}
}
]
}
如果,某一条数据不存在,不影响整体响应,需要通过found的值进行判断是否查询到数据
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_mget
#请求体
{
"ids":[1001,1009]
}
#响应体
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1001",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 1001,
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"sex": "男"
}
},
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1009",
"found": false
}
]
}
2.5.4.2._bulk操作
在ElasticSearch中,支持批量的插入,修改,删除操作,都是通过_bulk的api完成的.
请求格式如下:(请求格式不同寻常)
{ action:{ metadata}}n
{ request body}n
{ action:{ metadata}}n
{ request body}n
...
2.5.4.2.1.批量插入数据
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_bulk
#请求体
{"create":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2001}} {"id":2001,"name":"name1","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{"create":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2002}} {"id":2002,"name":"name2","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{"create":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2003}} {"id":2003,"name":"name3","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
#此处请求体需要有一个回车
#响应体
{
"took": 19,
"errors": false,
"items": [
{
"create": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2001",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
},
{
"create": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2002",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
},
{
"create": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2003",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 2,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
}
]
}
2.5.4.2.2.批量删除
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_bulk
#请求体
{"delete":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2001}}
{"delete":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2002}}
{"delete":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2003}}
#此处请求体需要有一个回车
#响应体
{
"took": 7,
"errors": false,
"items": [
{
"delete": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2001",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
},
{
"delete": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2002",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 3,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
},
{
"delete": {
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2003",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 4,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
}
]
}
2.5.5.分页
和SQL使用LIMIT关键字返回只有一页的结果一样,ElasticSearch接受from和size参数
-
from:跳过开始的结果数,默认是0 -
size:结果数,默认10;
GET http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search?size=1&from=2
#响应体
{
"took": 12,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 4,
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1003",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"id": 1003,
"name": "网五",
"age": 10,
"sex": "女"
}
}
]
}
}
应该当心分页太深或者一次请求太多的结果,结果在返回前会被排序,但是记住一个搜索请求常常涉及多个分片,每个分片生成自己排好序的结果,它们接着需要集中起来排序以确保整个排序正确.
为了理解为什么深度分页会有问题,让我们假设在一个有5个主分片的索引中搜索,当我们请求结果的第一页(结果1到10)时,每个分片产生自己最顶端10个结果然后返回它们给请求节点.它再排序这所有的50个结果以筛选出顶端的10个结果.现在假设我们请求第1000页.结果是10001-10010.工作方式都相同,不同的是每个分片都必须产生顶端的10010个结果,然后请求节点排序这50050个结果并丢弃50040个.
你可以看到在分布式系统中,排序结果的花费随着分页的深入而成倍的增长,这也是为什么网络搜索引擎中任何语句不能反悔多于1000个结果的原因.
2.5.6.映射
前面我们创建的索引以及插入数据,都是由ElasticSearch进行自动判断类型,有些时候我们是需要进行明确字段类型的,否则,自动判断的类型与实际的需求是不一样的.
自动判断的类型如下:
| JSON Type | Field Type |
|---|---|
Boolean:trueor false | “boolean” |
whole number:123 | “long” |
Floating point:123.45 | “double” |
String,valid date:2020-02-29 | “date” |
String:foo bar | “string” |
ElasticSearch中支持的类型如下:
| 类型 | 标识的数据类型 |
|---|---|
| String | string,text,keyword |
| Whole number | byte,short,integer,long |
| Floating point | float,double |
| Boolean | boolean |
| Date | date |
- **String(弃用)**类型在ElasticSearch就版本中使用较多,从ElasticSearch5.x开始就不再支持string,由text和keyword类型替代.
- text类型,当一个字段是要被全文检索的,设置text类型之后,字段的内容会被分析,在生成倒排索引以前,字符串会被分析器分成一个一个词项.text类型的字段不用于排序,很少用于聚合.
- keyword类型,它适合索引结构化的字段,如果字段需要进行过滤,排序,聚合.keyword类型的字段只能通过精确值搜索到.
PUT http://172.16.124.131:9200/fechin
#请求体
{
"settings":{
"index":{
"number_of_shards":"2",
"number_of_replicas":"0"
}
},
"mappings":{
"person":{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text"
},
"age":{
"type":"integer"
},
"mail":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"hobby":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}
}
}
#响应体
{
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true,
"index": "fechin"
}
查看映射
GET http://172.16.124.131:9200/fechin/_mapping
#响应体
{
"fechin": {
"mappings": {
"person": {
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"hobby": {
"type": "text"
},
"mail": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
}
2.5.7.结构化查询
2.5.7.1.term查询
term主要用于精确匹配哪些值,比如数值,日期,布尔值或not_analyzed的字符串(未经分析的文本数据类型)
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/fechin/person/_search
#请求体
{
"query":{
"term":{
"age":20
}
}
}
#响应体
{
"took": 5,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 2,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "fechin",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "zF3wkHABhf2JFmKcHnrC",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"mail": "111@qq.com",
"hobby": "羽毛球、乒乓球、足球"
}
}
]
}
}
2.5.7.2.terms查询
term根terms优点类似,但terms允许指定多个匹配条件.如果某个字段指定了多个值,那么文档需要一起去做匹配:
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/fechin/person/_search
#请求体
{
"query":{
"terms":{
"age":[20,21]
}
}
}
2.5.7.3.range查询
range过滤允许我们按照指定范围查找一批数据
范围操作符:
gt:大于gte:大于等于lt:小于lte:小于等于
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/fechin/person/_search
#请求体
{
"query":{
"range":{
"age":{
"gte":20,
"lt":30
}
}
}
}
#响应体
{
"took": 3,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 2,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 5,
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "fechin",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "zV3wkHABhf2JFmKcHnrC",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "李四",
"age": 21,
"mail": "222@qq.com",
"hobby": "羽毛球、乒乓球、足球、篮球"
}
},
{
"_index": "fechin",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "0F3wkHABhf2JFmKcHnrC",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "孙七",
"age": 24,
"mail": "555@qq.com",
"hobby": "听音乐、看电影"
}
},
{
"_index": "fechin",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "zF3wkHABhf2JFmKcHnrC",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"mail": "111@qq.com",
"hobby": "羽毛球、乒乓球、足球"
}
},
{
"_index": "fechin",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "zl3wkHABhf2JFmKcHnrC",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "王五",
"age": 22,
"mail": "333@qq.com",
"hobby": "羽毛球、篮球、游泳、听音乐"
}
},
{
"_index": "fechin",
"_type": "person",
"_id": "z13wkHABhf2JFmKcHnrC",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"name": "赵六",
"age": 23,
"mail": "444@qq.com",
"hobby": "跑步、游泳"
}
}
]
}
}
2.5.7.4.exists查询
exist查询可以用于查询文档中是否包含指定字段或没有某个字段,类似于SQL语句中的IS_NULL条件
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search
#请求体
{
"query":{
"exists":{
"field":"card"
}
}
}
#响应体
{
"took": 10,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 1.0,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1002",
"_score": 1.0,
"_source": {
"id": 1005,
"name": "呵呵",
"age": 22,
"sex": "男",
"card": {
"card_number": "123456"
}
}
}
]
}
}
2.5.7.5.match查询
match查询是一个标准查询,不管你需要全文本查询还是精确查询基本上都要使用到它.如果你使用match查询一个全文本字段,它会在真正查询之前用分析器先分析match以下查询字符:
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search
#请求体
{
"query":{
"match":{
"name":"张"
}
}
}
2.5.7.6.bool查询
bool查询可以用来合并多个条件查询结果的布尔逻辑:
must:多个查询条件的完全匹配,相当于andmust_not:多个查询条件的相反匹配,相当于not;should:至少有一个查询条件匹配,相当于or;
这些参数可以分别继承一个查询条件或者以个查询条件的数组
#请求体
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":{"term":{"folder":"inbox"}},
"must_not":{"term":{"tag":"spam"}},
"should":[
{"term":{"starred":true}},
{"term":{"unread":true}}
]
}
}
}
2.5.8.过滤查询
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/haoke/user/_search
#请求体
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"filter":{
"range":{
"age":{
"gt":15
}
}
}
}
}
}
查询和过滤的对比:
- 一条过滤语句会询问每个文档的字段值是否包含着特定值;
- 查询语句会询问每个文档的字段值与特定值的匹配程度如何
- 一条查询语句会计算每个文档与查询语句的相关性,会给出一个相关性评分_score,并且按照相关性对匹配到的文档进行排序,这种评分方式非常适用于一个没有完全配置结果的全文本搜索.
- 一个简单的文档列表,快速匹配运算并存入内存是非常方便的,每个文档仅需要1个直接.这些缓存的过滤结果与后续请求的结合使用是非常高效的.
- 查询语句不仅要查找相匹配的文档,还要计算每个文档的相关性,所以一般来说查询语句要比过滤语句更好使,并且查询结果也不可缓存.
- 做精确匹配时,最好使用过滤语句,因为过滤语句可以缓存数据
2.6.分词
2.6.1.分词介绍
分词就是将一个文本转换成一系列单词的过程,也叫文本分析,在ElasticSearch中称之为Analysis.
2.6.2.分词API
指定分词器进行分词:
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/_analyze
#请求体
{
"analyzer":"standard",
"text":"hello world"
}
#响应体
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "hello",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 5,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "world",
"start_offset": 6,
"end_offset": 11,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 1
}
]
}
指定索引分词
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/fechin/_analyze
#请求体
{
"analyzer":"standard",
"field":"hobby",
"text":"听音乐"
}
#响应体
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "听",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 1,
"type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "音",
"start_offset": 1,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position": 1
},
{
"token": "乐",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 3,
"type": "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position": 2
}
]
}
2.6.3.内置分词器
2.6.3.1.Standard
Standard标准分词,按单词切分,并且会转化成小写
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/_analyze
#请求体
{
"analyzer":"standard",
"text":"A man becomes learned by asking questions."
}
#响应体
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "a",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 1,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "man",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 5,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 1
},
{
"token": "becomes",
"start_offset": 6,
"end_offset": 13,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 2
},
{
"token": "learned",
"start_offset": 14,
"end_offset": 21,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 3
},
{
"token": "by",
"start_offset": 22,
"end_offset": 24,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 4
},
{
"token": "asking",
"start_offset": 25,
"end_offset": 31,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 5
},
{
"token": "questions",
"start_offset": 32,
"end_offset": 41,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 6
}
]
}
2.6.3.2.Simple
Simple分词器,按照非单词切分,并且做小写处理
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/_analyze
#请求体
{
"analyzer":"simple",
"text":"If the document doesn't already exist"
}
#响应体
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "if",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "word",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "the",
"start_offset": 3,
"end_offset": 6,
"type": "word",
"position": 1
},
{
"token": "document",
"start_offset": 7,
"end_offset": 15,
"type": "word",
"position": 2
},
{
"token": "doesn",
"start_offset": 16,
"end_offset": 21,
"type": "word",
"position": 3
},
{
"token": "t",
"start_offset": 22,
"end_offset": 23,
"type": "word",
"position": 4
},
{
"token": "already",
"start_offset": 24,
"end_offset": 31,
"type": "word",
"position": 5
},
{
"token": "exist",
"start_offset": 32,
"end_offset": 37,
"type": "word",
"position": 6
}
]
}
2.6.3.3.Whitespace
Whitespace是按照空格切分
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/_analyze
#请求体
{
"analyzer":"whitespace",
"text":"If the document doesn't already exist"
}
#响应体
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "If",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "word",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "the",
"start_offset": 3,
"end_offset": 6,
"type": "word",
"position": 1
},
{
"token": "document",
"start_offset": 7,
"end_offset": 15,
"type": "word",
"position": 2
},
{
"token": "doesn't",
"start_offset": 16,
"end_offset": 23,
"type": "word",
"position": 3
},
{
"token": "already",
"start_offset": 24,
"end_offset": 31,
"type": "word",
"position": 4
},
{
"token": "exist",
"start_offset": 32,
"end_offset": 37,
"type": "word",
"position": 5
}
]
}
2.6.3.4.Stop
Stop分词器是去除语气助词,如the,an等
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/_analyze
#请求体
{
"analyzer":"stop",
"text":"If the document doesn't already exist"
}
#响应体
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "document",
"start_offset": 7,
"end_offset": 15,
"type": "word",
"position": 2
},
{
"token": "doesn",
"start_offset": 16,
"end_offset": 21,
"type": "word",
"position": 3
},
{
"token": "t",
"start_offset": 22,
"end_offset": 23,
"type": "word",
"position": 4
},
{
"token": "already",
"start_offset": 24,
"end_offset": 31,
"type": "word",
"position": 5
},
{
"token": "exist",
"start_offset": 32,
"end_offset": 37,
"type": "word",
"position": 6
}
]
}
2.6.3.5.Keyword
Keyword分词器,意思是传入的就是关键词,不做分词处理
POST http://172.16.124.131:9200/_analyze
#请求体
{
"analyzer":"keyword",
"text":"If the document doesn't already exist"
}
#响应体
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "If the document doesn't already exist",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 37,
"type": "word",
"position": 0
}
]
}
2.6.4.中文分词
常用的中文分词器 IK,jieba,THULAC等,推荐使用IK分词器,地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik
#安装方法:将下载到的elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.5.4.zip解压到/elasticsearch/plugins/ik目录下即可。
#如果使用docker运行,先将压缩包方在/tmp目录下
docker cp /tmp/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.5.4.zip elasticsearch:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins/
#进入容器
docker exec -it elasticsearch /bin/bash
mkdir /usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins/ik
mv elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.5.4.zip ik
cd /usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins/ik
unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.5.4.zip
rm -rf elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.5.4.zip
#重启容器
docker restart elasticsearch
2.6.4.1.自定义词汇
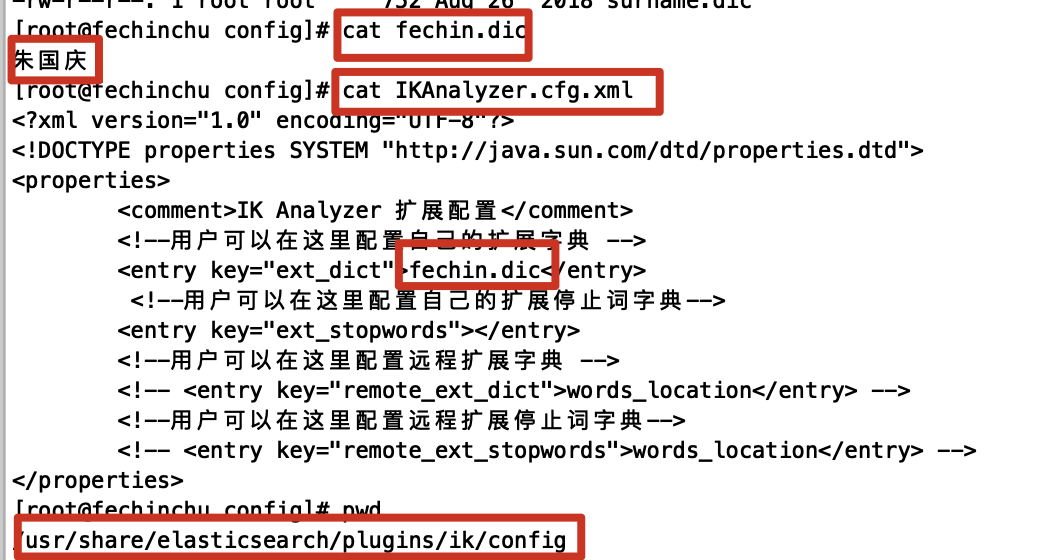
在/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins/ik/config中添加一个fechin.dic文件,写上词汇,并在IKAanlyzer.cfg.xml中引入即可.
最后
以上就是着急烧鹅最近收集整理的关于Elastic Stack系列--ElasticSearch基础1.Elastic Stack简介2.ElasticSearch的全部内容,更多相关Elastic内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复