一、理想质量 - 弹簧 - 阻尼系统
弹簧-质量-阻尼系统是一种比较普遍的机械振动系统,生活中也随处可见这种系统,例如汽车缓冲器就是一种可以耗减运动能量的装置,是保证驾驶员行车安全的必备装置。我们通过建立理想的质量 - 弹簧 - 阻尼系统的二阶物理系统模型,来学习simulink的应用。系统方程的的组成部分为质量,刚度和阻尼,方程如下所示:

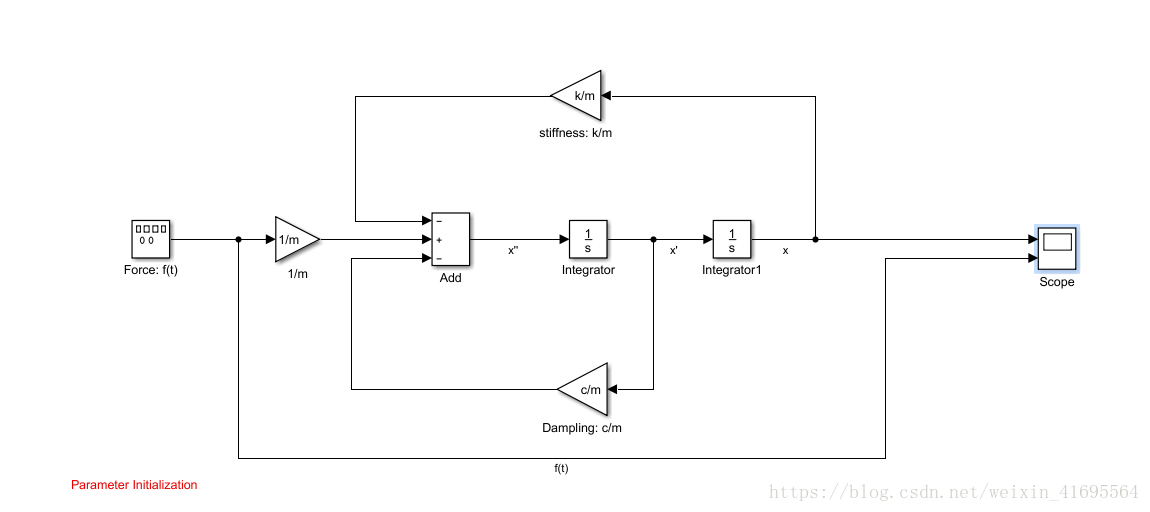
接下来我们建立模型如下所示:
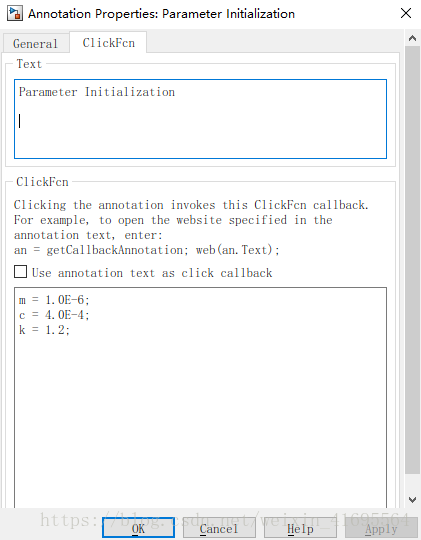
我们打开红色文本 Parameter Initialization,里面是一些参数初始化命令,如下所示:
在运行模型前,点击该文本,触发回调函数,完成参数初始化过程,点击之后,我们观察到工作空间中的变量如下: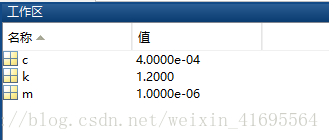
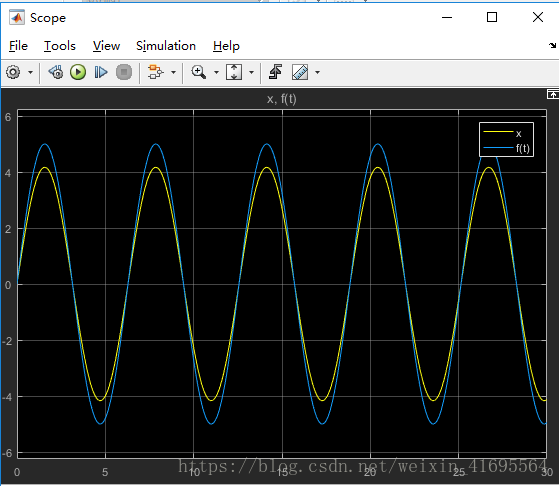
参数初始化以后,我们运行模型:
二、C代码自动生成
本示例学习如何为Simulink模型选择目标,生成用于实时模拟的C代码以及查看生成的文件。该模型代表一个8位计数器,为一个触发子系统提供信号,该子系统由常量模块INC,LIMIT和RESET等组成。 输入和输出表示模型的I / O,放大器子系统通过增益系数K放大输入信号,当信号equal_to_count为真时,增益系数K更新。
模型如下所示: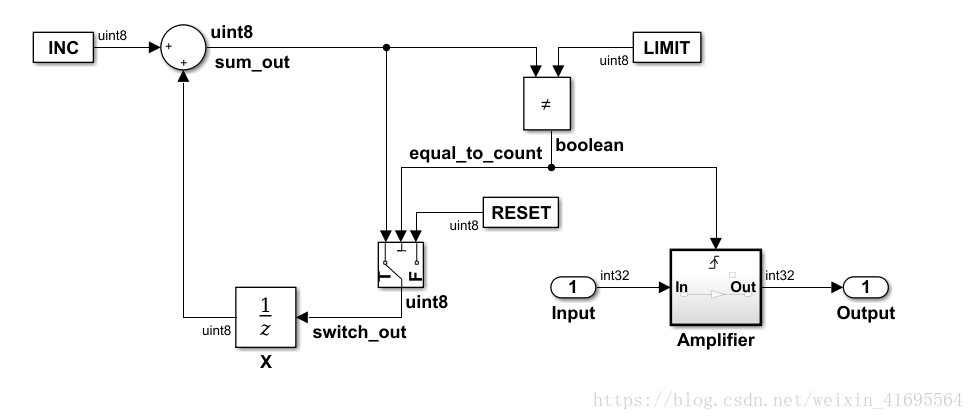
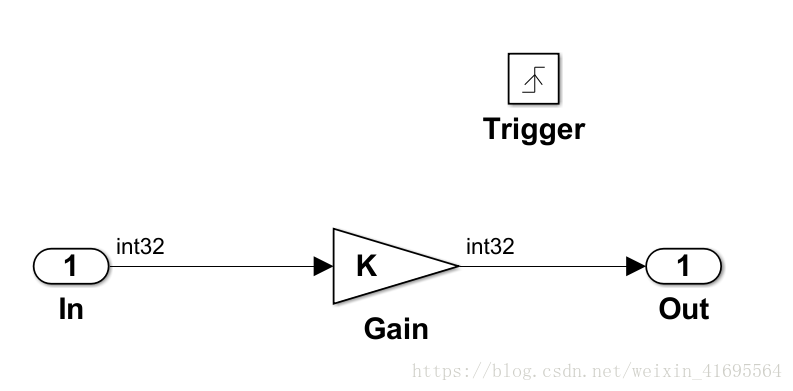
打开放大器子系统,可以看到内部结构如下:
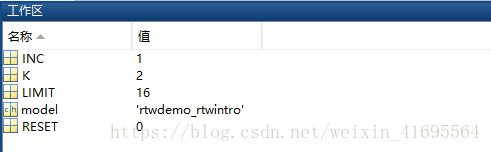
变量的参数初始化如下所示:
建立好模型以后,单击Simulation -> Configuration Parameters,从模型编辑器打开Configuration Parameters对话框:
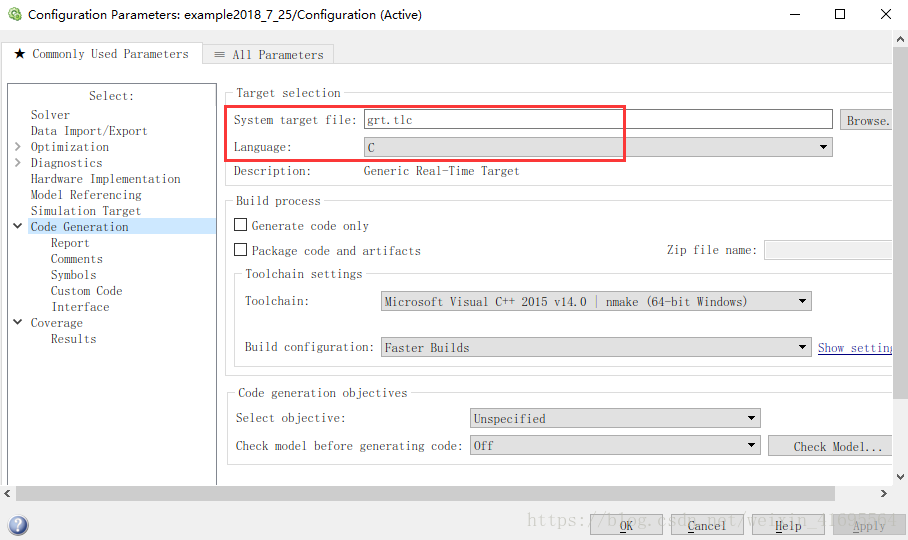
为了生成特定目标环境或目的代码,我们需要使用系统目标文件提供一些内置目标选项,系统目标文件控制目标代码的生成过程。
设置完成以后,回到模型窗口,使用快捷键Ctrl + B生成代码:
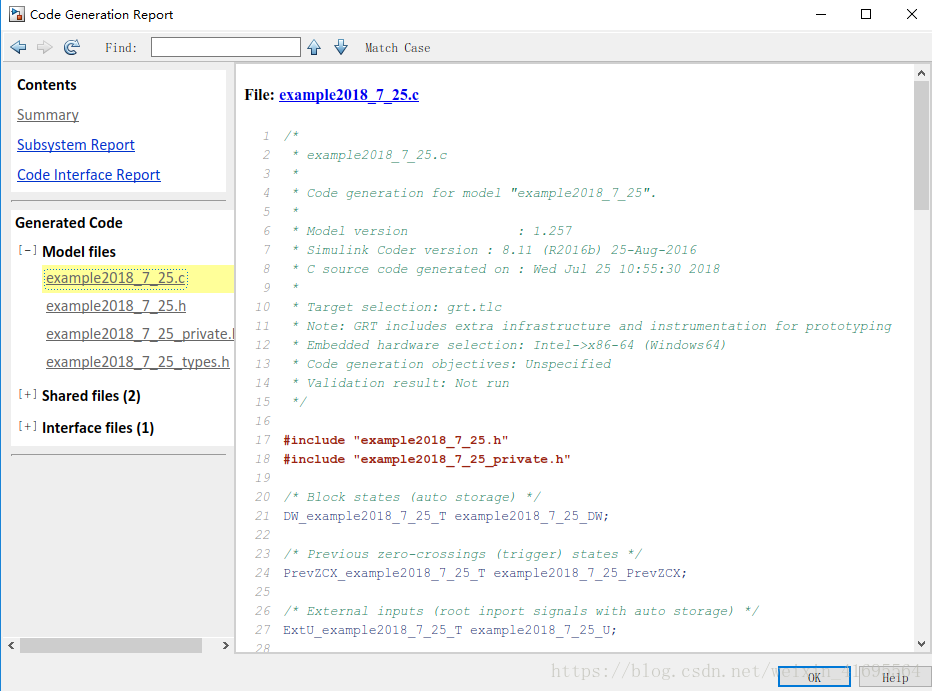
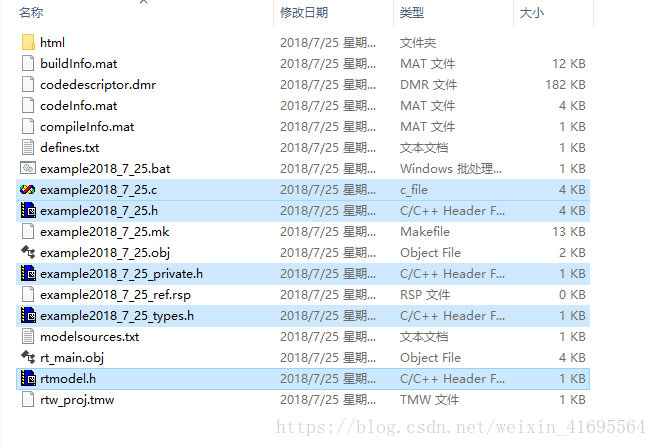
在生成的文件当中,我们找到这几个源文件和头文件:
接下来我们解读自动生成的代码,为了方便起见,我们把它的注释删除掉。
头文件 example2018_7_25.h 如下所示:
#ifndef RTW_HEADER_example2018_7_25_h_
#define RTW_HEADER_example2018_7_25_h_
#include <stddef.h>
#include <string.h>
#ifndef example2018_7_25_COMMON_INCLUDES_
# define example2018_7_25_COMMON_INCLUDES_
#include "rtwtypes.h"
#include "rtw_continuous.h"
#include "rtw_solver.h"
#endif
#include "example2018_7_25_types.h"
#include "multiword_types.h"
#ifndef rtmGetErrorStatus
# define rtmGetErrorStatus(rtm) ((rtm)->errorStatus)
#endif
#ifndef rtmSetErrorStatus
# define rtmSetErrorStatus(rtm, val) ((rtm)->errorStatus = (val))
#endif
typedef struct {
uint8_T X;
} DW_example2018_7_25_T;
typedef struct {
ZCSigState Amplifier_Trig_ZCE;
} PrevZCX_example2018_7_25_T;
typedef struct {
int32_T Input;
} ExtU_example2018_7_25_T;
typedef struct {
int32_T Output;
} ExtY_example2018_7_25_T;
struct tag_RTM_example2018_7_25_T {
const char_T *errorStatus;
};
extern DW_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_DW;
extern ExtU_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_U;
extern ExtY_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_Y;
extern void example2018_7_25_initialize(void);
extern void example2018_7_25_step(void);
extern void example2018_7_25_terminate(void);
extern RT_MODEL_example2018_7_25_T *const example2018_7_25_M;
#endif 头文件 example2018_7_25_private.h 如下所示:
#ifndef RTW_HEADER_example2018_7_25_private_h_
#define RTW_HEADER_example2018_7_25_private_h_
#include "rtwtypes.h"
#include "multiword_types.h"
#endif
源文件如下所示:
#include "example2018_7_25.h"
#include "example2018_7_25_private.h"
// UnitDelay Block states
DW_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_DW;
// Previous zero-crossings (trigger) states
PrevZCX_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_PrevZCX;
// External inputs
ExtU_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_U;
// External outputs
ExtY_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_Y;
// Real-time model
RT_MODEL_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_M_;
RT_MODEL_example2018_7_25_T *const example2018_7_25_M = &example2018_7_25_M_;
/* Model step function */
void example2018_7_25_step(void)
{
boolean_T rtb_equal_to_count;
// 定义了一个布尔变量,用来表示比较结果
example2018_7_25_DW.X++;
// example2018_7_25_DW.X是延时模块的值,即累加值,
// 由于模型中的INC为常数1,所以每次加1。
// 首先呢,变量example2018_7_25_DW是一个结构体,其变量声明语句如下所示:
// extern DW_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_DW;
// 显然,DW_example2018_7_25_T代表一个结构体,我们找到这个结构体的定义如下:
// typedef struct{
// uint8_T X;
// } DW_example2018_7_25_T;
rtb_equal_to_count = (example2018_7_25_DW.X != 16);
if ( rtb_equal_to_count && (example2018_7_25_PrevZCX.Amplifier_Trig_ZCE != POS_ZCSIG))
{
example2018_7_25_Y.Output = example2018_7_25_U.Input << 1;
// 对于逻辑(算术)左移,且不发生溢出时,结果增加两倍,
// 这正好对应于模型中触发子系统中的增益模块的增益值2
}
// 首先呢,变量example2018_7_25_PrevZCX 也是一个结构体变量,其变量声明语句如下所示:
// PrevZCX_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_PrevZCX;
// 显然,PrevZCX_example2018_7_25_T是一个结构体,其结构体定义如下:
// typedef struct {
// ZCSigState Amplifier_Trig_ZCE;
// } PrevZCX_example2018_7_25_T;
// 那么,变量example2018_7_25_U 的定义如下:
// ExtU_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_U;
// 结构体 ExtU_example2018_7_25_T的定义如下:
// typedef struct {
// int32_T Input;
// } ExtU_example2018_7_25_T;
// 最后,变量example2018_7_25_Y 的定义如下:
// ExtY_example2018_7_25_T example2018_7_25_Y;
// 结构体 ExtY_example2018_7_25_T 的定义如下:
// typedef struct {
// int32_T Output;
// } ExtY_example2018_7_25_T;
example2018_7_25_PrevZCX.Amplifier_Trig_ZCE = rtb_equal_to_count;
// 更新触发状态
if (!rtb_equal_to_count)
{
example2018_7_25_DW.X = 0U;
}
// 当布尔值rtb_equal_to_count为假时,代表计数器已经计数到16了,
// 当计数到16时,需要重新将延时模块UnitDelay的状态值(即累加值)归零,
// 此时0U表示无符号形式存储的零值
// 在头文件中,还有定义:
// Logical type definitions
/* #if (!defined(__cplusplus))
# ifndef false
# define false (0U)
# endif
# ifndef true
# define true (1U)
# endif
#endif
#endif
*/
}
/* Model initialize function */
void example2018_7_25_initialize(void)
{
rtmSetErrorStatus(example2018_7_25_M, (NULL));
// 首先,变量example2018_7_25_M的定义如下:
// RT_MODEL_example2018_7_25_T * const example2018_7_25_M = &example2018_7_25_M_;
// 那么,RT_MODEL_example2018_7_25_T又是个什么数据类型呢?可以看到定义如下:
// typedef struct tag_RTM_example2018_7_25_T RT_MODEL_example2018_7_25_T;
(void) memset((void *)&example2018_7_25_DW, 0,sizeof(DW_example2018_7_25_T));
// 将example2018_7_25_DW所在的内存空间赋0
// memset函数经常用于清0
example2018_7_25_U.Input = 0;
example2018_7_25_Y.Output = 0;
example2018_7_25_PrevZCX.Amplifier_Trig_ZCE = POS_ZCSIG;
example2018_7_25_DW.X = 0U;
example2018_7_25_Y.Output = 0;
}
/* Model terminate function */
void example2018_7_25_terminate(void)
{
/* (no terminate code required) */
}
显然自动生成的代码默认变量的数据类型为结构体,因此程序中运用了大量的结构体类型,读起来额外的费劲,后期可以自己手动完善来增强的代码的可读性。当然源文件当中没有主函数,不能直接运行,里面只是逻辑代码,也没有涉及到硬件的底层驱动。不过,基于模型的设计还是能够加快项目的研发速度,降低研发成本。
最后
以上就是帅气星月最近收集整理的关于Simlulink学习笔记——C代码自动生成解析的全部内容,更多相关Simlulink学习笔记——C代码自动生成解析内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复