常用时序逻辑电路设计
- 同步时序逻辑电路
- 序列检测器
- 异步时序逻辑电路
- 窄脉冲捕获电路
- MUX同步器
- 握手协议
- 单比特脉冲信号(控制信号)传输代码:
- 多比特信号(数据信号)传输代码:
本文主要用来存放各种时序电路代码,异步时序电路分析见另一篇文章,主要是一些跨时钟域处理电路及方法。
窄脉冲捕获电路.
MUX同步器.
握手协议.
同步时序逻辑电路
序列检测器
从一串二进制数据中找到指定的字符串并输出信号。找“1101”,序列为16’b1110_1010_1101_0011。
状态机:
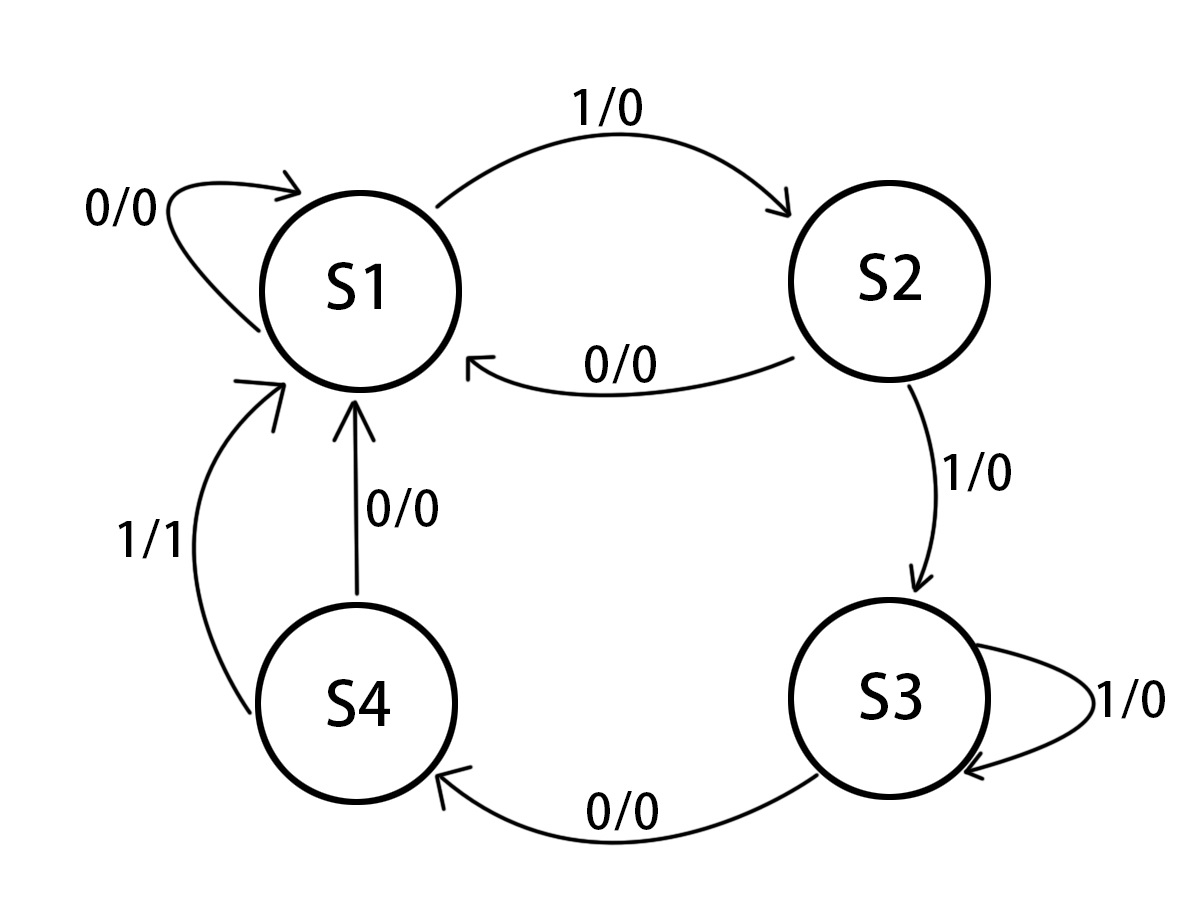
代码:
module test(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input data,
output reg y
);
localparam st0 = 2'b00;
localparam st1 = 2'b01;
localparam st2 = 2'b10;
localparam st3 = 2'b11;
reg [1:0] cur_stat;
reg [1:0] nxt_stat;
//1
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
cur_stat = st0;
else
cur_stat = nxt_stat;
end
//2
always @(*)begin
case(cur_stat)
st0:begin
if(!data)
nxt_stat = st0;
else
nxt_stat = st1;
end
st1:begin
if(!data)
nxt_stat = st0;
else
nxt_stat = st2;
end
st2:begin
if(!data)
nxt_stat = st3;
else
nxt_stat = st2;
end
st3:begin
if(!data)
nxt_stat = st0;
else
nxt_stat = st0;
end
endcase
end
//3
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
y<=1'd0;
else begin
case(cur_stat)
st0:begin
if(!data) y<=1'd0;
else y<=1'd1;
end
st1:y<=1'd0;
st2:y<=1'd0;
st3:y<=1'd0;
endcase
end
end
endmodule
testbench:
`timescale 1 ps/ 1 ps
module test_vlg_tst();
reg clk;
reg rst_n;
reg [15:0] data_t;
wire y;
wire data;
assign data = data_t[15];
test i1 (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.data(data),
.y(y)
);
initial
begin
rst_n = 0;
#50 rst_n =1;
#5000 $stop;
end
initial
begin
clk=0; forever #10 clk = ~clk;
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
data_t <= 16'b1110_1010_1101_0011;
else
data_t <= (data_t << 1);
end
endmodule
仿真结果:
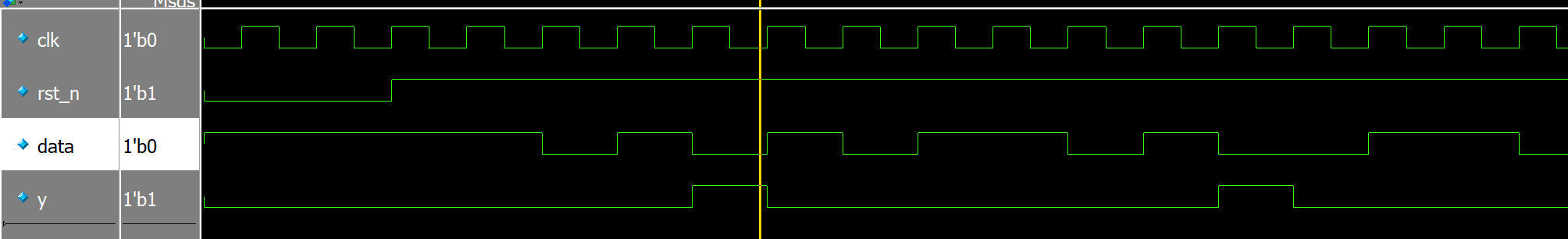
最基础的同步时序电路。
异步时序逻辑电路
窄脉冲捕获电路
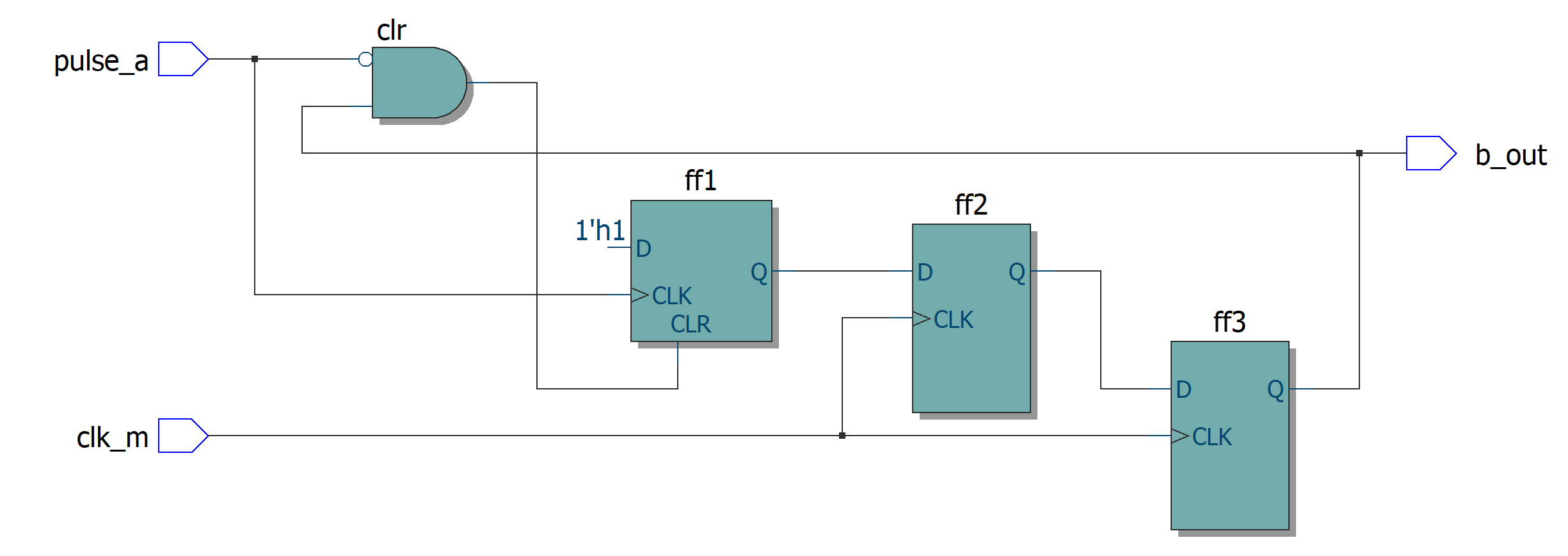
代码:
module test(
input clk_m,
input pulse_a, //快时钟域产生的异步窄脉冲控制信号
output b_out //慢时钟域同步的宽脉冲输出
);
reg ff1;//利用脉冲信号的上升沿进行输出脉冲信号,然后通过FF3的反馈进行清零
reg ff2;
reg ff3;//异步信号两级D触发器降低亚稳态
wire clr;
assign clr = (!pulse_a) & ff3; //组合逻辑电路
assign b_out = ff3;
always @(posedge pulse_a or posedge clr)begin
if(clr)
ff1<=1'd0;
else if(pulse_a)
ff1<=1'd1;
else
ff1<=ff1;
end
always @(posedge clk_m)begin
ff2<=ff1;
ff3 <= ff2;
end
endmodule
testbench:
`timescale 1 ps/ 1 ps
module test_vlg_tst();
reg clk_m;
reg pulse_a;
wire b_out;
test i1 (
.clk_m(clk_m),
.pulse_a(pulse_a),
.b_out(b_out)
);
initial
begin
#50000 $stop;
end
initial
begin
clk_m=0; #50 forever #25 clk_m = ~clk_m;
end
initial begin
pulse_a = 1'b0;
forever begin
#500 pulse_a = 1'b1;
#5 pulse_a = 1'b0;
end
end
endmodule
仿真:
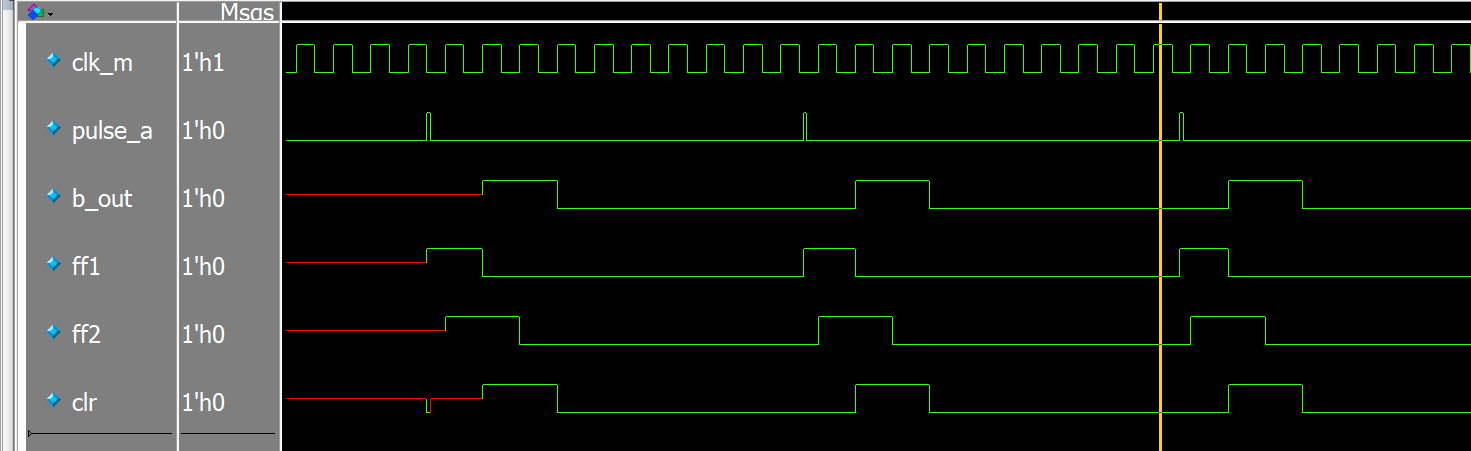
MUX同步器
链接:MUX同步器.
代码:
module test(
input clk_a,
input clk_b,
input rst_n,
input [7:0] data_in,
input data_en,
output reg [7:0] data_out
);
reg en_sync_a;
reg en_async_b;
reg en_sync_b;
reg [ 7:0] data_tmp_a;
wire [7:0] data_tmp_b;
assign data_tmp_b = en_sync_b?data_tmp_a:data_out;
//同步clk_a的en
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
en_sync_a <= 1'b0;
else
en_sync_a <= data_en;
end
always @(posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
en_async_b <= 1'b0;
en_sync_b <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
en_async_b <= en_sync_a;
en_sync_b <= en_async_b;
end
end
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
data_tmp_a <= 8'b0;
else if(en_sync_a)
data_tmp_a <= data_in;
else
data_tmp_a <= data_tmp_a;
end
always @(posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
data_out <= 8'd0;
else
data_out <= data_tmp_b;
end
endmodule
testbench:
`timescale 1 ps/ 1 ps
module test_vlg_tst();
reg clk_a;
reg clk_b;
reg rst_n;
reg [7:0] data_in = 8'd0;
reg data_en;
wire [7:0] data_out;
test i1(
.clk_a(clk_a),
.clk_b(clk_b),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.data_in(data_in),
.data_en(data_en),
.data_out(data_out)
);
initial begin
rst_n = 1'b0;
#50 rst_n =1'b1;
#5000 $stop;
end
initial begin
data_en = 1'b0;
clk_a = 1'b0; forever begin #13 clk_a = ~clk_a; end
end
initial begin
clk_b = 1'b0; forever begin #8 clk_b = ~clk_b; end
end
always @(posedge clk_a)begin
data_in <= data_in +1'b1;
end
always begin
#273
data_en = 1'b1; #26;
data_en = 1'b0; #260;
data_en = 1'b1; #26;
data_en = 1'b0; #130;
end
endmodule
仿真:
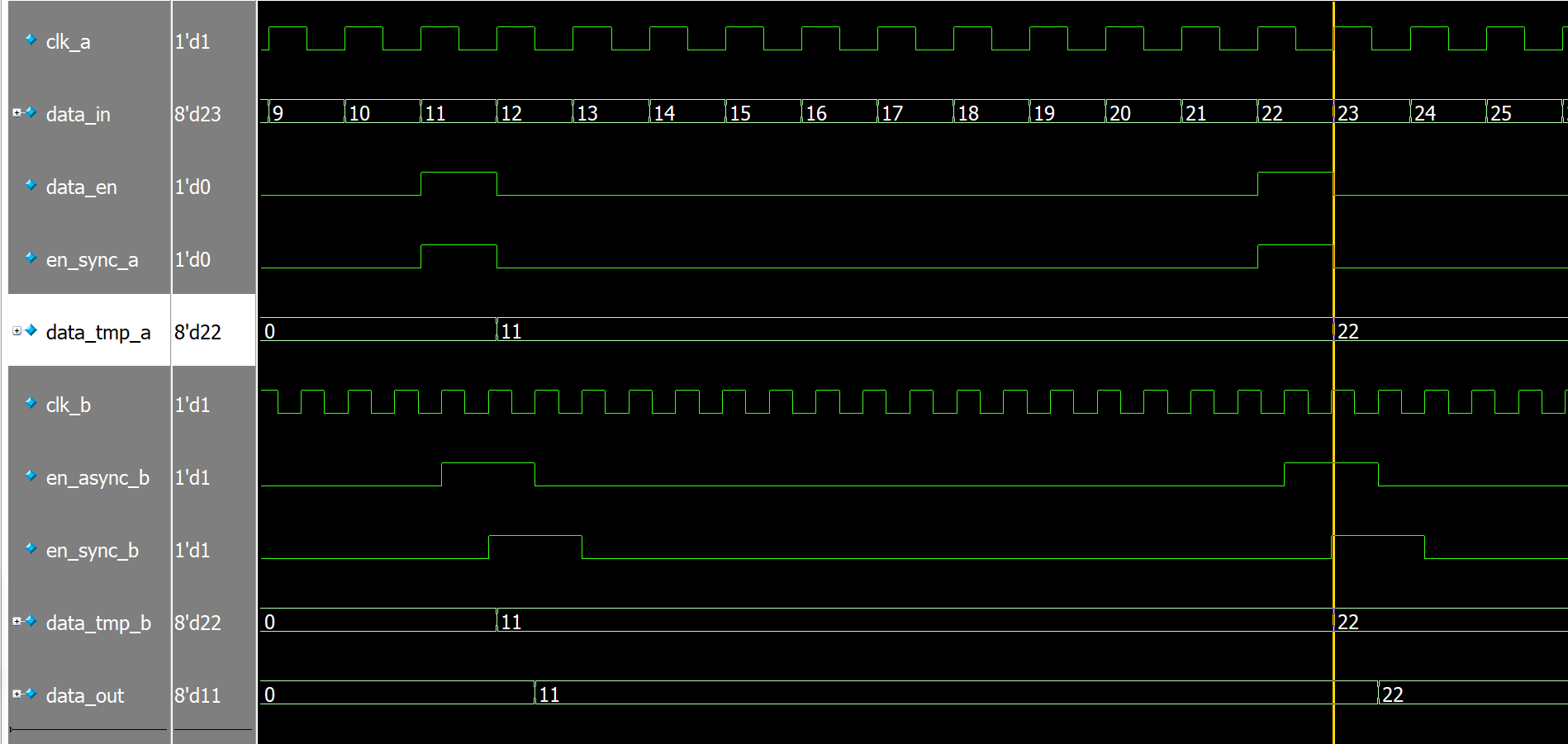
握手协议
单比特脉冲信号(控制信号)传输代码:
module test(
input clk_a,//快时钟
input clk_b,//慢时钟
input rst_n,
input pulse_in, //快时钟脉冲输入
output pulse_out //慢时钟输出脉冲信号
);
reg req_a; //clk_a发出请求
reg req_async; //clk_b下 打一拍接收到的异步请求
reg req_sync_b; //clk_b下 打两拍接收到的同步请求
reg req_sync_b1; //打三拍 进行边沿检测用
reg ack_async; // clk_a采到的clk_b发出的异步应答信号
reg ack_sync; // clk_a下打一拍的同步应答信号
assign pulse_out = req_sync_b & (~req_sync_b1);
//扩展脉冲pulse_in
always@(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
req_a <= 1'b0;
else if(pulse_in)
req_a <= 1'b1;
else if(ack_sync)//检测到clk_b发出的应答信号 关断req
req_a <= 1'b0;
else
req_a <= req_a;
end
//req_a to clk_b //打两拍
always@(posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
req_async <= 1'b0;
req_sync_b <= 1'b0;
req_sync_b1 <= 1'b0;
end
else
begin
req_async <= req_a; //打拍异步请求
req_sync_b <= req_async;//打两拍异步请求 降低亚稳态概率
req_sync_b1 <= req_sync_b; //打三拍异步请求 边沿检测
end
end
//req_sync_b作为反馈信号到clk_a中作为应答信号
always@(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
ack_async <= 1'b0;
ack_sync <= 1'b0;
end
else
begin
ack_async <= req_sync_b; //采集异步应答信号
ack_sync <= ack_async; //打两拍降低亚稳态
end
end
endmodule
testbench:
`timescale 1 ps/ 1 ps
module test_vlg_tst();
reg clk_a;
reg clk_b;
reg rst_n;
reg pulse_in;
reg [5:0] cnt;
wire pulse_out;
test i1 (
.clk_a(clk_a),//快时钟
.clk_b(clk_b),//慢时钟
.rst_n(rst_n),
.pulse_in(pulse_in), //快时钟脉冲输入
.pulse_out(pulse_out) //慢时钟输出脉冲信号
);
initial
begin
rst_n = 0;
#100 rst_n =1;
#50000 $stop;
end
initial
begin
clk_a=0; #25 forever #10 clk_a = ~clk_a;
end
initial
begin
clk_b=0; #43 forever #34 clk_b = ~clk_b;
end
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
pulse_in <= 1'd0;
else if(cnt == 6'd20)
pulse_in <= 1'd1;
else
pulse_in <= 1'd0;
end
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
cnt <= 6'd0;
else if(cnt == 6'd20)
cnt <= 6'd0;
else
cnt <= cnt +1'd1;
end
endmodule
仿真结果:
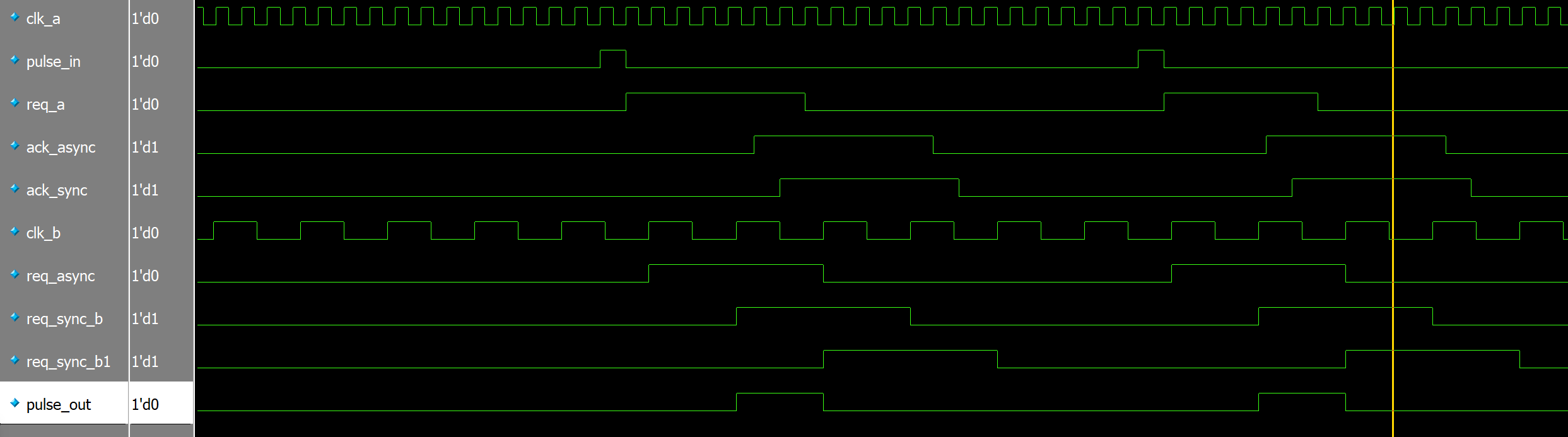
多比特信号(数据信号)传输代码:
module test(
input clk_a,//快时钟
input clk_b,//慢时钟
input rst_n,
input [7:0] data_in, //8位数据信号
input pulse_in, //快时钟脉冲输入
output pulse_out, //慢时钟输出脉冲信号
output reg [7:0] data_out
);
reg [7:0] data_tmp; //数据缓存寄存器
reg req_a; //clk_a发出请求
reg req_async; //clk_b下 打一拍接收到的异步请求
reg req_sync_b; //clk_b下 打两拍接收到的同步请求
reg req_sync_b1; //打三拍 进行边沿检测用
reg ack_async; // clk_a采到的clk_b发出的异步应答信号
reg ack_sync; // clk_a下打一拍的同步应答信号
assign pulse_out = req_sync_b & (~req_sync_b1);//上升沿检测
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
data_tmp <= 8'd0;
else if(pulse_in)
data_tmp <= data_in;
else
data_tmp <= data_tmp;
end
//扩展脉冲pulse_in
always@(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
req_a <= 1'b0;
else if(pulse_in)
req_a <= 1'b1;
else if(ack_sync)//检测到clk_b发出的应答信号 关断req
req_a <= 1'b0;
else
req_a <= req_a;
end
//req_a to clk_b 打3拍
always@(posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
req_async <= 1'b0;
req_sync_b <= 1'b0;
req_sync_b1 <= 1'b0;
end
else
begin
req_async <= req_a; //打拍异步请求
req_sync_b <= req_async;//打两拍异步请求 降低亚稳态概率
req_sync_b1 <= req_sync_b; //打三拍异步请求 边沿检测
end
end
//req_sync_b作为反馈信号到clk_a中作为应答信号
always@(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
ack_async <= 1'b0;
ack_sync <= 1'b0;
end
else
begin
ack_async <= req_sync_b; //采集异步应答信号
ack_sync <= ack_async; //打两拍降低亚稳态
end
end
always @(posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
data_out <= 8'd0;
else if(pulse_out)
data_out <= data_tmp;
else
data_out <= data_out;
end
endmodule
testbench:
`timescale 1 ps/ 1 ps
module test_vlg_tst();
reg clk_a;
reg clk_b;
reg rst_n;
reg pulse_in;
reg [5:0] cnt;
reg [7:0] data_in;
wire[7:0] data_out;
wire pulse_out;
test i1 (
.clk_a(clk_a),//快时钟
.clk_b(clk_b),//慢时钟
.data_in(data_in),
.data_out(data_out),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.pulse_in(pulse_in), //快时钟脉冲输入
.pulse_out(pulse_out) //慢时钟输出脉冲信号
);
initial
begin
rst_n = 0;
#100 rst_n =1;
#50000 $stop;
end
initial
begin
clk_a=0; #25 forever #10 clk_a = ~clk_a;
end
initial
begin
clk_b=0; #43 forever #34 clk_b = ~clk_b;
end
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
pulse_in <= 1'd0;
else if(cnt == 6'd20)
pulse_in <= 1'd1;
else
pulse_in <= 1'd0;
end
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
data_in <= 8'd0;
else
data_in <= data_in +2'd3;
end
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
cnt <= 6'd0;
else if(cnt == 6'd20)
cnt <= 6'd0;
else
cnt <= cnt +1'd1;
end
endmodule
仿真结果:
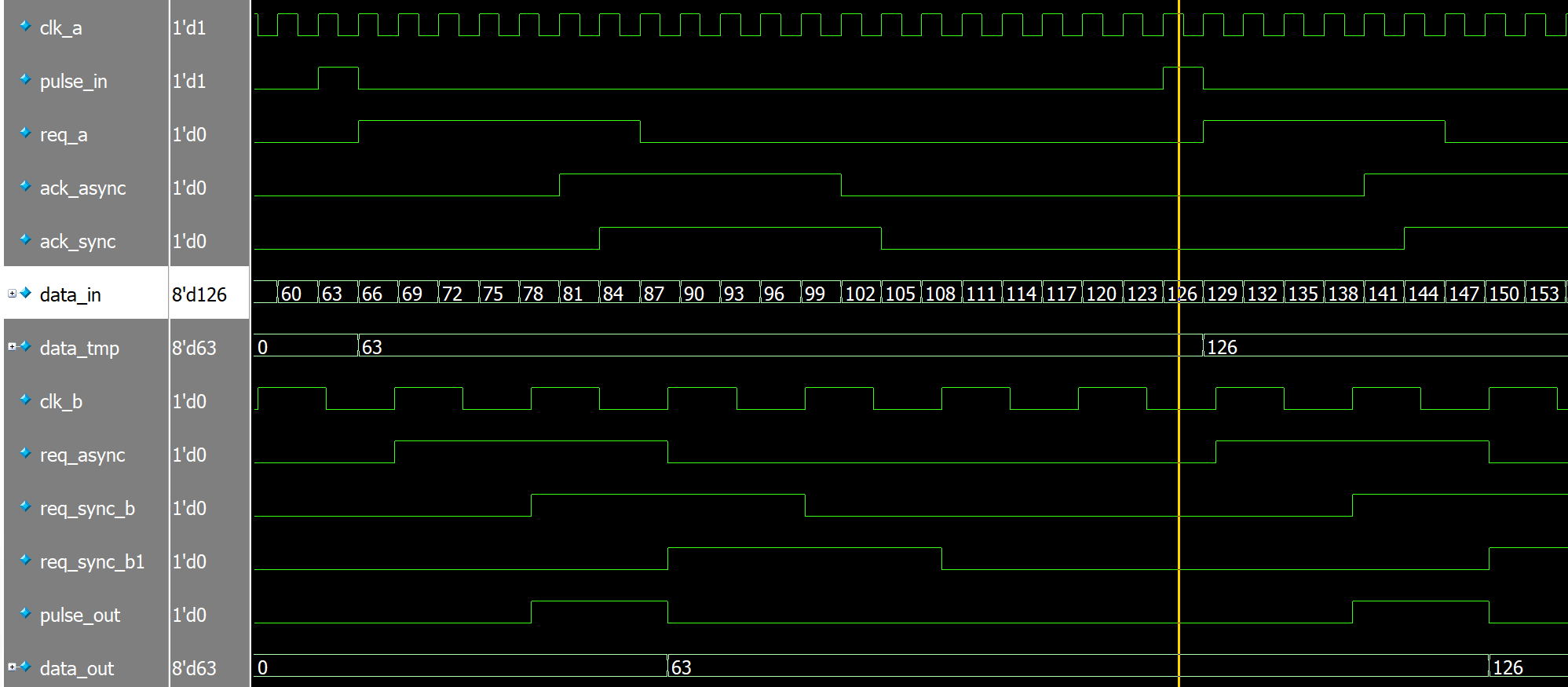
最后
以上就是落寞长颈鹿最近收集整理的关于常用时序逻辑电路设计同步时序逻辑电路异步时序逻辑电路的全部内容,更多相关常用时序逻辑电路设计同步时序逻辑电路异步时序逻辑电路内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复