一、前端 kinodynamic A*算法动力学路径搜索
1.1 路径搜索的主要函数为kinodynamicAstar类的search函数
int KinodynamicAstar::search(Eigen::Vector3d start_pt, Eigen::Vector3d start_v, Eigen::Vector3d start_a,
Eigen::Vector3d end_pt, Eigen::Vector3d end_v, bool init, bool dynamic, double time_start)
{
//初始化参数
start_vel_ = start_v;
start_acc_ = start_a;
PathNodePtr cur_node = path_node_pool_[0];
cur_node->parent = NULL;
cur_node->state.head(3) = start_pt;
cur_node->state.tail(3) = start_v;
cur_node->index = posToIndex(start_pt);
cur_node->g_score = 0.0;
Eigen::VectorXd end_state(6);
Eigen::Vector3i end_index;
double time_to_goal;
end_state.head(3) = end_pt;
end_state.tail(3) = end_v;
end_index = posToIndex(end_pt);
cur_node->f_score = lambda_heu_ * estimateHeuristic(cur_node->state, end_state, time_to_goal);
cur_node->node_state = IN_OPEN_SET;
open_set_.push(cur_node);
use_node_num_ += 1;
if (dynamic)
{
time_origin_ = time_start;
cur_node->time = time_start;
cur_node->time_idx = timeToIndex(time_start);
expanded_nodes_.insert(cur_node->index, cur_node->time_idx, cur_node);
// cout << "time start: " << time_start << endl;
}
else
expanded_nodes_.insert(cur_node->index, cur_node);
PathNodePtr neighbor = NULL;
PathNodePtr terminate_node = NULL;
bool init_search = init;
const int tolerance = ceil(1 / resolution_);
while (!open_set_.empty())
{
cur_node = open_set_.top();
// Terminate?
bool reach_horizon = (cur_node->state.head(3) - start_pt).norm() >= horizon_;
bool near_end = abs(cur_node->index(0) - end_index(0)) <= tolerance &&
abs(cur_node->index(1) - end_index(1)) <= tolerance &&
abs(cur_node->index(2) - end_index(2)) <= tolerance;
//当前节点超出horizon或接近目标点,计算一条直达的曲线,并检查曲线是否存在。
//主要为了解决稀疏采样,最终不能精准的到达目标点的问题
if (reach_horizon || near_end)
{
terminate_node = cur_node;
retrievePath(terminate_node);
if (near_end)
{
// Check whether shot traj exist
estimateHeuristic(cur_node->state, end_state, time_to_goal);
computeShotTraj(cur_node->state, end_state, time_to_goal);
if (init_search)
ROS_ERROR("Shot in first search loop!");
}
}
if (reach_horizon)
{
if (is_shot_succ_)
{
std::cout << "reach end" << std::endl;
return REACH_END;
}
else
{
std::cout << "reach horizon" << std::endl;
return REACH_HORIZON;
}
}
if (near_end)
{
if (is_shot_succ_)
{
std::cout << "reach end" << std::endl;
return REACH_END;
}
else if (cur_node->parent != NULL)
{
std::cout << "near end" << std::endl;
return NEAR_END;
}
else
{
std::cout << "no path" << std::endl;
return NO_PATH;
}
}
//开始节点扩展
open_set_.pop();
cur_node->node_state = IN_CLOSE_SET;
iter_num_ += 1;
double res = 1 / 2.0, time_res = 1 / 1.0, time_res_init = 1 / 20.0;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> cur_state = cur_node->state;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> pro_state;
vector<PathNodePtr> tmp_expand_nodes;
Eigen::Vector3d um;
double pro_t;
vector<Eigen::Vector3d> inputs;
vector<double> durations;
//获取采样输入
if (init_search)
{
inputs.push_back(start_acc_);
for (double tau = time_res_init * init_max_tau_; tau <= init_max_tau_ + 1e-3;
tau += time_res_init * init_max_tau_)
durations.push_back(tau);
init_search = false;
}
else
{
for (double ax = -max_acc_; ax <= max_acc_ + 1e-3; ax += max_acc_ * res)
for (double ay = -max_acc_; ay <= max_acc_ + 1e-3; ay += max_acc_ * res)
for (double az = -max_acc_; az <= max_acc_ + 1e-3; az += max_acc_ * res)
{
um << ax, ay, az;
inputs.push_back(um);
//输入也储存下,方便后面采样用
}
for (double tau = time_res * max_tau_; tau <= max_tau_; tau += time_res * max_tau_)
durations.push_back(tau);
//输入持续时间
}
// cout << "cur state:" << cur_state.head(3).transpose() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < inputs.size(); ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < durations.size(); ++j)
{
um = inputs[i];
double tau = durations[j];
stateTransit(cur_state, pro_state, um, tau);
//前向积分成路径
pro_t = cur_node->time + tau;
Eigen::Vector3d pro_pos = pro_state.head(3);
// Check if in close set
Eigen::Vector3i pro_id = posToIndex(pro_pos);
int pro_t_id = timeToIndex(pro_t);
PathNodePtr pro_node = dynamic ? expanded_nodes_.find(pro_id, pro_t_id) : expanded_nodes_.find(pro_id);
if (pro_node != NULL && pro_node->node_state == IN_CLOSE_SET)
{
if (init_search)
std::cout << "close" << std::endl;
continue;
}
// Check maximal velocity
Eigen::Vector3d pro_v = pro_state.tail(3);
if (fabs(pro_v(0)) > max_vel_ || fabs(pro_v(1)) > max_vel_ || fabs(pro_v(2)) > max_vel_)
{
if (init_search)
std::cout << "vel" << std::endl;
continue;
}
// Check not in the same voxel
Eigen::Vector3i diff = pro_id - cur_node->index;
int diff_time = pro_t_id - cur_node->time_idx;
if (diff.norm() == 0 && ((!dynamic) || diff_time == 0))
{
if (init_search)
std::cout << "same" << std::endl;
continue;
}
// Check safety
Eigen::Vector3d pos;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> xt;
bool is_occ = false;
for (int k = 1; k <= check_num_; ++k)
{
double dt = tau * double(k) / double(check_num_);
stateTransit(cur_state, xt, um, dt);
pos = xt.head(3);
if (edt_environment_->sdf_map_->getInflateOccupancy(pos) == 1 )
{
is_occ = true;
break;
}
}
if (is_occ)
{
if (init_search)
std::cout << "safe" << std::endl;
continue;
}
//计算代价
double time_to_goal, tmp_g_score, tmp_f_score;
tmp_g_score = (um.squaredNorm() + w_time_) * tau + cur_node->g_score;
tmp_f_score = tmp_g_score + lambda_heu_ * estimateHeuristic(pro_state, end_state, time_to_goal);
//节点裁剪
/*********
首先判断当前临时扩展节点与current node的其他临时扩展节点是否在同一个voxel中,如果是的话,
就要进行剪枝。要判断当前临时扩展节点的fscore是否比同一个voxel的对比fscore小,如果是的话,
则更新这一Voxel节点为当前临时扩展节点。
如果不剪枝的话,则首先判断当前临时扩展节点pro_node是否出现在open集中,如果是不是的话,
则可以直接将pro_node加入open集中。如果存在于open集但还未扩展的话,
则比较当前临时扩展节点与对应VOXEL节点的fscore,若更小,则更新voxel中的节点。
需要进行说明的是,在Fast planner的实现中,open集是通过两个数据结构实现的,
一个队列用来存储,弹出open集中的节点。
另一个哈希表NodeHashtable 用来查询节点是否已经存在于open集中。
而判断一个节点是否存在于close set中,则是通过Nodehashtable 与nodestate来决定的,如果nodeState 是 InCloseSet, 且存在于NodeHashtable,
则说明该节点已经被扩展过了,存在于close set中。
*****************/
// Compare nodes expanded from the same parent
bool prune = false;
for (int j = 0; j < tmp_expand_nodes.size(); ++j)
{
PathNodePtr expand_node = tmp_expand_nodes[j];
if ((pro_id - expand_node->index).norm() == 0 && ((!dynamic) || pro_t_id == expand_node->time_idx))
{
prune = true;
if (tmp_f_score < expand_node->f_score)
{
expand_node->f_score = tmp_f_score;
expand_node->g_score = tmp_g_score;
expand_node->state = pro_state;
expand_node->input = um;
expand_node->duration = tau;
if (dynamic)
expand_node->time = cur_node->time + tau;
}
break;
}
}
// This node end up in a voxel different from others
if (!prune)
{
if (pro_node == NULL)
{
pro_node = path_node_pool_[use_node_num_];
pro_node->index = pro_id;
pro_node->state = pro_state;
pro_node->f_score = tmp_f_score;
pro_node->g_score = tmp_g_score;
pro_node->input = um;
pro_node->duration = tau;
pro_node->parent = cur_node;
pro_node->node_state = IN_OPEN_SET;
if (dynamic)
{
pro_node->time = cur_node->time + tau;
pro_node->time_idx = timeToIndex(pro_node->time);
}
open_set_.push(pro_node);
if (dynamic)
expanded_nodes_.insert(pro_id, pro_node->time, pro_node);
else
expanded_nodes_.insert(pro_id, pro_node);
tmp_expand_nodes.push_back(pro_node);
use_node_num_ += 1;
if (use_node_num_ == allocate_num_)
{
cout << "run out of memory." << endl;
return NO_PATH;
}
}
else if (pro_node->node_state == IN_OPEN_SET)
{
if (tmp_g_score < pro_node->g_score)
{
// pro_node->index = pro_id;
pro_node->state = pro_state;
pro_node->f_score = tmp_f_score;
pro_node->g_score = tmp_g_score;
pro_node->input = um;
pro_node->duration = tau;
pro_node->parent = cur_node;
if (dynamic)
pro_node->time = cur_node->time + tau;
}
}
else
{
cout << "error type in searching: " << pro_node->node_state << endl;
}
}
}
// init_search = false;
}
cout << "open set empty, no path!" << endl;
cout << "use node num: " << use_node_num_ << endl;
cout << "iter num: " << iter_num_ << endl;
return NO_PATH;
}1.2 启发式函数设置
主要是利用庞特里亚金原理解决两点边界问题,得到最优解后,同时得到代价。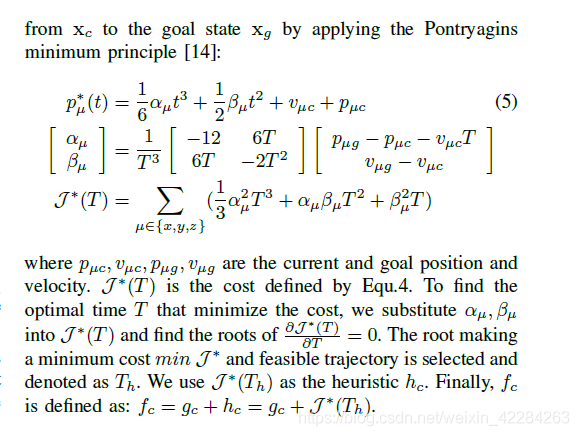
首先通过设置启发函数对时间求导等于0,得到启发函数关于时间T的四次方程,再通过求解该四次方程,得到一系列实根,通过比较这些实根所对应的cost大小,得到最优时间。这里需要注意,关于时间的一元四次方程是通过费拉里方法求解的,需要嵌套一个元三次方程进行求解,也就是代码中应的cubic()函数。
double KinodynamicAstar::estimateHeuristic(Eigen::VectorXd x1, Eigen::VectorXd x2, double& optimal_time)
{
const Vector3d dp = x2.head(3) - x1.head(3);
const Vector3d v0 = x1.segment(3, 3);
const Vector3d v1 = x2.segment(3, 3);
double c1 = -36 * dp.dot(dp);
double c2 = 24 * (v0 + v1).dot(dp);
double c3 = -4 * (v0.dot(v0) + v0.dot(v1) + v1.dot(v1));
double c4 = 0;
double c5 = w_time_;
std::vector<double> ts = quartic(c5, c4, c3, c2, c1);
double v_max = max_vel_ * 0.5;
double t_bar = (x1.head(3) - x2.head(3)).lpNorm<Infinity>() / v_max;
ts.push_back(t_bar);
double cost = 100000000;
double t_d = t_bar;
for (auto t : ts)
{
if (t < t_bar)
continue;
double c = -c1 / (3 * t * t * t) - c2 / (2 * t * t) - c3 / t + w_time_ * t;
if (c < cost)
{
cost = c;
t_d = t;
}
}
optimal_time = t_d;
return 1.0 * (1 + tie_breaker_) * cost;
}公式推导参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_16775293/article/details/124845417
1.3 这里我们遇到了第二个重要的函数ComputeShotTraj. 即利用庞特里亚金原理解一个两点边值问题。因为最优控制时间已经在estimateHeuristic中计算过了,所以这里只要引入该时间进行多项式计算即可。这部分的目的是为了验证该轨迹是安全的,即不发生碰撞,速度、加速度不超限。
bool KinodynamicAstar::computeShotTraj(Eigen::VectorXd state1, Eigen::VectorXd state2, double time_to_goal)
{
/* ---------- get coefficient ---------- */
const Vector3d p0 = state1.head(3);
const Vector3d dp = state2.head(3) - p0;
const Vector3d v0 = state1.segment(3, 3);
const Vector3d v1 = state2.segment(3, 3);
const Vector3d dv = v1 - v0;
double t_d = time_to_goal;
MatrixXd coef(3, 4);
end_vel_ = v1;
Vector3d a = 1.0 / 6.0 * (-12.0 / (t_d * t_d * t_d) * (dp - v0 * t_d) + 6 / (t_d * t_d) * dv);
Vector3d b = 0.5 * (6.0 / (t_d * t_d) * (dp - v0 * t_d) - 2 / t_d * dv);
Vector3d c = v0;
Vector3d d = p0;
// 1/6 * alpha * t^3 + 1/2 * beta * t^2 + v0
// a*t^3 + b*t^2 + v0*t + p0
coef.col(3) = a, coef.col(2) = b, coef.col(1) = c, coef.col(0) = d;
Vector3d coord, vel, acc;
VectorXd poly1d, t, polyv, polya;
Vector3i index;
Eigen::MatrixXd Tm(4, 4);
Tm << 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0;
/* ---------- forward checking of trajectory ---------- */
double t_delta = t_d / 10;
for (double time = t_delta; time <= t_d; time += t_delta)
{
t = VectorXd::Zero(4);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
t(j) = pow(time, j);
for (int dim = 0; dim < 3; dim++)
{
poly1d = coef.row(dim);
coord(dim) = poly1d.dot(t);
vel(dim) = (Tm * poly1d).dot(t);
acc(dim) = (Tm * Tm * poly1d).dot(t);
if (fabs(vel(dim)) > max_vel_ || fabs(acc(dim)) > max_acc_)
{
// cout << "vel:" << vel(dim) << ", acc:" << acc(dim) << endl;
// return false;
}
}
if (coord(0) < origin_(0) || coord(0) >= map_size_3d_(0) || coord(1) < origin_(1) || coord(1) >= map_size_3d_(1) ||
coord(2) < origin_(2) || coord(2) >= map_size_3d_(2))
{
return false;
}
// if (edt_environment_->evaluateCoarseEDT(coord, -1.0) <= margin_) {
//
return false;
// }
if (edt_environment_->sdf_map_->getInflateOccupancy(coord) == 1)
{
return false;
}
}
coef_shot_ = coef;
t_shot_ = t_d;
is_shot_succ_ = true;
return true;
}二、后端优化
2.1 离散采样,获取一些轨迹点和速度、加速度。
void KinodynamicAstar::getSamples(double& ts, vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& point_set,
vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& start_end_derivatives)
{
/* ---------- path duration ---------- */
double T_sum = 0.0;
if (is_shot_succ_)
T_sum += t_shot_;
PathNodePtr node = path_nodes_.back();
while (node->parent != NULL)
{
T_sum += node->duration;
node = node->parent;
}
// cout << "duration:" << T_sum << endl;
// Calculate boundary vel and acc
Eigen::Vector3d end_vel, end_acc;
double t;
if (is_shot_succ_)
{
t = t_shot_;
end_vel = end_vel_;
for (int dim = 0; dim < 3; ++dim)
{
Vector4d coe = coef_shot_.row(dim);
end_acc(dim) = 2 * coe(2) + 6 * coe(3) * t_shot_;
}
}
else
{
t = path_nodes_.back()->duration;
end_vel = node->state.tail(3);
end_acc = path_nodes_.back()->input;
}
// Get point samples
int seg_num = floor(T_sum / ts);
seg_num = max(8, seg_num);
ts = T_sum / double(seg_num);
bool sample_shot_traj = is_shot_succ_;
node = path_nodes_.back();
for (double ti = T_sum; ti > -1e-5; ti -= ts)
{
if (sample_shot_traj)
{
// samples on shot traj
Vector3d coord;
Vector4d poly1d, time;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
time(j) = pow(t, j);
for (int dim = 0; dim < 3; dim++)
{
poly1d = coef_shot_.row(dim);
coord(dim) = poly1d.dot(time);
}
point_set.push_back(coord);
t -= ts;
/* end of segment */
if (t < -1e-5)
{
sample_shot_traj = false;
if (node->parent != NULL)
t += node->duration;
}
}
else
{
// samples on searched traj
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> x0 = node->parent->state;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> xt;
Vector3d ut = node->input;
stateTransit(x0, xt, ut, t);
point_set.push_back(xt.head(3));
t -= ts;
// cout << "t: " << t << ", t acc: " << T_accumulate << endl;
if (t < -1e-5 && node->parent->parent != NULL)
{
node = node->parent;
t += node->duration;
}
}
}
reverse(point_set.begin(), point_set.end());
// calculate start acc
Eigen::Vector3d start_acc;
if (path_nodes_.back()->parent == NULL)
{
// no searched traj, calculate by shot traj
start_acc = 2 * coef_shot_.col(2);
}
else
{
// input of searched traj
start_acc = node->input;
}
start_end_derivatives.push_back(start_vel_);
start_end_derivatives.push_back(end_vel);
start_end_derivatives.push_back(start_acc);
start_end_derivatives.push_back(end_acc);
}2.2 前端离散点拟合成B样条曲线
每获得一个轨迹点就认为是一段?就有多少个控制点?这样控制点有点多啊
void NonUniformBspline::parameterizeToBspline(const double& ts, const vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& point_set,
const vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& start_end_derivative,
Eigen::MatrixXd&
ctrl_pts) {
if (ts <= 0) {
cout << "[B-spline]:time step error." << endl;
return;
}
if (point_set.size() < 2) {
cout << "[B-spline]:point set have only " << point_set.size() << " points." << endl;
return;
}
if (start_end_derivative.size() != 4) {
cout << "[B-spline]:derivatives error." << endl;
}
int K = point_set.size();
// write A
Eigen::Vector3d prow(3), vrow(3), arow(3);
prow << 1, 4, 1;
vrow << -1, 0, 1;
arow << 1, -2, 1;
Eigen::MatrixXd A = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(K + 4, K + 2);
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) A.block(i, i, 1, 3) = (1 / 6.0) * prow.transpose();
A.block(K, 0, 1, 3)
= (1 / 2.0 / ts) * vrow.transpose();
A.block(K + 1, K - 1, 1, 3) = (1 / 2.0 / ts) * vrow.transpose();
A.block(K + 2, 0, 1, 3)
= (1 / ts / ts) * arow.transpose();
A.block(K + 3, K - 1, 1, 3) = (1 / ts / ts) * arow.transpose();
// cout << "A:n" << A << endl;
// A.block(0, 0, K, K + 2) = (1 / 6.0) * A.block(0, 0, K, K + 2);
// A.block(K, 0, 2, K + 2) = (1 / 2.0 / ts) * A.block(K, 0, 2, K + 2);
// A.row(K + 4) = (1 / ts / ts) * A.row(K + 4);
// A.row(K + 5) = (1 / ts / ts) * A.row(K + 5);
// write b
Eigen::VectorXd bx(K + 4), by(K + 4), bz(K + 4);
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) {
bx(i) = point_set[i](0);
by(i) = point_set[i](1);
bz(i) = point_set[i](2);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
bx(K + i) = start_end_derivative[i](0);
by(K + i) = start_end_derivative[i](1);
bz(K + i) = start_end_derivative[i](2);
}
// solve Ax = b
Eigen::VectorXd px = A.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(bx);
Eigen::VectorXd py = A.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(by);
Eigen::VectorXd pz = A.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(bz);
// convert to control pts
ctrl_pts.resize(K + 2, 3);
ctrl_pts.col(0) = px;
ctrl_pts.col(1) = py;
ctrl_pts.col(2) = pz;
// cout << "[B-spline]: parameterization ok." << endl;
}虽然在计算B样条曲线上某一点的值时论文用的是DeBoor公式,但是在使用均匀B样条对前端路径进行拟合时用的是B样条的矩阵表达方法,具体参见论文:K. Qin, “General matrix representations for b-splines,” The Visual Computer, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 177–186, 2000.
2.3 B样条优化
Eigen::MatrixXd BsplineOptimizer::BsplineOptimizeTraj(const Eigen::MatrixXd& points, const double& ts,
const int& cost_function, int max_num_id,
int max_time_id) {
setControlPoints(points);
setBsplineInterval(ts);
setCostFunction(cost_function);
setTerminateCond(max_num_id, max_time_id);
optimize();
return this->control_points_;
}
void BsplineOptimizer::optimize() {
/* initialize solver */
iter_num_
= 0;
min_cost_
= std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
const int pt_num = control_points_.rows();
g_q_.resize(pt_num);
g_smoothness_.resize(pt_num);
g_distance_.resize(pt_num);
g_feasibility_.resize(pt_num);
g_endpoint_.resize(pt_num);
g_waypoints_.resize(pt_num);
g_guide_.resize(pt_num);
if (cost_function_ & ENDPOINT) {
variable_num_ = dim_ * (pt_num - order_);
// end position used for hard constraint
end_pt_ = (1 / 6.0) *
(control_points_.row(pt_num - 3) + 4 * control_points_.row(pt_num - 2) +
control_points_.row(pt_num - 1));
} else {
variable_num_ = max(0, dim_ * (pt_num - 2 * order_)) ;
}
/* do optimization using NLopt slover */
nlopt::opt opt(nlopt::algorithm(isQuadratic() ? algorithm1_ : algorithm2_), variable_num_);
opt.set_min_objective(BsplineOptimizer::costFunction, this);//设置优化函数
opt.set_maxeval(max_iteration_num_[max_num_id_]);//优化最大次数
opt.set_maxtime(max_iteration_time_[max_time_id_]);//优化最大时间
opt.set_xtol_rel(1e-5);//最后停止阈值
vector<double> q(variable_num_);
for (int i = order_; i < pt_num; ++i) {
if (!(cost_function_ & ENDPOINT) && i >= pt_num - order_) continue;
for (int j = 0; j < dim_; j++) {
q[dim_ * (i - order_) + j] = control_points_(i, j);
}
}
if (dim_ != 1) {
vector<double> lb(variable_num_), ub(variable_num_);
const double
bound = 10.0;
for (int i = 0; i < variable_num_; ++i) {
lb[i] = q[i] - bound;
ub[i] = q[i] + bound;
}
opt.set_lower_bounds(lb);//设置下限
opt.set_upper_bounds(ub);//设置上限
}
try {
// cout << fixed << setprecision(7);
// vec_time_.clear();
// vec_cost_.clear();
// time_start_ = ros::Time::now();
double
final_cost;
nlopt::result result = opt.optimize(q, final_cost);
/* retrieve the optimization result */
// cout << "Min cost:" << min_cost_ << endl;
} catch (std::exception& e) {
ROS_WARN("[Optimization]: nlopt exception");
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
for (int i = order_; i < control_points_.rows(); ++i) {
if (!(cost_function_ & ENDPOINT) && i >= pt_num - order_) continue;
for (int j = 0; j < dim_; j++) {
control_points_(i, j) = best_variable_[dim_ * (i - order_) + j];
}
}
if (!(cost_function_ & GUIDE)) ROS_INFO_STREAM("iter num: " << iter_num_);
}2.4 cost设计
2.4.1 平滑度cost:
三次B样条公式为:
$p(t) = p_{0} * F_{0,3}(t) + p_{1} * F_{1,3}(t) + p_{2} * F_{2,3}(t) + p_{3} * F_{3,3}(t) $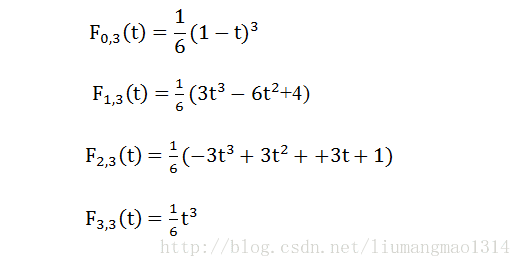
jerk就是对p(t)求三次导,这时会发现是一个常数,将每一段的jerk平方加起来,就得到cost。
梯度的求法:cost对控制点的求导。运用链式求导法则。
转变为cost对jerk的求导 * jerk对控制点的求导。
void BsplineOptimizer::calcSmoothnessCost(const vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& q, double& cost,
vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& gradient) {
cost = 0.0;
Eigen::Vector3d zero(0, 0, 0);
std::fill(gradient.begin(), gradient.end(), zero);
Eigen::Vector3d jerk, temp_j;
for (int i = 0; i < q.size() - order_; i++) {
/* evaluate jerk */
jerk = q[i + 3] - 3 * q[i + 2] + 3 * q[i + 1] - q[i];
cost += jerk.squaredNorm();
temp_j = 2.0 * jerk;
/* jerk gradient */
gradient[i + 0] += -temp_j;
gradient[i + 1] += 3.0 * temp_j;
gradient[i + 2] += -3.0 * temp_j;
gradient[i + 3] += temp_j;
}
}最后
以上就是大气路灯最近收集整理的关于fast planner总结的全部内容,更多相关fast内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复