先看代码
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> a=new LinkedList<>();
for (int i=0;i<11;i++){
a.add(i);
}
System.out.println(a);
for (Integer b:a){
if (b.equals(new Integer(3))) a.remove(new Integer(3));
}
System.out.println(a);
}
}
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> a=new LinkedList<>();
for (int i=0;i<11;i++){
a.add(i);
}
System.out.println(a);
Iterator<Integer> it= a.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
if (it.next().equals(new Integer(3))) a.remove(new Integer(3));
}
System.out.println(a);
}
}执行结果同为下图。
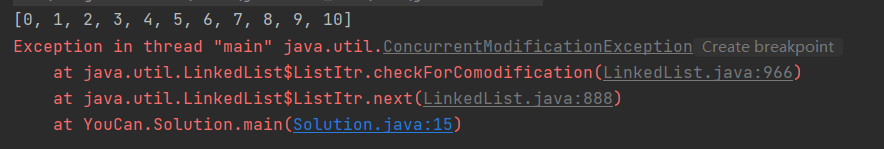
案例一运行结果看来,是不能这样对集合进行修改的,加强for循环,遍历数组时使用的普通for循环,而遍历集合时使用的Iterator迭代器。
而案例二,使用的是迭代器,但是同样报错。
在借助一个集合定义迭代器后,在遍历过程中,对集合做出修改,是不合理的。
解决方案:
一:
在if判断语句中,重新定义迭代器。
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> a=new LinkedList<>();
for (int i=0;i<11;i++){
a.add(i);
}
System.out.println(a);
Iterator<Integer> it= a.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
if (it.next().equals(new Integer(3))) {
a.remove(new Integer(3));
it= a.iterator();
}
}
System.out.println(a);
}
}二:
借助Inteager的remove()放法进行删除。
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> a=new LinkedList<>();
for (int i=0;i<11;i++){
a.add(i);
}
System.out.println(a);
Iterator<Integer> it= a.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
if (it.next().equals(new Integer(3))) it.remove();//**********
}
System.out.println(a);
}
}最后
以上就是独特猫咪最近收集整理的关于加强for循环和迭代器的全部内容,更多相关加强for循环和迭代器内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复