原文地址
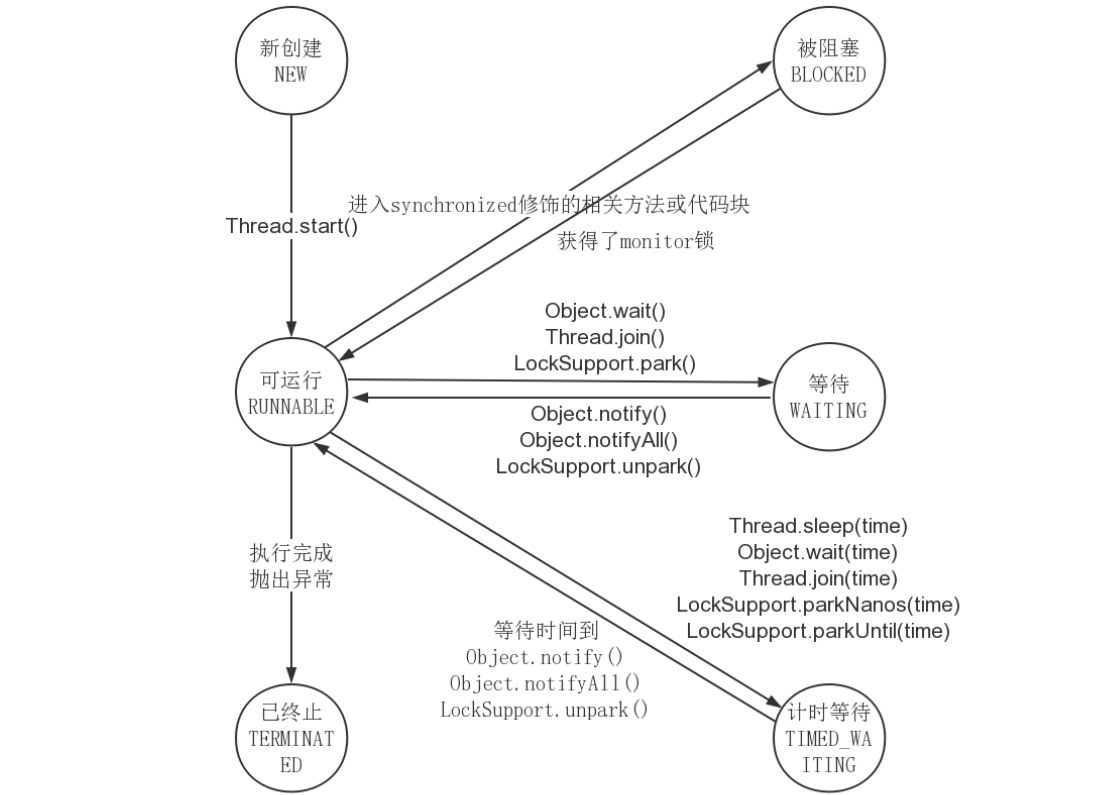
线程的 6 种状态
- New:已创建,未启动,已做好准备工作
- Runnable:可运行的,调用start()方法后
- Blocked:阻塞,进入synchronized相关方法或代码块,未持有锁
- Waiting:进入等待状态(wait(), join(), park()),同样唤醒方法(notify(), notifyAll(),
unpark(), 其中join方法要等到join执行的线程执行完毕才被唤醒) - Timed Waiting:计时等待,需要指定时间参数,可提前被唤醒,或者等待超时后
- Terminated:终止,run方法执行完毕;出现未捕获的异常意外终止
Blocked、Waiting、TimedWaiting都成为阻塞状态
代码演示
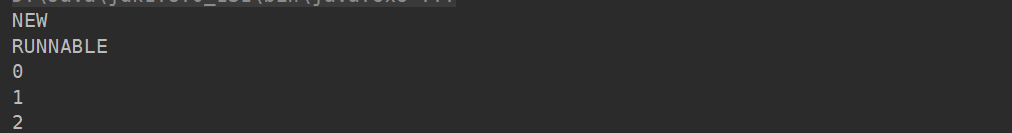
New / Runnable / Terminated 状态
public class NewRunnableTerminated implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new NewRunnableTerminated());
// 创建线程,未启动
System.out.println(thread.getState());
thread.start();
// 启动线程,可能还未运行
System.out.println(thread.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 已运行
System.out.println(thread.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 运行完毕
System.out.println(thread.getState());
}
}
结果展示


Blocked / Waiting / TimedWaiting 状态
public class BlockedWaitingTimedWaiting implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
syn();
}
private synchronized void syn() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockedWaitingTimedWaiting runnable = new BlockedWaitingTimedWaiting();
Thread thread01 = new Thread(runnable);
thread01.start();
Thread thread02 = new Thread(runnable);
thread02.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 线程1正在执行 Thread.sleep(1000),状态为 TIMED_WAITING
System.out.println(thread01.getName() + ": " + thread01.getState());
// 线程2未拿到锁,处于 BLOCKED 状态
System.out.println(thread02.getName() + ": " + thread02.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(1400);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// wait() 使得进入 WAITING 状态
System.out.println(thread01.getName() + ": " + thread01.getState());
}
}

最后
以上就是忐忑铅笔最近收集整理的关于线程的生命周期(6 种状态)的全部内容,更多相关线程的生命周期(6内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复