任务要求:
完成一个java application应用程序,完成字符串的各种操作。
- 操作包括字符串的初始化赋值和输出。
- 操作包括两个字符串相加合成为一个新字符串。
- 操作包括两个字符串比较其是否相同。
- 操作包括已知一个字符串,查找某一子字符串是否被包含在此字符串之中,如果包含,包含了多少次。
- 操作包括已知一个字符串及其包含的某一子字符串,把此子字符串替换为其他的新的指定字符串。
- 操作包括对特定字符串与数值之间的相互转换。
- 操作包括字符串与字节数组之间的相互转换。
- 操作包括从格式化字符串输入数值和利用格式化字符串输出数值。
1.Java String 类
字符串广泛应用 在Java 编程中,在 Java 中字符串属于对象,Java 提供了 String 类来创建和操作字符串。
只要创建了一个String对象,那么就不能再修改它的值,如果一个操作要修改某个字符串的内容或长度,并不能直接做到,而是要返回一个新的String对象。
2.练习
(1)字符串的初始化赋值和输出
代码如下:
class StrDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="To be or not to be"; //创建字符串
System.out.println(str); //输出字符串
}
}
结果如下:

(2)两个字符串相加合成为一个新字符串
代码如下:
class StrDemo1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str1="Twinkle Twinkle little star, ";//创建字符串1
String str2="How I wonder what you are";//创建字符串2
String str=str1+str2;//字符串相加
System.out.println(str);//输出字符串
}
}
结果如下:
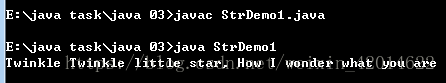
(3)比较两个字符串是否相同
代码如下:
class StrDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str1="Twinkle Twinkle little star, ";//创建字符串1
String str2="How I wonder what you are";//创建字符串2
boolean b=str1.equals(str2);//比较两个字符串,相同输出true,否则输出false
System.out.println(b);//输出字符串
}
}
结果如下:
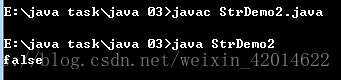
(4)已知一个字符串,查找某一子字符串是否被包含在此字符串之中,如果包含,包含了多少次
代码如下:
class StrDemo3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="Twinkle Twinkle little star, ";//创建字符串1
String str1="Twinkle";//创建字符串2
boolean b=str.contains(str1);//子字符串是否被包含在此字符串之中,包含输出true,否则输出false
System.out.println("子字符串是否被包含在此字符串之中:"+b);
System.out.println("包含次数为:"+count(str,str1));//调用count,输出包含次数
}
//统计子字符串被包含次数
static int count(String s1,String s2)
{
int c=0;
int index=-1;
while((index=s1.indexOf(s2,index))>-1)//indexOf查找一个字符或字符串的第一次出现
{
index+=s2.length();
c++;
}
return c;
}
}
结果如下:
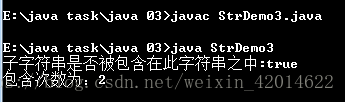
(5)已知一个字符串及其包含的某一子字符串,把此子字符串替换为其他的新的指定字符串
代码如下:
class StrDemo4
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="Hello xx ,how are you? ";//创建字符串
String s=str.replace("xx","Jay");//将xx替换为Jay
System.out.println("替换前:"+str);
System.out.println("替换后:"+s);
}
}
结果如下:
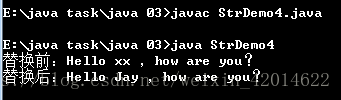
(6)特定字符串与数值之间的相互转换
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
class StrDemo5
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(true)
{
System.out.println("请输入:");
String str=sc.next();//创建字符串
int s=str.charAt(0);//输出对应ASCII值
System.out.println("输出:"+s);
}
}
}
结果如下:

(7)字符串与字节数组之间的相互转换
代码如下:
class ByteConvert
{
//整型转化为字节数组
public byte[] int2Byte(int id)
{
byte[] arr=new byte[4];
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
arr[i]=(byte)((id>>i*8)&0xff);
}
return arr;
}
//字节数组转化为整型
public int byte2Int(byte[] arr)
{
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int add=(int)((arr[i]&0xff)<<(i*8));
count+=add;
}
return count;
}
//long型转化为byte[]
public byte[] long2Byte(long id)
{
byte[] arr=new byte[8];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
{
arr[i]=(byte)((id>>i*8)&0xff);
}
return arr;
}
//byte[]转化为long
public long byte2long(byte[] arr)
{
long result=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
{
long add=(long)((arr[i]&0xff)<<i*8);
result+=add;
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ByteConvert bc=new ByteConvert();
//int转化为byte[]
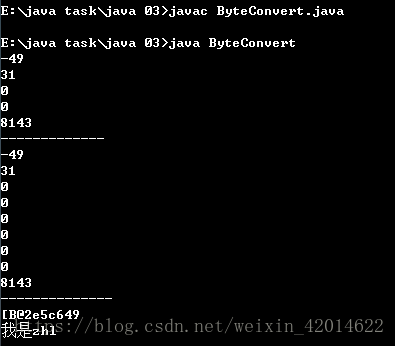
byte[] arr=bc.int2Byte(8143);
for(byte one:arr)
{
System.out.println(one);
}
//从字节数组转化为整型
System.out.println(bc.byte2Int(arr));
System.out.println("-------------");
//long转化为byte[]
byte[] arr2=bc.long2Byte(8143);
for(byte one:arr2)
{
System.out.println(one);
}
//byte[]转化为long
System.out.println(bc.byte2long(arr2));
System.out.println("--------------");
//String转化为byte[]
String str="我是zhl";
byte[] arr3=str.getBytes();
System.out.println(arr3);
//byte[]转化为String
String str2=new String(arr3);
System.out.println(str2);
}
}
结果如下:
(8)从格式化字符串输入数值和利用格式化字符串输出数值
通过 format() 方法来格式化字符串,除此之外,format方法还可以进行时间格式化。
| 转换符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| %s | 字符串类型 |
| %c | 字符类型 |
| %b | 布尔类型 |
| %d | 整数类型(十进制) |
| %x | 整数类型(十六进制) |
| %o | 整数类型(八进制) |
| %f | 浮点类型 |
| %a | 十六进制浮点类型 |
| %e | 指数类型 |
| %g | 通用浮点类型(f和e类型中较短的) |
| %h | 散列码 |
| %% | 百分比类型 |
| %n | 换行符 |
| %tx | 日期与时间类型(x代表不同的日期与时间转换符) |
| c | 包括全部日期和时间信息 |
| F | 年-月-日 |
| D | 月/日/年 |
| r | HH:MM:SS PM 12小时制 |
| T | HH:MM:SS 24小时制 |
| R | HH:MM |
代码如下:
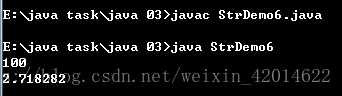
public class StrDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args){
String str=String.format("%o",64);//格式化输入数值
System.out.println(str);
double e = Math.E;
System.out.format("%f%n", e);//格式化输出数值
}
}
结果如下:
最后
以上就是彪壮星月最近收集整理的关于java 字符串操作的全部内容,更多相关java内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复