文章目录
- 剑32. 从上到下打印二叉树 1
- 剑32. 从上到下打印二叉树 2
- 剑32. 从上到下打印二叉树 3
- 剑32. 从上到下打印二叉树 4
- 剑33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- 全排列模板系列
- 剑34. 二叉树中和为某一值路径
- 剑37. 序列化和反序列化二叉树
- 剑38. 字符串的排列
- 力扣46. 全排列(不含重复元素)
- 力扣47. 全排列(含重复元素)
- 力扣77. 组合
- 力扣39. 组合总和1
- 力扣40. 组合总和2
- 力扣78. 子集
- 剑35. 复杂链表的复制
- 剑36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
- 剑39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
- 剑40. 最小的k个数
- 剑41. 数据流中的中位数
- 剑42. 连续子数组的最大和
- 剑45. 把数组排成最小的数
- 剑46. 把数字翻译成字符串
- 剑47. 礼物的最大价值
- 剑48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
- 49. 丑数
- 剑50. 第一个只出现一次的字符
- 剑51. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
- 剑53. 在排序数组中查找数字(二分查找)
- 剑53. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
- 剑54. 二叉搜索树的第k大结点
- 剑55. 二叉树的深度
- 剑55. 平衡二叉树
- 剑56. 数组中数字出现的次数1
- 剑56. 数组中数字出现的次数2
- 剑57. 和为s的两个数字
- 剑57. 和为s的连续正数序列
- 剑58. 翻转单词顺序
- 剑58. 左旋转字符串
- 剑59. 滑动窗口的最大值
- 剑68.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 剑68. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
剑32. 从上到下打印二叉树 1
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31从上到下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同一层的节点按照从左到右的顺序打印。 例如: 给定二叉树: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7], 3 / 9 20 / 15 7 返回: [3,9,20,15,7] class Solution { public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) { ArrayList<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>(); if(root==null) return new int[]{}; Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList(); queue.add(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode cur=queue.poll(); if(cur.left!=null) queue.add(cur.left); if(cur.right!=null) queue.add(cur.right); res.add(cur.val); } int len=res.size(); int re[]=new int[len]; for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ re[i]=res.get(i); } return re; } }
剑32. 从上到下打印二叉树 2
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层的节点按从左到右的顺序打印,每一层打印到一行。 例如: 给定二叉树: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7], 3 / 9 20 / 15 7 返回其层次遍历结果: [ [3], [9,20], [15,7] ] class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList(); public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) { if(root==null) return res; Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList(); queue.add(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ //path在里面创建 List<Integer> path=new ArrayList(); int len=queue.size(); //比1多了for 循环,因为每层就是一个集合 for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ TreeNode cur=queue.poll(); if(cur.left!=null) queue.add(cur.left); if(cur.right!=null) queue.add(cur.right); path.add(cur.val); } res.add(path); } return res; } }
剑32. 从上到下打印二叉树 3
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45请实现一个函数按照之字形顺序打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右 到左的顺序打印,第三行再按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。 例如: 给定二叉树: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7], 3 / 9 20 / 15 7 返回其层次遍历结果: [ [3], [20,9], [15,7] ] class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList(); public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) { if(root==null) return res; Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList(); queue.add(root); int count=0; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ count++; int len=queue.size(); List<Integer> path=new ArrayList(); for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ TreeNode cur=queue.poll(); if(cur.left!=null) queue.add(cur.left); if(cur.right!=null) queue.add(cur.right); //之字形,头插法 if(count%2==0){ path.add(0,cur.val); } //默认尾插法 if(count%2==1){ path.add(cur.val); } } res.add(path); } return res; } }
剑32. 从上到下打印二叉树 4
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的 层,逐层从左向右遍历) 例如: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7], 3 / 9 20 / 15 7 返回其自底向上的层次遍历为: [ [15,7], [9,20], [3] ] class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) { if (root==null) return res; Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ List<Integer> path=new LinkedList<>(); int length=queue.size(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); if (cur.left!=null) queue.add(cur.left); if (cur.right!=null) queue.add(cur.right); path.add(cur.val); } //采用头插法,就是自底向上的层次遍历 res.add(0,path); } return res; } }
剑33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历结果。如果是则返回 true, 否则返回 false。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。 参考以下这颗二叉搜索树: 5 / 2 6 / 1 3 示例 1: 输入: [1,6,3,2,5] 输出: false 方法一:递归分治 * 根据二叉搜索树的定义,可以通过递归,判断所有子树的 正确性 (即其后序遍历是否满足二叉搜索树的定义) ,若所有子树都正确,则此序列为二叉搜索树的后序遍历。 * 递归解析: * 终止条件: 当 i geq ji≥j ,说明此子树节点数量 leq 1≤1 ,无需判别正确性,因此直接返回 truetrue ; * 递推工作: * 划分左右子树: 遍历后序遍历的 [i, j][i,j] 区间元素,寻找 第一个大于根节点 的节点,索引记为 mm 。此时,可划分出左子树区间 [i,m-1][i,m−1] 、右子树区间 [m, j - 1][m,j−1] 、根节点索引 jj 。 * 判断是否为二叉搜索树: * 左子树区间 [i, m - 1][i,m−1] 内的所有节点都应 << postorder[j]postorder[j] 。而第 1.划分左右子树 步骤已经保证左子树区间的正确性,因此只需要判断右子树区间即可。 * 右子树区间 [m, j-1][m,j−1] 内的所有节点都应 >> postorder[j]postorder[j] 。实现方式为遍历,当遇到 leq postorder[j]≤postorder[j] 的节点则跳出;则可通过 p = jp=j 判断是否为二叉搜索树。 * 返回值: 所有子树都需正确才可判定正确,因此使用 与逻辑符 &&&& 连接。 * p = jp=j : 判断 此树 是否正确。 * recur(i, m - 1)recur(i,m−1) : 判断 此树的左子树 是否正确。 * recur(m, j - 1)recur(m,j−1) : 判断 此树的右子树 是否正确。 public class Solution { public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) { return result(0,postorder.length-1,postorder); } private boolean result(int left, int right, int[] postorder) { if (left>=right) return true; int index=left; while (postorder[index]<postorder[right]) index++; int temp=index; while (postorder[index]>postorder[right]) index++; return right==index&&result(left,temp-1,postorder)&&result(temp,right-1,postorder); } }
全排列模板系列
剑34. 二叉树中和为某一值路径
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中节点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。 从树的根节点开始往下一直到叶节点所经过的节点形成一条路径。 示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22, 5 / 4 8 / / 11 13 4 / / 7 2 5 1 返回: [ [5,4,11,2], [5,8,4,5] ] class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList(); public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) { if(root==null||sum<0) return res; List<Integer> path=new ArrayList(); dfs(sum,path,root); return res; } public void dfs(int sum,List<Integer> path,TreeNode root){ if(root==null) return; path.add(root.val); sum-=root.val; if(sum==0&&root.left==null&&root.right==null){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); } dfs(sum,path,root.left); dfs(sum,path,root.right); path.remove(path.size()-1); } }
剑37. 序列化和反序列化二叉树
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树。 你可以将以下二叉树: 1 / 2 3 / 4 5 序列化为 "[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]" public class Codec { // Encodes a tree to a single string. public String serialize(TreeNode root) { if(root==null) return "[]"; StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(); sb.append("["); Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList(); queue.add(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode cur=queue.poll(); if(cur!=null){ queue.add(cur.left); queue.add(cur.right); sb.append(cur.val+","); }else{ sb.append("null,"); } } sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1); sb.append("]"); return String.valueOf(sb); } // Decodes your encoded data to tree. public TreeNode deserialize(String data) { if (data.equals("[]")) return null; String []str = data.substring(1,data.length()-1).split(","); Queue <TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList(); TreeNode root=new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str[0])); queue.add(root); int i=1; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode cur=queue.poll(); if(!str[i].equals("null")){ cur.left=new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str[i])); queue.add(cur.left); } i++; if(!str[i].equals("null")){ cur.right=new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str[i])); queue.add(cur.right); } i++; } return root; } }
剑38. 字符串的排列
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32输入一个字符串,打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。 你可以以任意顺序返回这个字符串数组,但里面不能有重复元素。 输入:s = "abc" 输出:["abc","acb","bac","bca","cab","cba"] class Solution { ArrayList<String> res=new ArrayList(); public String[] permutation(String s) { if(s==null||s.length()==0) return res.toArray(new String[0]); char[] chars=s.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(chars); StringBuilder path=new StringBuilder(); boolean [] used=new boolean[chars.length]; dfs(chars,path,used); return res.toArray(new String[0]); } public void dfs(char[] chars,StringBuilder path,boolean [] used){ if(path.length()==chars.length){ res.add(path.toString()); return; } for(int i=0;i<chars.length;i++){ if(used[i]) continue; if(i>0&&chars[i]==chars[i-1]&&used[i-1]) continue; path.append(chars[i]); used[i]=true; dfs(chars,path,used); path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1); used[i]=false; } } }
力扣46. 全排列(不含重复元素)
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40给定一个 没有重复 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。 示例: 输入: [1,2,3] 输出: [ [1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], [3,2,1] ] public class Solution1 { List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { if (nums==null||nums.length==0) return res; List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>(); boolean[] used=new boolean[nums.length]; Arrays.sort(nums); dfs(nums,path,used); return res; } private void dfs(int[] nums, List<Integer> path, boolean[] used) { if (path.size()==nums.length){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { if (used[i]) continue; if (i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1]&&used[i])continue; used[i]=true; path.add(nums[i]); dfs(nums,path,used); used[i]=false; path.remove(path.size()-1); } } }
力扣47. 全排列(含重复元素)
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66给定一个可包含重复数字的序列,返回所有不重复的全排列。 示例: 输入: [1,1,2] 输出: [ [1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1] ] //回溯算法:剪枝递归,1.回溯结束条件 2.路径 3.选择分支 public class Solution { //存放所有的符合结果 List<List<Integer>> res= new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) { //溢出条件 if (nums==null||nums.length==0) return res; //定义一个路径path,用来每次添加元素,这里的类型是以集合List里的泛型为准List<Integer> //仅表示每次添加的一个数,与res存放所有的结果不同 List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); //因为回溯算法要剪枝,所以要排序,方便剪枝 Arrays.sort(nums); //定义选择条件:一个boolean数组,用于判断每一层的数据有没有选择过,默认false boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length]; //定义回溯算法:深度递归 dfs(nums,path,used); return res; } private void dfs(int[] nums, List<Integer> path, boolean[] used) { //一.回溯结束条件:定义回溯终止条件:找到了符合的结果 if (path.size()==nums.length){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } //三.选择分支:遍历选择列表 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { //排除掉不合法的选择 1和2 //1.已经在路径中的就不必再选择了 if (used[i]){ continue; } //2.刚被撤销的数就不必再选择了,既然这个数刚才被我撤销,我为撒还选它呢 //包含重复数字的序列[1,1,2]:所以当前数=前一个数,撤销选择used[i-1]==false //不包含重复数字的序列就不需要写这一行[1,2,3] if (i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1] && used[i-1]==false){ continue; } //做出选择:上面的条件不满足,说明这个数已经合法 used[i]=true; //二.路径:把当前这个数添加到路径 path.add(nums[i]); //递归回溯 dfs(nums,path,used); //撤销选择,回退到上一个节点 used[i]=false; //剪枝:删除调要撤销的数,准备从上一个节点重新选择 path.remove(path.size()-1); } } }
力扣77. 组合
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 ... n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。 示例: 输入: n = 4, k = 2 输出: [ [2,4], [3,4], [2,3], [1,2], [1,3], [1,4], ] public class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); dfs(n,k,1,path); return res; } private void dfs(int n, int k, int start, ArrayList<Integer> path) { if (path.size()==k){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = start; i <= n; i++) { path.add(i); //一个数不能重复出现,同时组合1,2和2,1是一样的,所以递归都是从i+1开始 //保证从下一位开始 dfs(n,k,i+1,path); path.remove(path.size()-1); } } }
力扣39. 组合总和1
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可 以使数字和为 target 的组合。candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。 说明: 所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。 解集不能包含重复的组合。 示例 1: 输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7, 所求解集为: [ [7], [2,2,3] ] public class Solution {List<List<Integer>>res=new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); dfs(0,candidates,target,path); return res; } private void dfs(int start,int[] candidates, int target, ArrayList<Integer> path) { if (target<0) return; if (target==0){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) { if (target-candidates[i]<0) continue;//如果已经小于0,就跳过,避免进入dfs,还得return path.add(candidates[i]); //保证i是从本位开始,不会从i-1前一位开始,2,2,3已出现,不能在3,2,2 //因为组合是一样的,可以重复使用所以从本位开始。 dfs(i,candidates,target-candidates[i],path); path.remove(path.size()-1); } } }
力扣40. 组合总和2
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。 candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。 说明: 所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。 解集不能包含重复的组合。 示例 1: 输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8, 所求解集为: [ [1, 7], [1, 2, 5], [2, 6], [1, 1, 6] ] public class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) { ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); Arrays.sort(candidates); dfs(0,candidates,target,path); return res; } private void dfs(int start, int[] candidates, int target, ArrayList<Integer> path) { if (target<0) return; if (target==0) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = start; i <candidates.length; i++) { // 小剪枝:同一层相同数值的结点,从第 2 个开始,候选数更少,结果一定发生重复,因此跳过,用 continue if (i>start&&candidates[i]==candidates[i-1]) continue; // 大剪枝:减去 candidates[i] 小于 0,减去后面的 candidates[i + 1]、candidates[i + 2] 肯定也小于 0,因此用 break if (target-candidates[i]<0) break; path.add(candidates[i]); // 因为元素不可以重复使用,这里递归传递下去的是 i + 1 而不是 i dfs(i+1,candidates,target-candidates[i],path); path.remove(path.size()-1); } } }
力扣78. 子集
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。 说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。 示例: 输入: nums = [1,2,3] 输出: [ [3], [1], [2], [1,2,3], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2], [] ] public class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { if (nums==null) return res; ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); dfs(0,nums,path); return res; } private void dfs(int start, int[] nums, ArrayList<Integer> path) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); for (int j = start; j < nums.length; j++) { path.add(nums[j]); dfs(j+1,nums,path); path.remove(path.size()-1); } } }
剑35. 复杂链表的复制
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。 值复制和关系复制 public class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if(head==null) return null; //定义一个HashMap存放父链表与子链表 HashMap<Node,Node> map=new HashMap(); Node cur=head; //1.将父链表与子链表的值val拷贝 while(cur!=null){ //key=父;value=子链表的值 map.put(cur,new Node(cur.val)); cur=cur.next; } //2.关系的复制 cur=head; while(cur!=null){ //将子链表的next指向下一个节点,与父链表保持一致 map.get(cur).next=map.get(cur.next); //将子链表的random指向下一个节点,与父链表保持一致 map.get(cur).random=map.get(cur.random); cur=cur.next; } //返回子链表的头结点 return map.get(head); } }
剑36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的循环双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的节 点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向。 public class Solution { ArrayList<Node> res=new ArrayList(); public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) { if(root==null) return null; //有序可重复集合存放中序遍历后的节点:都是按照升序排列好的,原先是二叉搜素树 Inorder(root); Node head=res.get(0); head.left=null; Node cur=head; //将节点用双向链表表示,前驱和后继串起来 for(int i=1;i<res.size();i++){ //其实这里的left表示前驱结点,right表示后继节点,就是prev和next cur.right=res.get(i); res.get(i).left=cur; //指针cur每次循环后都后移一位 cur=cur.right; } //将头尾指针串起来 head.left=res.get(res.size()-1); res.get(res.size()-1).right=head; return head; } public void Inorder(Node root){ if(root==null) return; Inorder(root.left); res.add(root); Inorder(root.right); } }
剑39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。 你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。 示例 1: 输入: [1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 5, 4, 2] 输出: 2 class Solution { public int majorityElement(int[] nums) { quickSort(0,nums.length-1,nums); return nums[nums.length/2]; } public void quickSort(int left,int right,int[] nums){ if(left<right){ int mid=findZhou(left,right,nums); quickSort(left,mid-1,nums); quickSort(mid+1,right,nums); } } public int findZhou(int left,int right,int[] nums){ int temp=nums[left]; while(left<right){ while(left<right){ if(nums[right]>temp){ right--; }else{ nums[left++]=nums[right]; break; } } while(left<right){ if(nums[left]<temp){ left++; }else{ nums[right--]=nums[left]; break; } } } nums[left]=temp; return left; } }
剑40. 最小的k个数
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15输入整数数组 arr ,找出其中最小的 k 个数。例如,输入4、5、1、6、2、7、3、8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1、2、3、4。 示例 1: 输入:arr = [3,2,1], k = 2 输出:[1,2] 或者 [2,1] class Solution { public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) { Arrays.sort(arr); int []res=new int[k]; for(int i=0;i<k;i++){ res[i]=arr[i]; } return res; } }
剑41. 数据流中的中位数
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就 是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位 数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。 例如, [2,3,4] 的中位数是 3 [2,3] 的中位数是 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5 public class Solution { //优先队列默认是按照从小到大排:按照小顶堆顺序,升序 Queue<Integer> min=new PriorityQueue<>(); //创建队列实现大顶堆 Queue<Integer> max=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() { @Override //比较器默认是每次比较相邻的两个数,且o1是第二个数,o2是第一个数,逆着来很奇怪 public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { //默认o2-o1>1(第一个数-第二个数>1 降序) 或者o1-o2>1(第二个数-第一个数>1 升序) return o2-o1; } } ); //保证大顶堆在下半区,栈顶是最大数;小顶堆是在上半区,栈顶是最小数。 //所以将较大的数放在小顶堆,较小的数放在大顶推,这样由下半区到上半区是一个升序队列,而中间的两个数 //就是各自的栈顶,可能和是偶数,中位数取两个数的平均;和是奇数,本题取大顶堆栈顶(也可以取小顶堆栈顶,自己设置添加顺序) public void Insert(Integer num) { if (max.size() != min.size()) {//当两个队列元素不相等时 //先将元素添加到大顶堆中(会大顶堆排序:前面是优先队列) max.add(num); //将大顶堆栈顶元素取出放到小顶堆中(会按照优先队列小顶堆排序) min.add(max.poll()); } else { //两个队列相等,就将元素放到小顶堆中 min.add(num); //将小顶堆栈顶元素取出放到大顶堆中(会按照优先队列大顶堆排序) max.add(min.poll()); } } public Double GetMedian() { //和为奇数 if (max.size() != min.size()) { //按照上面的添加顺序会使大顶堆比小顶堆元素多1 return (double) max.peek(); } else { //和是偶数,中位数取两个数的平均 return (double) (min.peek() + max.peek())/2; } } }
剑42. 连续子数组的最大和
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17输入一个整型数组,数组中的一个或连续多个整数组成一个子数组。 求所有子数组的和的最大值。 示例1: 输入: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] 输出: 6 解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。 class Solution { public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { int res=nums[0]; for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){ nums[i]+=Math.max(nums[i-1],0); res=Math.max(res,nums[i]); } return res; } }
剑45. 把数组排成最小的数
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29输入一个非负整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的 所有数字中最小的一个。 示例 1: 输入: [10,2] 输出: "102" class Solution { public String minNumber(int[] nums) { //1.把整型转成字符串 String [] strs=new String[nums.length]; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { strs[i] = String.valueOf(nums[i]); } //2.把String数组进行排序 Arrays.sort(strs, new Comparator<String>() { @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { //字符串按照从小到大排 return (o1+o2).compareTo(o2+o1); } }); //3.把字符数组拼成一个字符串输出 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); for(String s:strs){ sb.append(s); } return sb.toString(); } }
剑46. 把数字翻译成字符串
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24给定一个数字,我们按照如下规则把它翻译为字符串:0 翻译成 “a” ,1 翻译成 “b”,……,11 翻译成 “l”,……,25 翻译成 “z”。一个数字可能有多个翻译。请编程实现一个函数,用来计算一个数字有多少种不同的翻译方法。 示例 1: 输入: 12258 输出: 5 解释: 12258有5种不同的翻译,分别是"bccfi", "bwfi", "bczi", "mcfi"和"mzi" class Solution { public int translateNum(int num) { String s = String.valueOf(num); int leng=s.length(); if (leng<2) return leng; char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); int []dp=new int[leng+2]; dp[0]=1; dp[1]=1; for (int i =2 ; i < leng+1; i++) { dp[i]=dp[i-1]; int current=10*(chars[i-1]-'0')+(chars[i]-'0'); if (current>9&¤t<26) dp[i]=dp[i-2]+dp[i-1]; } return dp[leng]; } }
剑47. 礼物的最大价值
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29在一个 m*n 的棋盘的每一格都放有一个礼物,每个礼物都有一定的价值(价值大于 0)。你可以从棋盘的左上角开始拿格子里的礼物,并每次向右或者向下移动一格、直到到达棋盘的右下角。给定一个棋盘及其上面的礼物的价值,请计算你最多能拿到多少价值的礼物? 示例 1: 输入: [ [1,3,1], [1,5,1], [4,2,1] ] 输出: 12 解释: 路径 1→3→5→2→1 可以拿到最多价值的礼物 class Solution { public int maxValue(int[][] grid) { int m=grid.length; int n=grid[0].length; int dp[][]=new int[m][n]; dp[0][0]=grid[0][0]; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { //分为四种情况 if (i==0&&j==0) continue; else if (i==0) dp[i][j]=grid[i][j]+dp[i][j-1]; else if (j==0) dp[i][j]=grid[i][j]+dp[i-1][j]; else dp[i][j]=grid[i][j]+Math.max(dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j]); } } return dp[m-1][n-1]; } }
剑48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29请从字符串中找出一个最长的不包含重复字符的子字符串,计算该最长子字符串的长度。 示例 1: 输入: "abcabcbb" 输出: 3 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。 class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) { // 哈希集合,记录每个字符是否出现过 Set<Character> occ = new HashSet<Character>(); int n = s.length(); // 右指针,初始值为 -1,相当于我们在字符串的左边界的左侧,还没有开始移动 int rk = -1, ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (i != 0) { // 左指针向右移动一格,移除一个字符 occ.remove(s.charAt(i - 1)); } while (rk + 1 < n && !occ.contains(s.charAt(rk + 1))) { // 不断地移动右指针 occ.add(s.charAt(rk + 1)); ++rk; } // 第 i 到 rk 个字符是一个极长的无重复字符子串 ans = Math.max(ans, rk - i + 1); } return ans; } }
49. 丑数
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25我们把只包含质因子 2、3 和 5 的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。求按从小到大的顺序的第 n 个丑数。 示例: 输入: n = 10 输出: 12 解释: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12 是前 10 个丑数。 class Solution { public int nthUglyNumber(int n) { if (n<=0) return 0; int [] uglyaddr=new int[n]; uglyaddr[0]=1; //定义 2,3,5的下标 int p2=0,p3=0,p5=0; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { //上一个丑数 int lastugly=uglyaddr[i-1]; //当uglyaddr[p2/p3/p5]*2>lastugly的一刻,就找到这次的3个丑数,在取最小值作为这次循环的丑数 while (lastugly>=uglyaddr[p2]*2)p2++; while (lastugly>=uglyaddr[p3]*3)p3++; while (lastugly>=uglyaddr[p5]*5)p5++; uglyaddr[i]=Math.min(Math.min(uglyaddr[p2]*2,uglyaddr[p3]*3),uglyaddr[p5]*5); } return uglyaddr[n-1]; } }
剑50. 第一个只出现一次的字符
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23在字符串 s 中找出第一个只出现一次的字符。如果没有,返回一个单空格。 s 只包含小写字母。 示例: s = "abaccdeff" 返回 "b" s = "" 返回 " " class Solution { public char firstUniqChar(String s) { Map<Character, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { if (map.containsKey(s.charAt(i))){ map.put(s.charAt(i),2); }else { map.put(s.charAt(i),1); } } for(Map.Entry<Character, Integer> d : map.entrySet()){ if(d.getValue()==1) return d.getKey(); } return ' '; } }
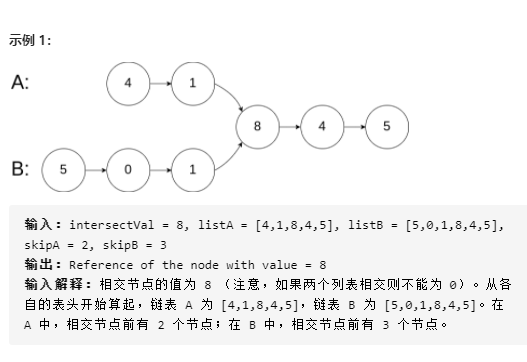
剑51. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } } /** * 利用A先走第一个链表再走第二个链表,B先走第二个链表再走第一个链表, * 当他们遇到第一个重合点时,走的节点数是相同的。利用这个求 * */ public class Solution { public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { //首先定义两个节点:A和B,双指针, ListNode A = pHead1; ListNode B = pHead2; while (A != B) {//当节点相遇时,说明这就是第一个公共节点,直接返回该公共节点 //当A从pHead1自己这条链表走到尾时,还没有相遇,当下一个节点为null,直接从B的链表pHead2走 if (A == null) A = pHead2; //不断的后移 else A = A.next; //当B从pHead2自己这条链表走到尾时,还没有相遇,当下一个节点为null,直接从A的链表pHead1走 if (B == null) B = pHead1; //不断的后移 else B = B.next; } return A; } }
剑53. 在排序数组中查找数字(二分查找)
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60统计一个数字在排序数组中出现的次数。 示例 1: 输入: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8 输出: 2 示例 2: 输入: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6 输出: 0 public class Solution { public int GetNumberOfK(int [] array , int k) { if (array==null||array.length==0) return 0; //可以采用最右边-最左边来计数,因为排序数组中相同的数都是在一起 //最左边的数left int left=findleft(array,k); //既然一轮二分查找后,没有找到与k相等的数,说明这个排序数组就没有这个k,就没必要再找最右边的数 if (left==-1) return 0; int right=findright(array,k); //最右边-最左边来计数,比如1,2,3,3,3,4 4-2+1=3,要+1否则少一个数 return right-left+1; } private int findleft(int[] array, int target) { //二分查找模板格式 int left=0,right=array.length-1; //当left+1=right,说明left和right相邻,可以直接对这2个数进行与target比较 while (left+1<right){ int mid=(right-left)/2+left; if (target>array[mid]){ left=mid; }else {//target<=array[mid]情况:有=情况说明right的值在不断往左边查找,直到找到最左边 right=mid; } } //当遍历到相邻的两个数,跳出循环,target就需要比较了 先返回left,再返回right,=往左边查找,left最先,之后到right if (target==array[left]) return left; if (target==array[right]) return right; return -1; } private int findright(int[] array, int target) { //二分查找模板格式 int left=0,right=array.length-1; //当left+1=right,说明left和right相邻,可以直接对这2个数进行与target比较 while (left+1<right){ int mid=(right-left)/2+left; //target>=array[mid]情况:有=情况说明left的值在不断往右边查找,直到找到最右边的数 if (target>=array[mid]){ left=mid; }else { right=mid; } } //当遍历到相邻的两个数,跳出循环,target就需要比较了 //先返回right,再返回left,=往右边查找,right最先,之后到left if (target==array[right]) return right; if (target==array[left]) return left; return -1; } }
剑53. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16一个长度为n-1的递增排序数组中的所有数字都是唯一的,并且每个数字都在范围0~n-1之内。在范围0~n-1内的n个数字中有且只有一个数字不在该数组中,请找出这个数字。 示例 1: 输入: [0,1,3] 输出: 2 示例 2: 输入: [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,9] 输出: 8 class Solution { public int missingNumber(int[] nums) { for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ if(nums[i]!=i) return i; } return nums.length; } }
剑54. 二叉搜索树的第k大结点
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中第k大的节点。 示例 1: 输入: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1 3 / 1 4 2 输出: 4 class Solution { ArrayList<Integer> res=new ArrayList(); public int kthLargest(TreeNode root, int k) { Inorder(root); return res.get(res.size()-k); } public void Inorder(TreeNode root){ if(root==null) return; Inorder(root.left); res.add(root.val); Inorder(root.right); } }
剑55. 二叉树的深度
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16输入一棵二叉树的根节点,求该树的深度。从根节点到叶节点依次经过的节点(含根、叶节点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。 例如: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7], 3 / 9 20 / 15 7 返回它的最大深度 3 。 class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if(root==null) return 0; return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))+1; } }
剑55. 平衡二叉树
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23输入一棵二叉树的根节点,判断该树是不是平衡二叉树。如果某二叉树中任意节点的左右子树的深度相差不超过1,那么它就是一棵平衡二叉树。 示例 1: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 3 / 9 20 / 15 7 class Solution { public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { if(root==null) return true; int left=height(root.left); int right=height(root.right); //左右子树的高度差小于1 return Math.abs(right-left)>1?false:true&&isBalanced(root.left)&&isBalanced(root.right); } //计算树的高度 public int height(TreeNode root){ if(root==null) return 0; return Math.max(height(root.left),height(root.right))+1; } }
剑56. 数组中数字出现的次数1
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25一个整型数组 nums 里除两个数字之外,其他数字都出现了两次。请写程序找出这两个只出现一次的数字。要求时间复杂度是O(n),空间复杂度是O(1)。 示例 1: 输入:nums = [4,1,4,6] 输出:[1,6] 或 [6,1] public class Solution { public int[] singleNumbers(int[] nums) { int res=0; for(int num:nums){ //每一位异或后 res^=num; } //得出mask值 int mask=res&(-res); int result[] =new int[2]; for (int num:nums){ if ((num&mask)==0){ result[0]^=num; }else { result[1]^=num; } } return result; } }
剑56. 数组中数字出现的次数2
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27在一个数组 nums 中除一个数字只出现一次之外,其他数字都出现了三次。请找出那个只出现一次的数字。 示例 1: 输入:nums = [3,4,3,3] 输出:4 示例 2: 输入:nums = [9,1,7,9,7,9,7] 输出:1 public class Solution { public int singleNumber(int[] nums) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); int count=0; for (int num:nums){ if (map.containsKey(num)){ map.put(num,count+1); }else { map.put(num,count); } } for (Integer key:map.keySet()){ if (map.get(key)==0){ return key; } } return -1; } }
剑57. 和为s的两个数字
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字s,在数组中查找两个数,使得它们的和正好是s。如果有多对数字的和等于s,则输出任意一对即可。 示例 1: 输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 输出:[2,7] 或者 [7,2] public class Solution { //双指针做法 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { int left=0; int right=nums.length-1; int []res=new int[2]; while (left < right) { if (nums[left] + nums[right] < target) { left++; } else if (nums[left] + nums[right] > target) { right--; } else { res[0] = nums[left]; res[1] = nums[right]; return res; } } return res; } }
剑57. 和为s的连续正数序列
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40输入一个正整数 target ,输出所有和为 target 的连续正整数序列(至少含有两个数)。 序列内的数字由小到大排列,不同序列按照首个数字从小到大排列。 示例 1: 输入:target = 9 输出:[[2,3,4],[4,5]] 示例 2: 输入:target = 15 输出:[[1,2,3,4,5],[4,5,6],[7,8]] public int[][] findContinuousSequence(int target) { int i = 1; // 滑动窗口的左边界 int j = 1; // 滑动窗口的右边界 int sum = 0; // 滑动窗口中数字的和 List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>(); while (i <= target / 2) { if (sum < target) { // 右边界向右移动 sum += j; j++; } else if (sum > target) { // 左边界向右移动 sum -= i; i++; } else { // 记录结果 int[] arr = new int[j-i]; for (int k = i; k < j; k++) { arr[k-i] = k; } res.add(arr); // 左边界向右移动 sum -= i; i++; } } return res.toArray(new int[res.size()][]); }
剑58. 翻转单词顺序
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27输入一个英文句子,翻转句子中单词的顺序,但单词内字符的顺序不变。为简单起见,标点符号和普通字母一样处理。例如输入字符串"I am a student. ",则输出"student. a am I"。 示例 1: 输入: "the sky is blue" 输出: "blue is sky the" public class Solution { public static void main(String[] args) { String s="I am a student. "; reverseWords(s); } public static String reverseWords(String s) { String[] split = s.trim().split(" "); StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(); for (int i = split.length-1; i >=0; i--) { if (split[i].equals("")){ continue; } if (i==0){ stringBuffer.append(split[i]); }else { stringBuffer.append(split[i]+" "); } } return stringBuffer.toString(); } }
剑58. 左旋转字符串
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13字符串的左旋转操作是把字符串前面的若干个字符转移到字符串的尾部。请定义一个函数实现字符串左旋转操作的功能。比如,输入字符串"abcdefg"和数字2,该函数将返回左旋转两位得到的结果"cdefgab"。 示例 1: 输入: s = "abcdefg", k = 2 输出: "cdefgab" public class Solution { public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) { String substring1 = s.substring(0, n); String substring2 = s.substring(n, s.length()); return substring2+substring1; } }
剑59. 滑动窗口的最大值
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41给定一个数组 nums 和滑动窗口的大小 k,请找出所有滑动窗口里的最大值。 示例: 输入: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3 输出: [3,3,5,5,6,7] 解释: 滑动窗口的位置 最大值 --------------- ----- [1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7 public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int [] num, int size) { if(num==null || size<1 || num.length<size){ return new ArrayList<>(); } LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); int n = num.length; for(int i=0;i<=n-1;i++){ //如果窗口尾部的元素比当前元素小,或者相等,就让窗口尾部的元素弹出 while(!queue.isEmpty() && num[queue.peekLast()] <= num[i]){ queue.pollLast(); } //否则当前运算正常入队 queue.addLast(i); //如果滑动窗口已经略过了队列中头部的元素,则将头部元素弹出 if(queue.peekFirst()==(i-size)){ queue.pollFirst(); } //如果窗口形成了,就开始取出最大值 //一开始进入队列,要看看窗口有没有形成,只有形成了大小为 k 的窗口,我才能收集窗口内的最大值 //一旦窗口形成,之后每进入一个元素就可以取出最大值了 if(i-size+1>=0){ res.add(num[queue.peekFirst()]); } } return res; } }
剑68.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。 百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。” 例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] 示例 1: 输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出: 3 解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。 public class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { /**1.迭代 * 循环搜索: 当节点 rootroot 为空时跳出; * 当 p, qp,q 都在 rootroot 的 右子树 中,则遍历至 root.rightroot.right ; * 否则,当 p, qp,q 都在 rootroot 的 左子树 中,则遍历至 root.leftroot.left ; * 否则,说明找到了 最近公共祖先 ,跳出。 * 返回值: 最近公共祖先 rootroot 。 * */ /*while (root!=null){ if (root.val<p.val&&root.val<q.val){ root=root.right; }else if (root.val>p.val&&root.val>q.val){ root=root.left; }else { break; } } return root;*/ /**2.递归 * 递推工作: * 当 p, q都在 rootroot 的 右子树 中,则开启递归 root.rightroot.right 并返回; * 否则,当 p, q都在 rootroot 的 左子树 中,则开启递归 root.leftroot.left 并返回; * 返回值: 最近公共祖先 root 。 * */ if (root.val<p.val&&root.val<q.val){ return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q); }else if (root.val>p.val&&root.val>q.val){ return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q); } return root; } }
剑68. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
复制代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root==null||root==p||root==q) return root; TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q); TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q); if (left==null) return right; if (right==null) return left; return root; } } --------------------------------------- public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int o1, int o2) { // write code here if (root == null) { return 0; } if (root.val == o1 || root.val == o2) { return root.val; } int left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,o1,o2); int right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,o1,o2); if (left==0) return right; if (right==0) return left; return root.val; }
最后
以上就是飞快钢笔最近收集整理的关于剑指Offer(力扣剑后30)的全部内容,更多相关剑指Offer(力扣剑后30)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。







发表评论 取消回复