文章目录
- 一.Sentinel下载安装运行
- 二.Sentinel初始化监控
- 三.流控规则
- 1. 阈值类型
- 1.1 QPS
- 1.2 线程数
- 2. 流控模式
- 2.1 直接
- 2.2 关联
- 2.3 链路
- 3. 流控效果
- 3.1 快速失败
- 3.2 WarmUp预热
- 3.3 排队等待
- 四.降级规则
- 1. RT
- 2. 异常比例
- 3. 异常数
- 五.Sentinel 热点key
- 1. 基本使用
- 2. 参数例外项
- 六.Sentinel系统规则
- 七.@SentinelResource 注解
- 1. 资源名称限流+后续处理
- 2. url地址限流+后续处理
- 3. 客户自定义限流处理逻辑
- 八.服务熔断
- 1. 初始化测试环境
- 1.1 创建消费者
- 1.2 创建消费者
- 2. 服务熔断无配置
- 3. 服务熔断只配置fallback
- 4. 服务熔断只配置blockHandler
- 5. fallback和blockHandler都配置
- 6. 忽略异常exceptionsToIgnore
- 7. Sentinel服务熔断OpenFeign
- 九.熔断框架比较
- 十.规则持久化
官方Github:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel
官方文档:https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/docs/introduction.html
一.Sentinel下载安装运行
Sentinel 分为两个部分:
- 核心库(Java 客户端)不依赖任何框架/库,能够运行于所有 Java 运行时环境,同时对 Dubbo / Spring Cloud 等框架也有较好的支持。
- 控制台(Dashboard)基于 Spring Boot 开发,打包后可以直接运行,不需要额外的 Tomcat 等应用容器。
安装步骤:
下载:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/releases/tag/1.7.0(本次使用的是1.7.0版本)
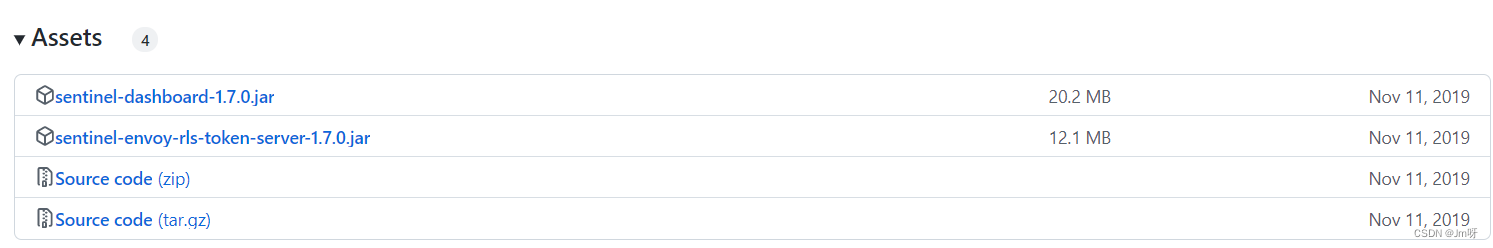
运行Sentinel:
前提:Java 8 环境、8080端口不能被占用
命令:java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.7.0.jar
访问Sentinel管理界面:
- localhost:8080
- 登录账号密码均为sentinel
二.Sentinel初始化监控
新建工程 : cloudalibaba-sentinel-service8401
POM.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>cloud2022</artifactId>
<groupId>com.jm.springcloud</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloudalibaba-sentinel-service8401</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency><!-- 引入自己定义的api通用包,可以使用Payment支付Entity -->
<groupId>com.jm.springcloud</groupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--SpringCloud ailibaba nacos -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringCloud ailibaba sentinel-datasource-nacos 后续做持久化用到-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringCloud ailibaba sentinel -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--openfeign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- SpringBoot整合Web组件+actuator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--日常通用jar包配置-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>4.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Application.yml
server:
port: 8401
spring:
application:
name: cloudalibaba-sentinel-service
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
# nacos 服务注册中心地址
server-addr: localhost:8848
sentinel:
transport:
# 配置 sentinel dashboard 地址
dashboard: localhost:8080
# 默认8719端口,假如被占用会自动从 8719开始依次加1,直到找到未被占用的端口
port: 8719
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
主启动类
@RestController
public class FlowLimitController {
@GetMapping("/testA")
public String testA() {
return " test A";
}
@GetMapping("/testB")
public String testB() {
return " test B";
}
}
业务类:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class MainApp8401 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApp8401.class, args);
}
}
测试:
- 启动 nacos-server 服务
- 启动 sentinel 服务
- 启动 8401 微服务
多次访问:http://localhost:8401/testA、http://localhost:8401/testB
在sentinel中能查看到访问:
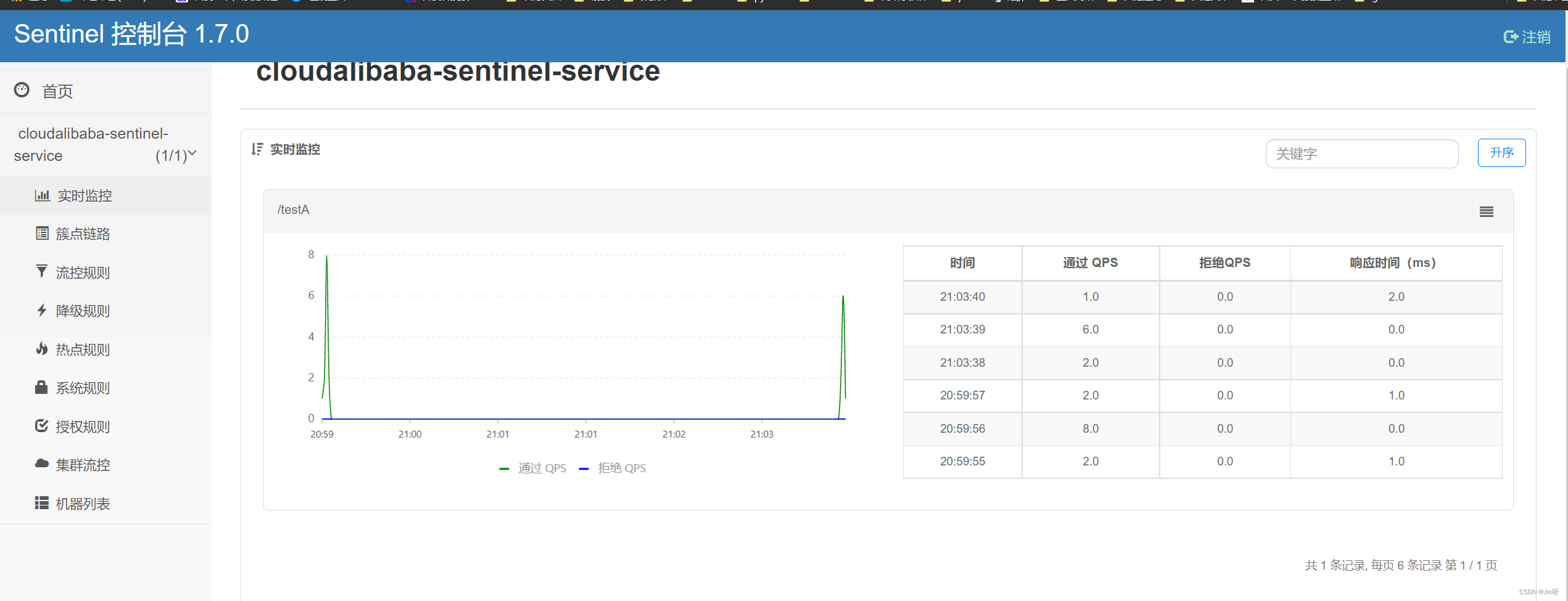
三.流控规则
基本介绍
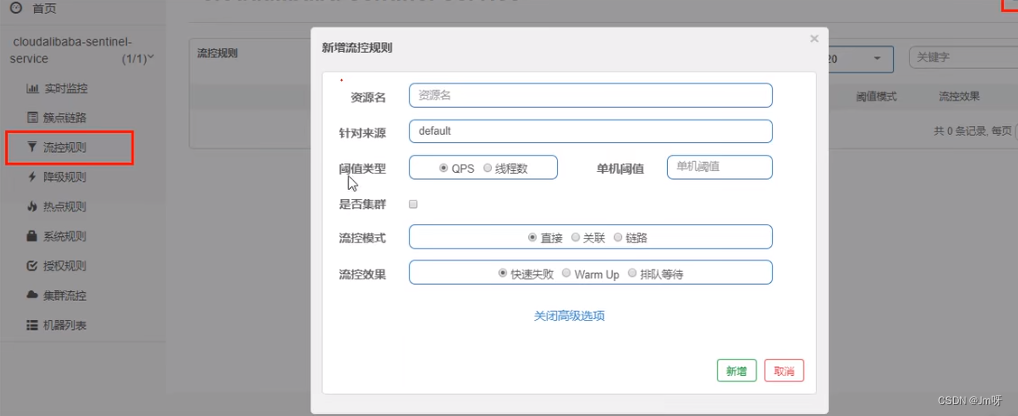
- 资源名:唯一名称,默认请求路径。
- 针对来源:Sentinel可以针对调用者进行限流,填写微服务名,默认default(不区分来源)。
- 阈值类型/单机阈值:
- QPS(每秒钟的请求数量)︰当调用该API的QPS达到阈值的时候,进行限流。
- 线程数:当调用该API的线程数达到阈值的时候,进行限流。
- 是否集群:不需要集群。
- 流控模式:
- 直接:API达到限流条件时,直接限流。
- 关联:当关联的资源达到阈值时,就限流自己。
- 链路:只记录指定链路上的流量(指定资源从入口资源进来的流量,如果达到阈值,就进行限流)【API级别的针对来源】。
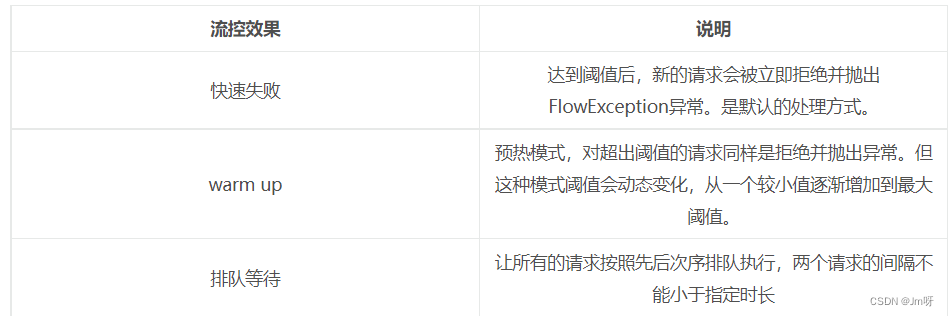
- 流控效果:
- 快速失败:直接失败,抛异常。
- Warm up:根据Code Factor(冷加载因子,默认3)的值,从阈值/codeFactor,经过预热时长,才达到设置的QPS阈值。
- 排队等待:匀速排队,让请求以匀速的速度通过,阈值类型必须设置为QPS,否则无效。
1. 阈值类型
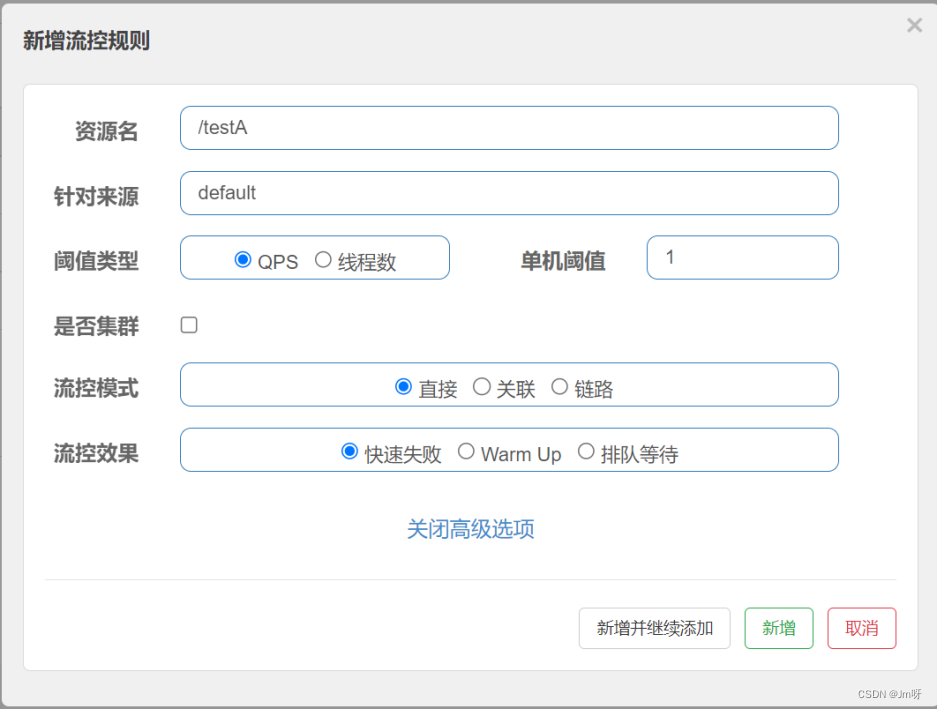
1.1 QPS
(每秒钟的请求数量)︰当调用该API的QPS达到阈值的时候,进行限流。
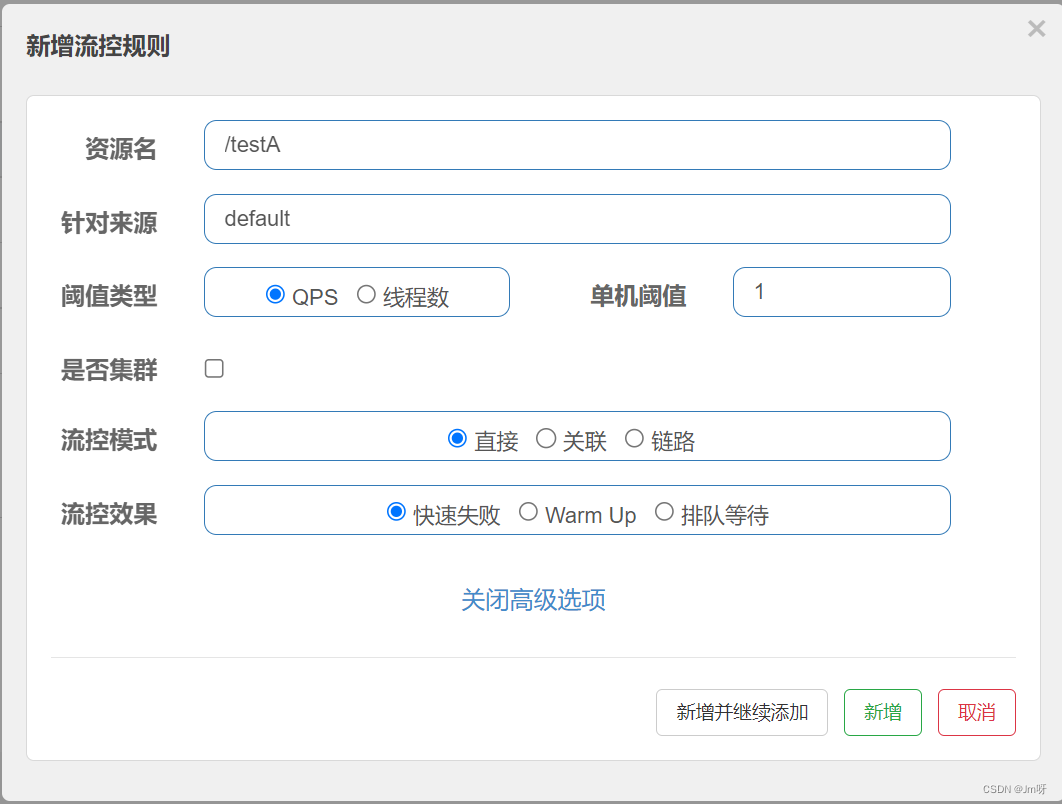
配置及说明:表示1秒钟内查询1次就是OK,若超过次数1,就直接->快速失败,报默认错误
1.2 线程数
当调用该API的线程数达到阈值的时候,进行限流。
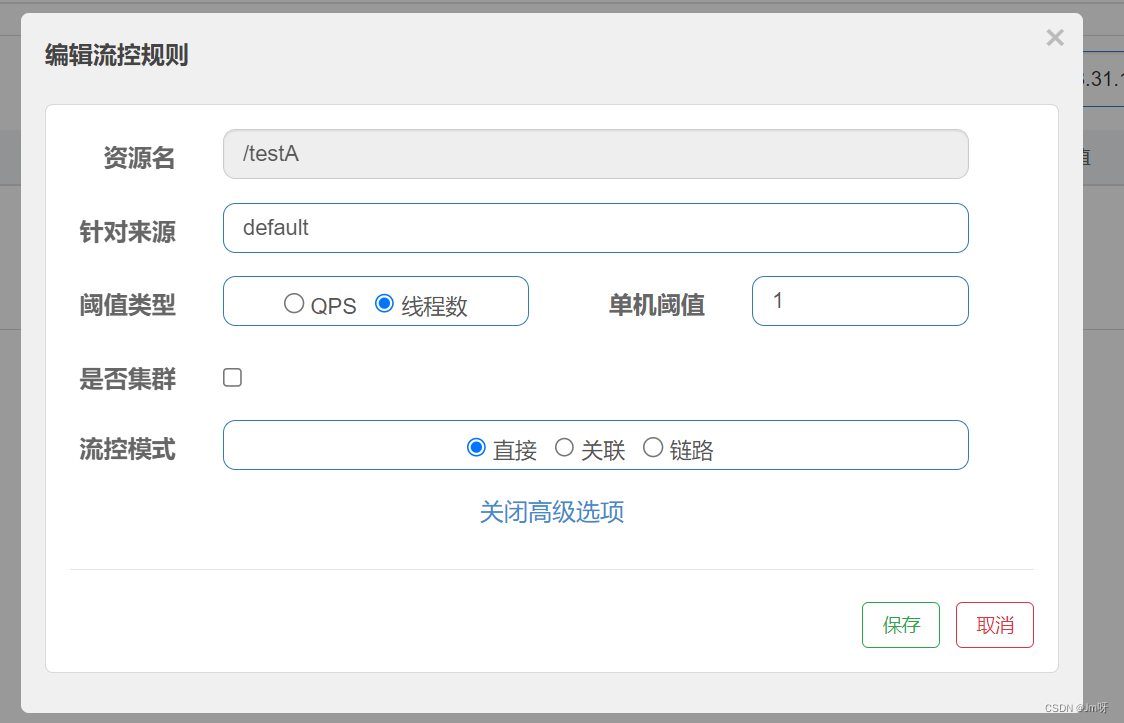
2. 流控模式
2.1 直接
API自身达到限流条件时,直接限流。
配置及说明:表示1秒钟内查询1次就是OK,若超过次数1,就直接->快速失败,报默认错误
2.2 关联
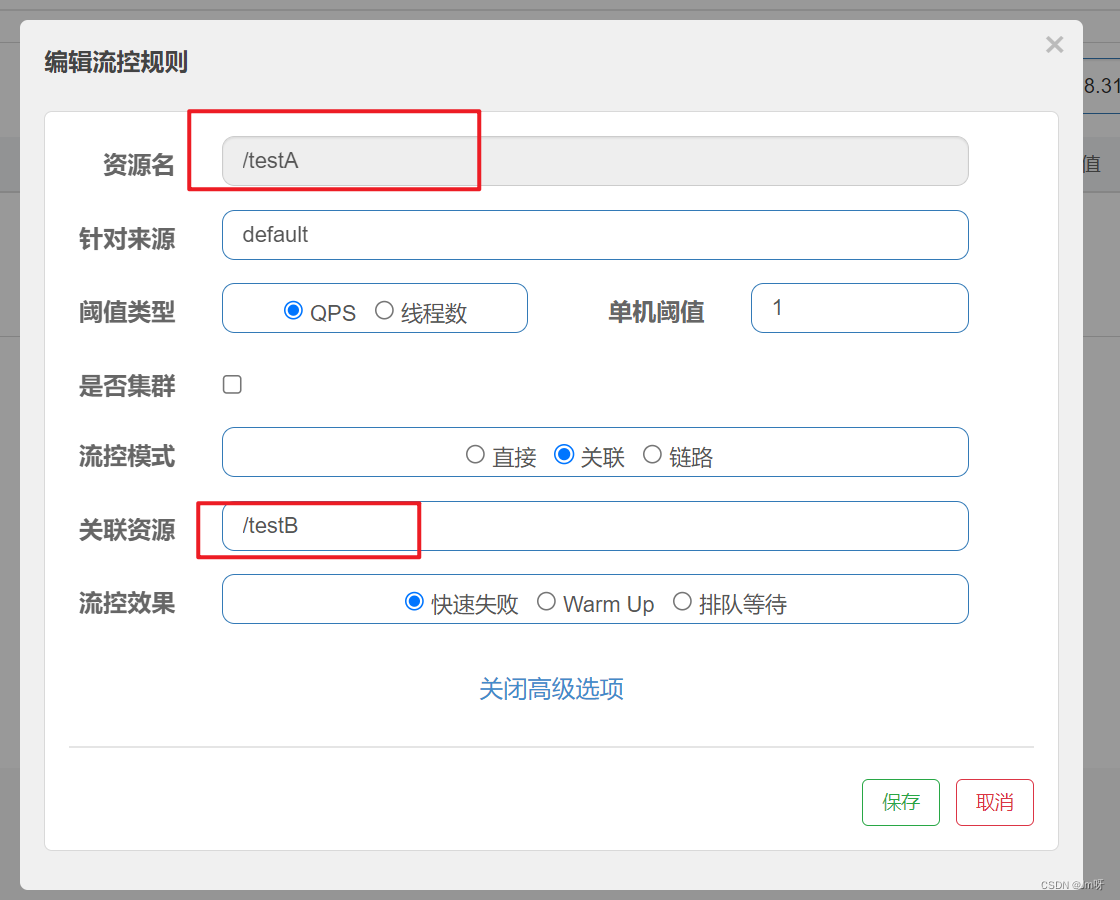
- 当自己关联的资源达到阈值时,就限流自己
- 当与A关联的资源B达到阀值后,就限流A自己(B支付访问接口达到阈值,A订单接口就限制自己)
设置testA
当关联资源/testB的QPS阀值超过1时,就限流/testA的Rest访问地址,当关联资源到阈值后限制配置好的资源名。
测试:
postman 并发访问testB,Run - 大批量线程高并发访问B
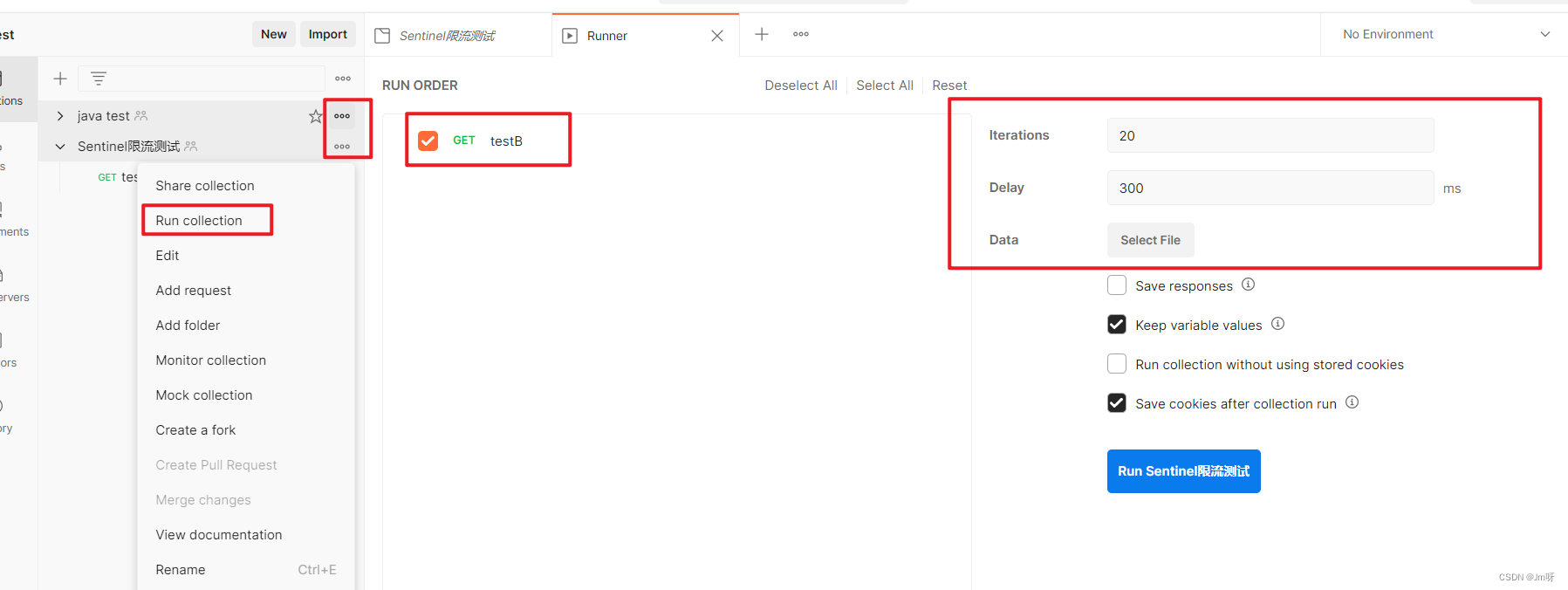
Postman运行后,点击访问http://localhost:8401/testA,发现testA挂了
2.3 链路
链路流控模式指的是,当从指定接口过来的资源请求达到限流条件时,开启限流,这里得先讲解一下@SentinelResource的使用。
我们可以对某一个方法进行限流控制,无论是谁在何处调用了它,这里需要使用到@SentinelResource,一旦方法被标注,那么就会进行监控,比如我们这里创建两个请求映射,都来调用Service的被监控方法:
@Resource
private SentinelServiceimpl sentinelServiceimpl;
@GetMapping("/testgetAllA")
public String testAllA() {
sentinelServiceimpl.getAll();
return " test A";
}
@GetMapping("/testgetAllB")
public String testAllB() {
sentinelServiceimpl.getAll();
return " test B";
}
Service:
@Service
public class SentinelServiceimpl {
//监控此方法,无论被谁执行都在监控范围内,这里给的value是自定义名称,
// 这个注解可以加在任何方法上,包括Controller中的请求映射方法,跟HystrixCommand贼像
@SentinelResource("getAll")
public String getAll() {
System.out.println(" 这里调用了 getAll 方法");
return "success ok";
}
}
接着添加配置:
spring:
application:
name: cloudalibaba-sentinel-service
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
# nacos 服务注册中心地址
server-addr: localhost:8848
sentinel:
transport:
# 配置 sentinel dashboard 地址
dashboard: localhost:8080
# 默认8719端口,假如被占用会自动从 8719开始依次加1,直到找到未被占用的端口
port: 8719
# 关闭Context收敛,这样被监控方法可以进行不同链路的单独控制
web-context-unify: false
然后我们在Sentinel控制台中添加流控规则,注意是针对此方法,可以看到已经自动识别到getAll接口下调用了这个方法:
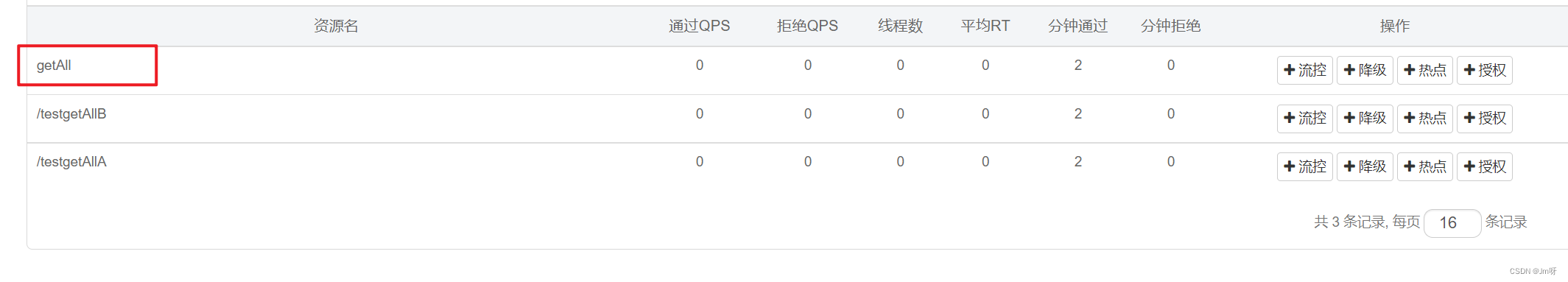
最后我们在浏览器中对这两个接口都进行测试,会发现,无论请求哪个接口,只要调用了Service中的getAll这个方法,都会被限流。注意限流的形式是后台直接抛出异常,至于怎么处理我们后面再说。
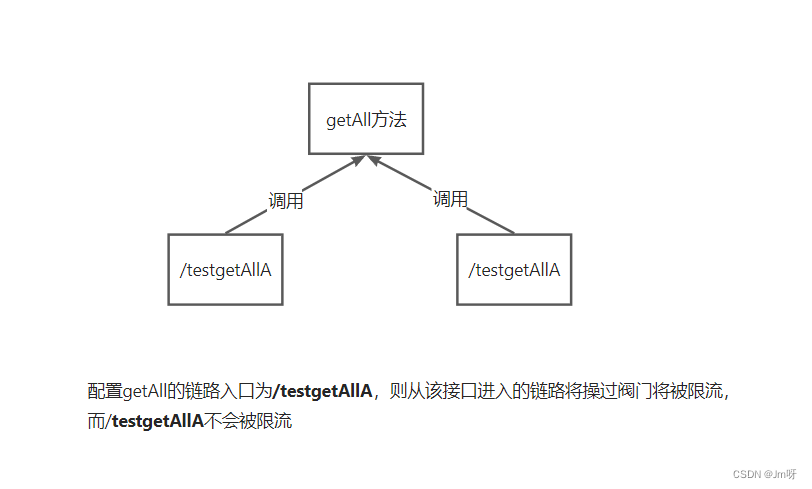
那么这个链路选项实际上就是决定只限流从哪个方向来的调用,比如我们只对getAll这个接口对/testgetAllA接口的调用进行限流,那么我们就可以为其指定链路:
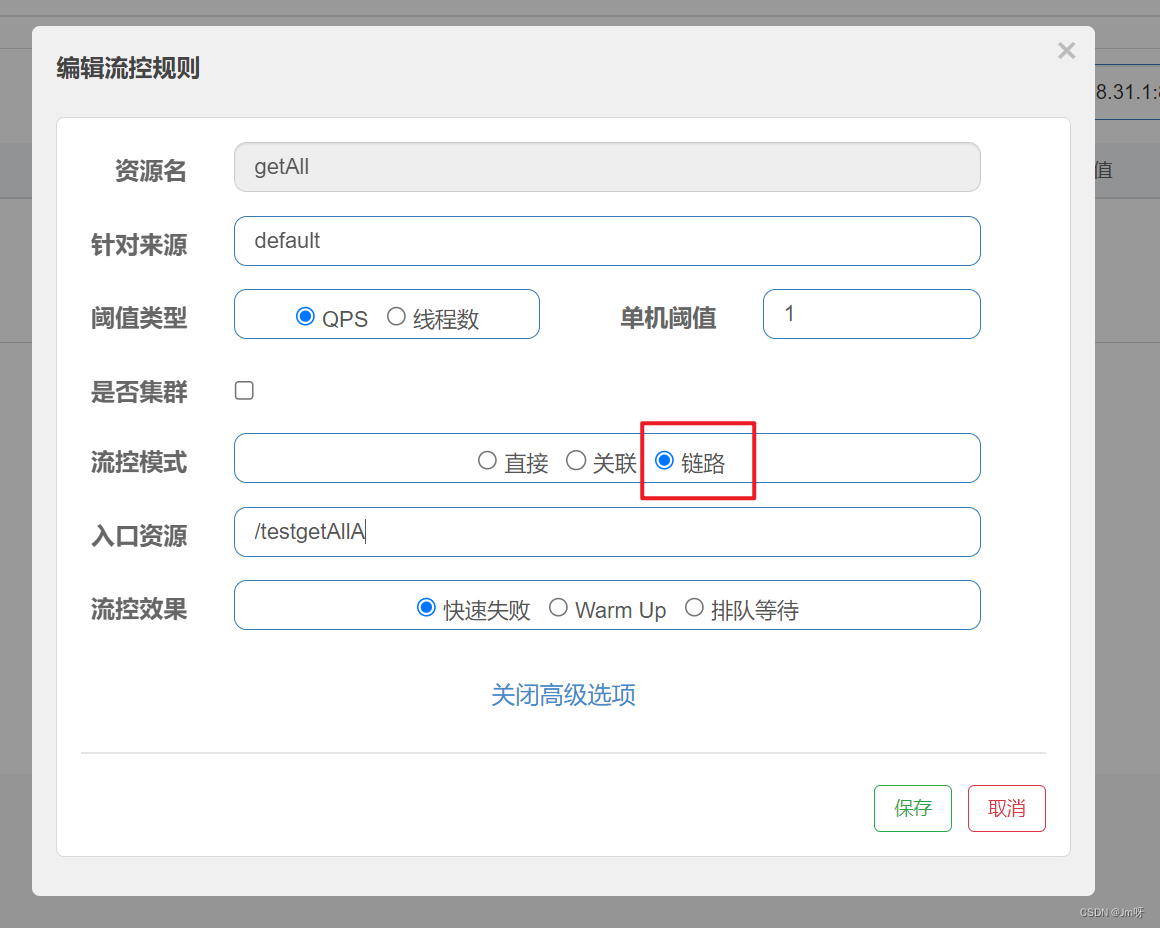
然后我们会发现,限流效果只对我们配置的链路接口有效,而其他链路是不会被限流的。
3. 流控效果
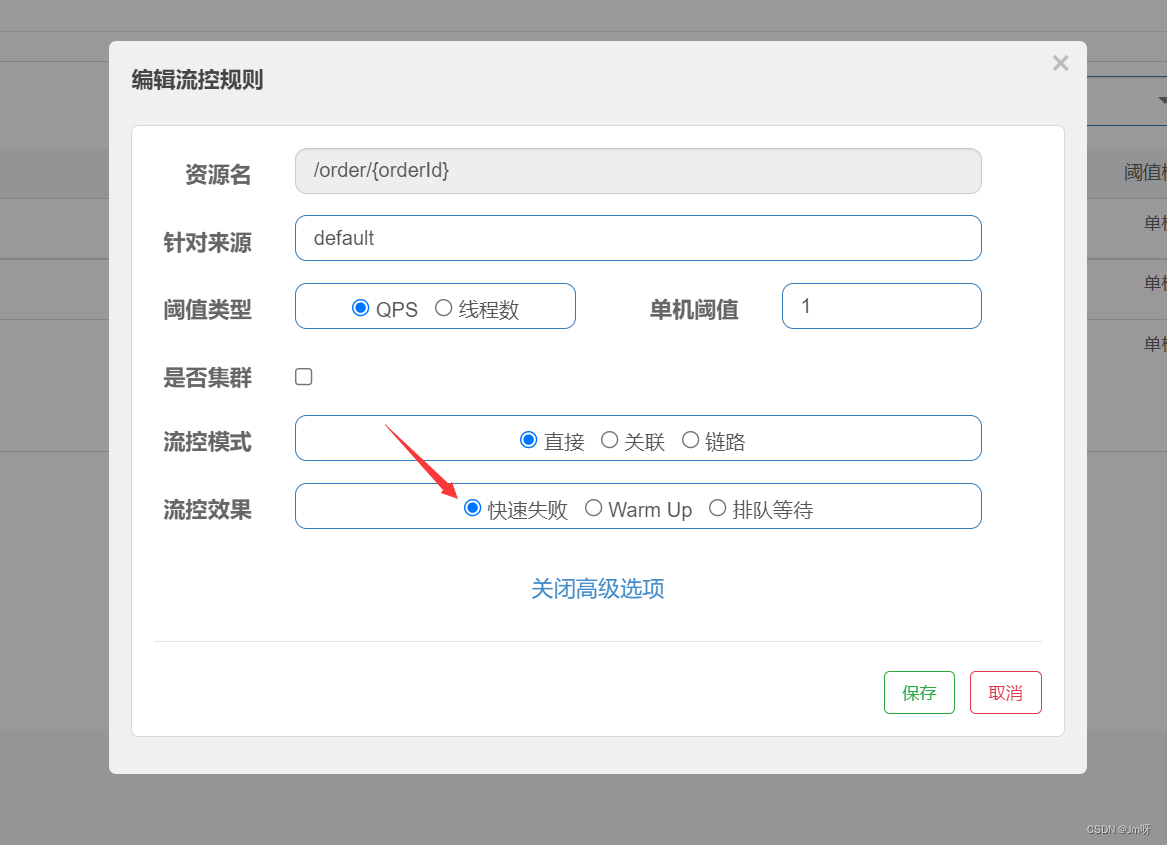
3.1 快速失败
快速失败是默认的处理方式,当请求达到阈值后,新的请求会被立即拒绝并抛出FlowException异常。
例如我们设置阈值为一秒一个请求,当我们请求QPS超过阈值时候,在浏览器中会直接报错:
浏览器中打印报错:
3.2 WarmUp预热
阈值一般是一个微服务能承担的最大QPS,但是一个服务刚刚启动时,一切资源尚未初始化(冷启动),如果直接将QPS跑到最大值,可能导致服务瞬间宕机。
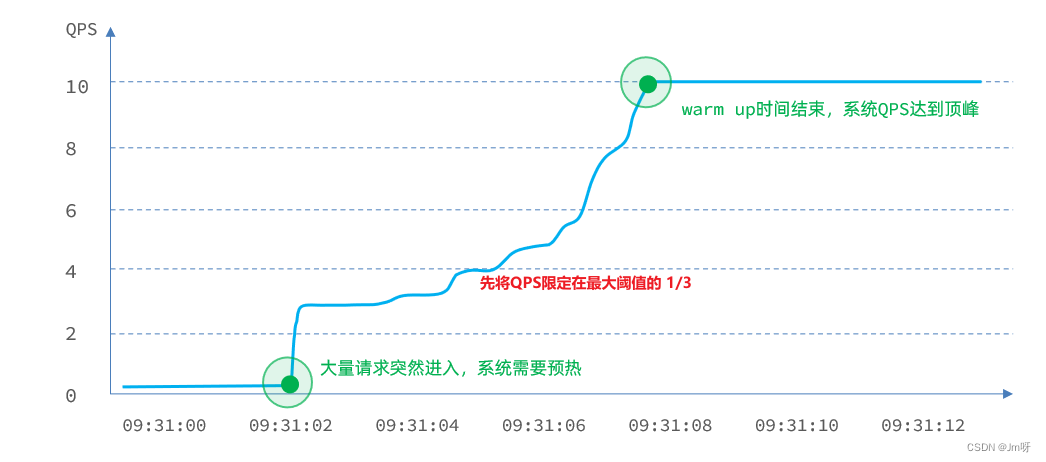
Warm Up(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP)方式,即预热/冷启动方式。当系统长期处于低水位的情况下,当流量突然增加时,直接把系统拉升到高水位可能瞬间把系统压垮。通过"冷启动",让通过的流量缓慢增加,在一定时间内逐渐增加到阈值上限,给冷系统一个预热的时间,避免冷系统被压垮。详细文档可以参考 流量控制 - Warm Up 文档,具体的例子可以参见 WarmUpFlowDemo。
默认coldFactor为3,即请求QPS 从 threshold / 3开始,经预热时长逐渐升至设定的QPS阈值。
源码地址:com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.controller.WarmUpController
SentinelConfig.DEFAULT_COLD_FACTOR = 3
例如,我设置QPS的maxThreshold为10,预热时间为5秒,那么初始阈值就是 10 / 3 ,也就是3,然后在5秒后逐渐增长到10.
案例:
阀值为10+预热时长设置5秒。系统初始化的阀值为10/ 3约等于3,即阀值刚开始为3;然后过了5秒后阀值才慢慢升高恢复到10
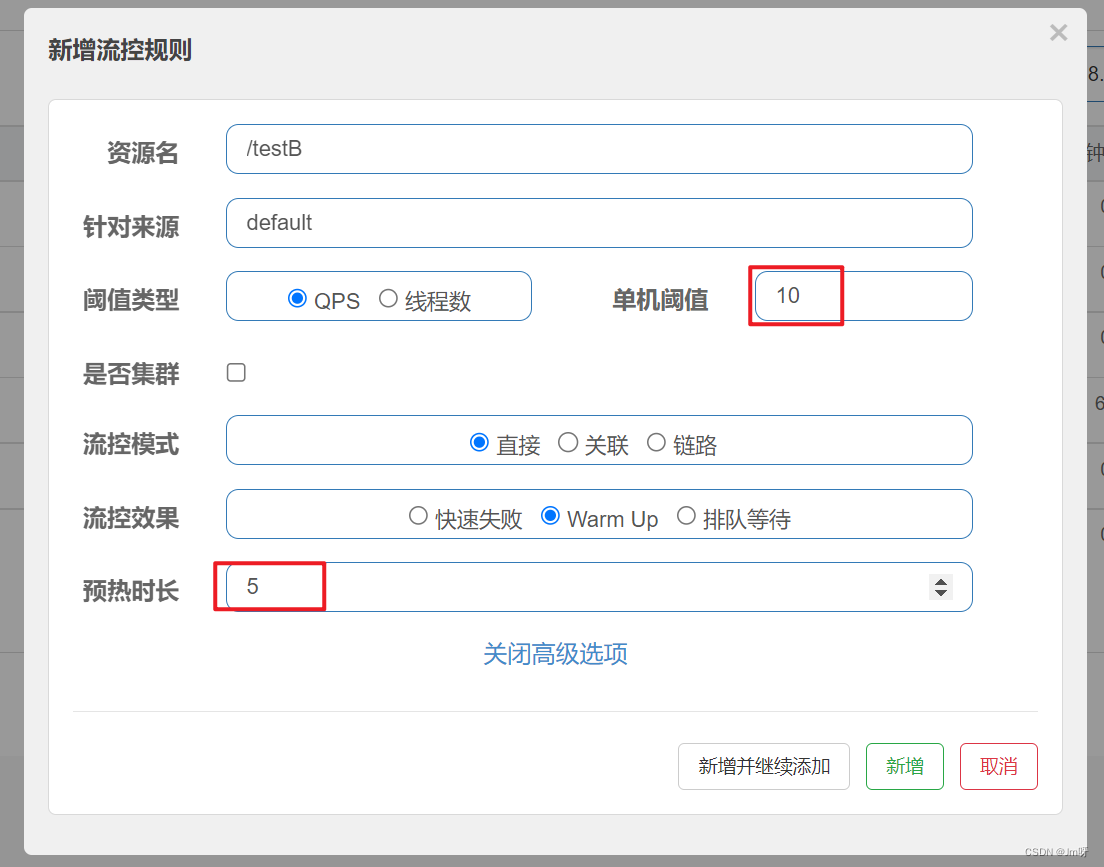
多次快速点击http://localhost:8401/testB - 刚开始不行,后续慢慢OK
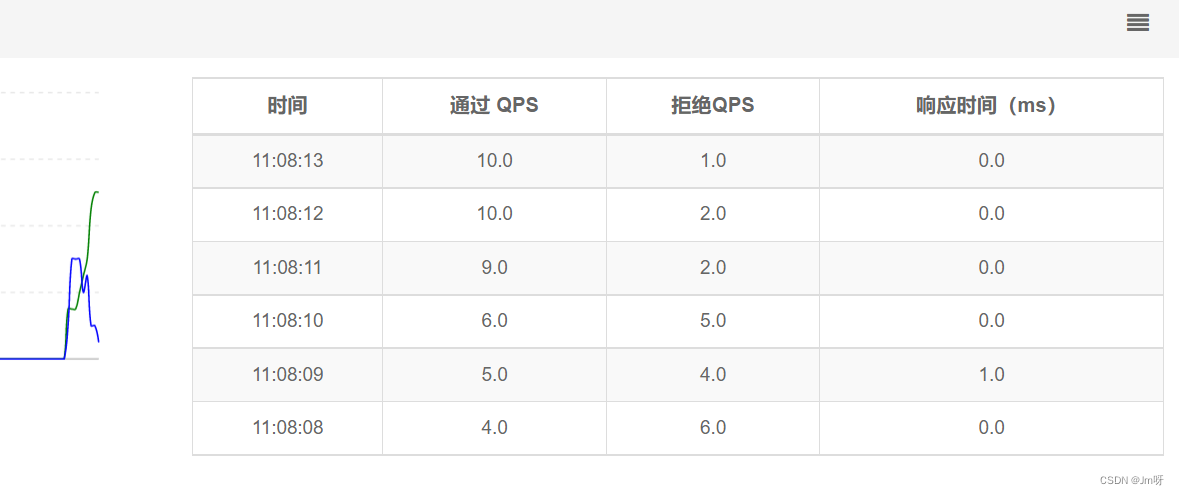
应用场景:如秒杀系统在开启的瞬间,会有很多流量上来,很有可能把系统打死,预热方式就是把为了保护系统,可慢慢的把流量放进来,慢慢的把阀值增长到设置的阀值。
3.3 排队等待
当请求超过QPS阈值时,快速失败和warm up 会拒绝新的请求并抛出异常。
排队等待则是让所有请求进入一个队列中,然后按照阈值允许的时间间隔依次执行。后来的请求必须等待前面执行完成,如果请求预期的等待时间超出最大时长,则会被拒绝。
匀速排队(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_RATE_LIMITER)方式会严格控制请求通过的间隔时间,也即是让请求以均匀的速度通过,对应的是漏桶算法。详细文档可以参考 流量控制 - 匀速器模式,具体的例子可以参见 PaceFlowDemo。
该方式的作用如下图所示:
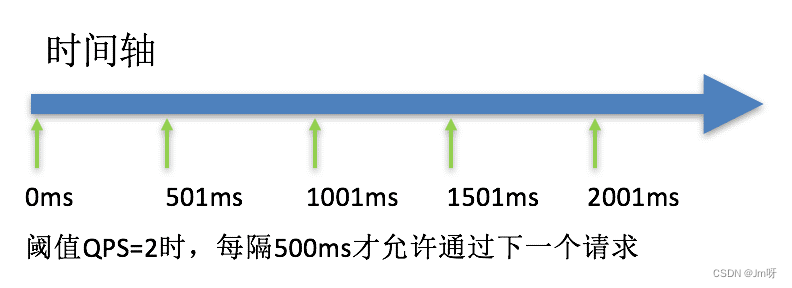
这种方式主要用于处理间隔性突发的流量,例如消息队列。想象一下这样的场景,在某一秒有大量的请求到来,而接下来的几秒则处于空闲状态,我们希望系统能够在接下来的空闲期间逐渐处理这些请求,而不是在第一秒直接拒绝多余的请求。
注意:匀速排队模式暂时不支持 QPS > 1000 的场景。
源码 - com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.controller.RateLimiterController
例如:现在一下子来了12 个请求,因为每200ms执行一个请求,那么:
第6个请求的预期等待时长 = 200 * (6 - 1) = 1000ms
第12个请求的预期等待时长 = 200 * (12-1) = 2200ms
现在,第1秒同时接收到10个请求,但第2秒只有1个请求,此时QPS的曲线这样的:
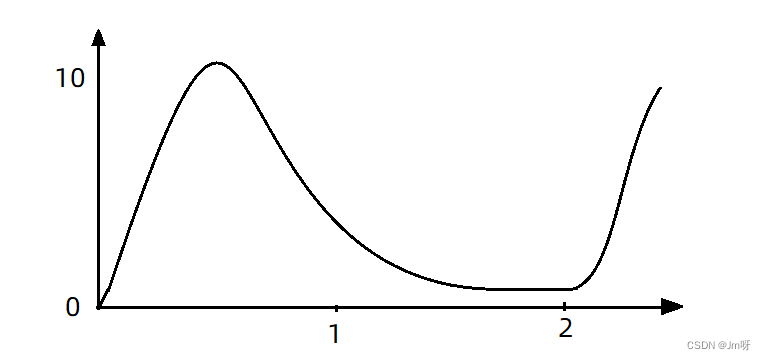
如果使用队列模式做流控,所有进入的请求都要排队,以固定的200ms的间隔执行,QPS会变的很平滑:
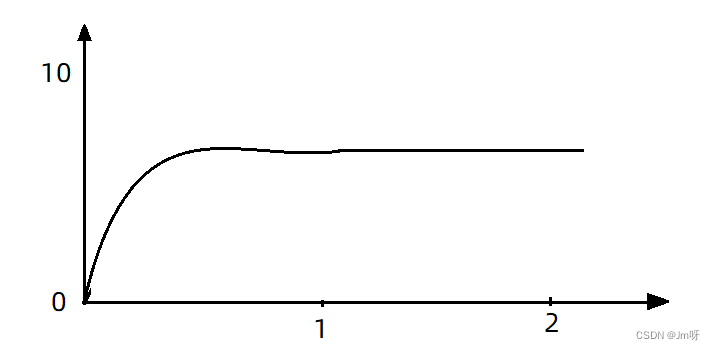
这样平滑的QPS曲线,对于服务器来说是更友好的。
案例:
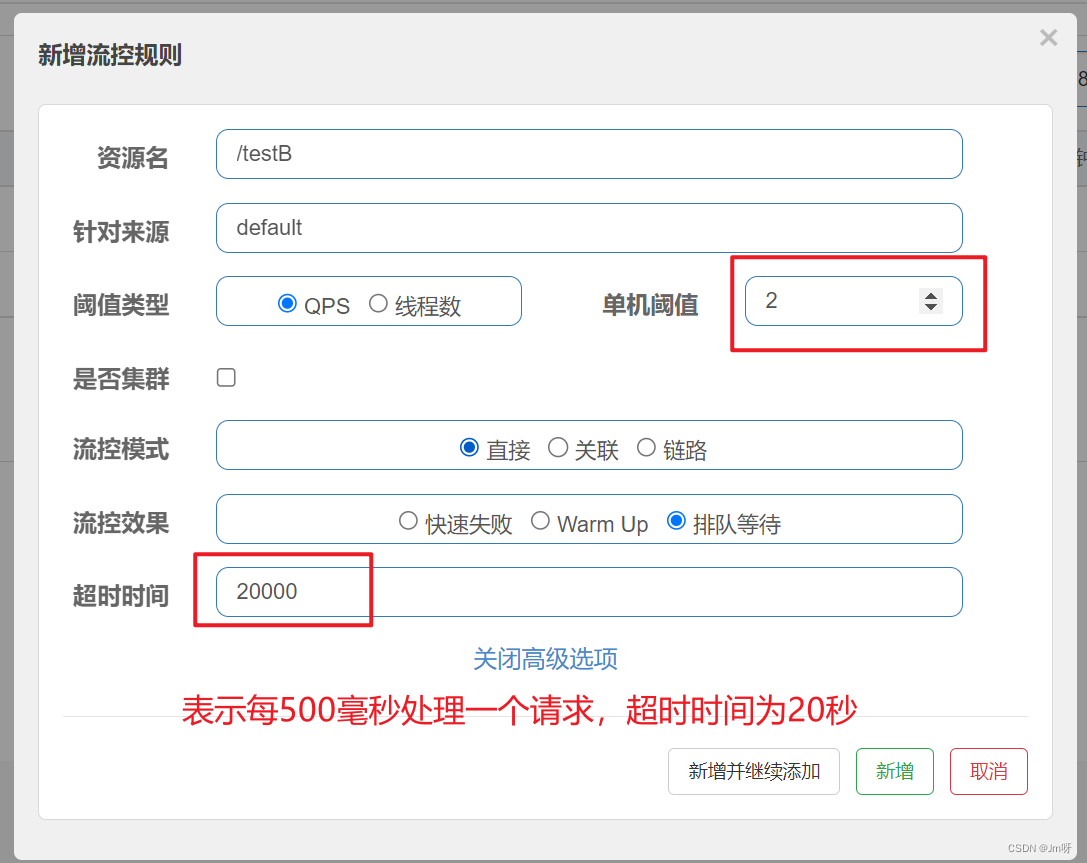
QPS非常平滑,一致保持在2,但是超出的请求没有被拒绝,而是放入队列。因此响应时间(等待时间)会越来越长。
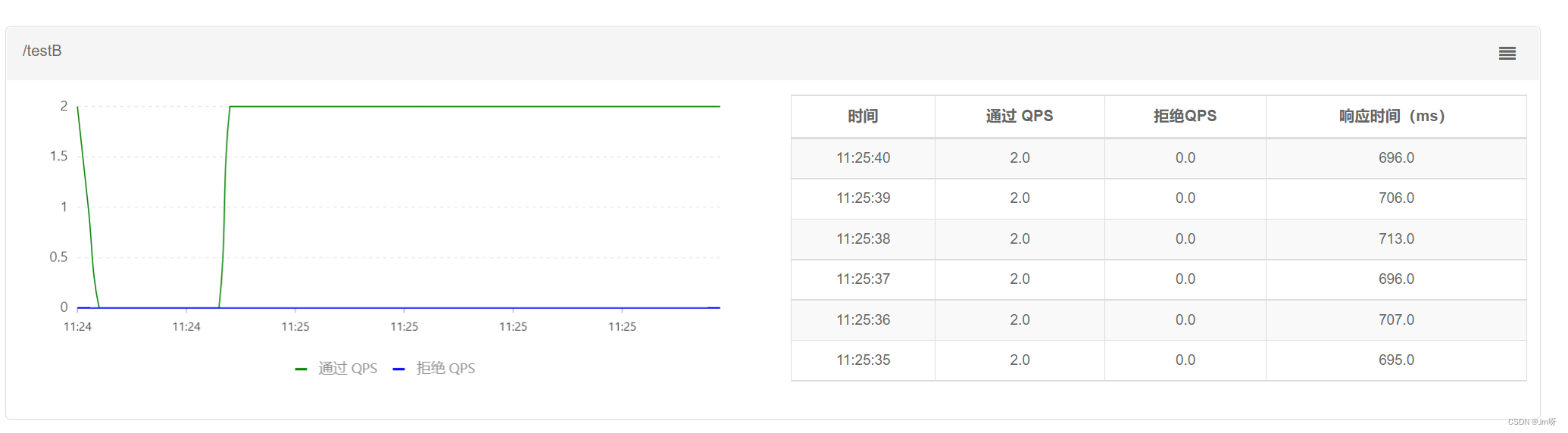
流控效果有哪些?
四.降级规则
官方文档描述:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E7%86%94%E6%96%AD%E9%99%8D%E7%BA%A7
熔断降级概述
除了流量控制以外,对调用链路中不稳定的资源进行熔断降级也是保障高可用的重要措施之一。一个服务常常会调用别的模块,可能是另外的一个远程服务、数据库,或者第三方 API 等。例如,支付的时候,可能需要远程调用银联提供的 API;查询某个商品的价格,可能需要进行数据库查询。然而,这个被依赖服务的稳定性是不能保证的。如果依赖的服务出现了不稳定的情况,请求的响应时间变长,那么调用服务的方法的响应时间也会变长,线程会产生堆积,最终可能耗尽业务自身的线程池,服务本身也变得不可用。
现代微服务架构都是分布式的,由非常多的服务组成。不同服务之间相互调用,组成复杂的调用链路。以上的问题在链路调用中会产生放大的效果。复杂链路上的某一环不稳定,就可能会层层级联,最终导致整个链路都不可用。因此我们需要对不稳定的弱依赖服务调用进行熔断降级,暂时切断不稳定调用,避免局部不稳定因素导致整体的雪崩。熔断降级作为保护自身的手段,通常在客户端(调用端)进行配置。
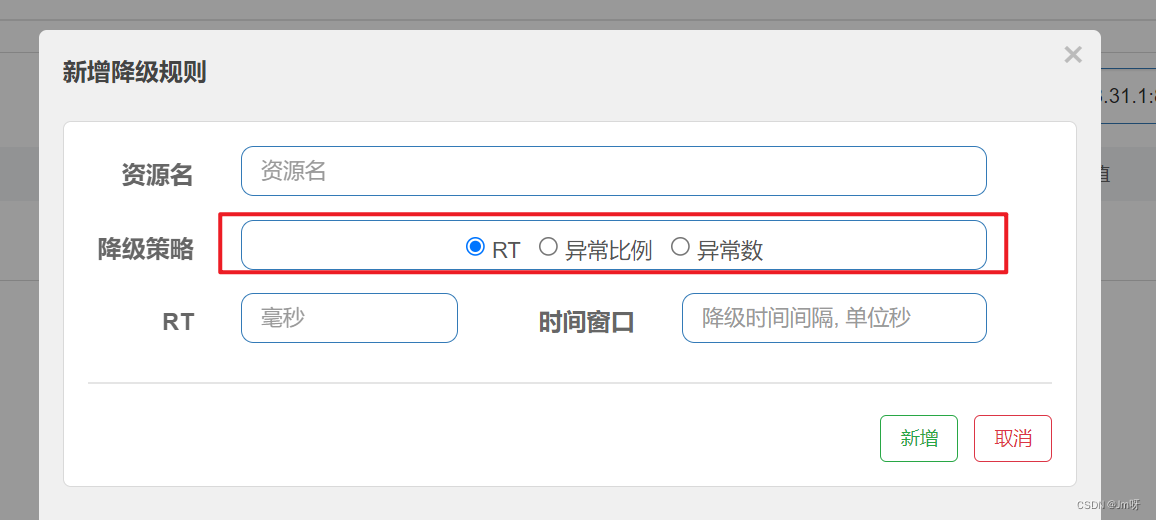
RT(平均响应时间,秒级)
- 平均响应时间 超出阈值 且 在时间窗口内通过的请求>=5,两个条件同时满足后触发降级。
- 窗口期间过后关闭断路器
- RT最大4900(更大的需要通过-Dcsp.sentinel.statistic.max.rt=XXXX才能生效)。
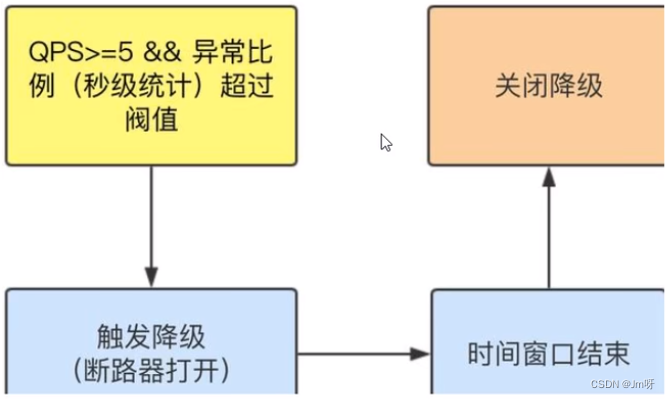
异常比列(秒级)
- QPS >= 5且异常比例(秒级统计)超过阈值时,触发降级;时间窗口结束后,关闭降级 。
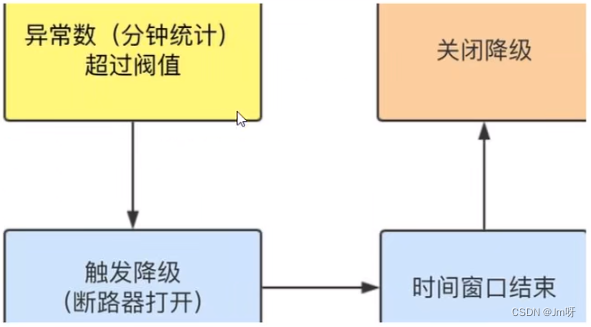
异常数(分钟级)
- 异常数(分钟统计)超过阈值时,触发降级;时间窗口结束后,关闭降级
Sentinel熔断降级会在调用链路中某个资源出现不稳定状态时(例如调用超时或异常比例升高),对这个资源的调用进行限制,让请求快速失败,避免影响到其它的资源而导致级联错误。
当资源被降级后,在接下来的降级时间窗口之内,对该资源的调用都自动熔断(默认行为是抛出 DegradeException)。
Sentinei的断路器是没有类似Hystrix半开状态的。(Sentinei 1.8.0 已有半开状态),半开的状态系统自动去检测是否请求有异常,没有异常就关闭断路器恢复使用,有异常则继续打开断路器不可用。
具体可以参考:https://www.yuque.com/toufayouheiyouchang/gwrwfp/pmtznz
1. RT
是什么?
平均响应时间(
DEGRADE_GRADE_RT):当1s内持续进入5个请求,对应时刻的平均响应时间(秒级)均超过阈值(count,以ms为单位),那么在接下的时间窗口(DegradeRule中的timeWindow,以s为单位)之内,对这个方法的调用都会自动地熔断(抛出DegradeException )。注意Sentinel 默认统计的RT上限是4900 ms,超出此阈值的都会算作4900ms,若需要变更此上限可以通过启动配置项-Dcsp.sentinel.statistic.max.rt=xxx来配置。
注意:Sentinel 1.7.0才有平均响应时间(DEGRADE_GRADE_RT),Sentinel 1.8.0的没有这项,取而代之的是慢调用比例 (SLOW_REQUEST_RATIO)。
慢调用比例 (
SLOW_REQUEST_RATIO):选择以慢调用比例作为阈值,需要设置允许的慢调用 RT(即最大的响应时间),请求的响应时间大于该值则统计为慢调用。当单位统计时长(statIntervalMs)内请求数目大于设置的最小请求数目,并且慢调用的比例大于阈值,则接下来的熔断时长内请求会自动被熔断。经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求响应时间小于设置的慢调用 RT 则结束熔断,若大于设置的慢调用 RT 则会再次被熔断。
接下来讲解Sentinel 1.7.0的。
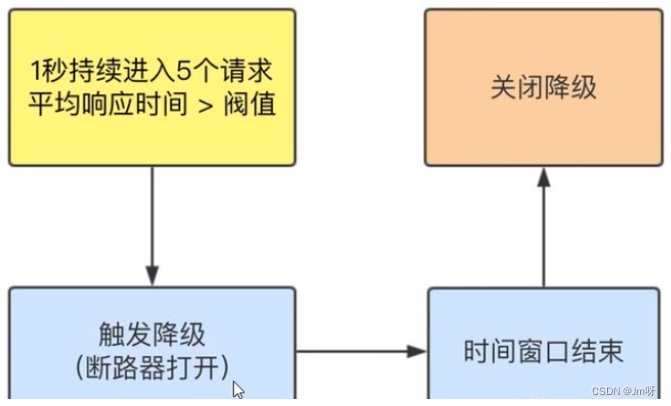
案例:
添加一个接口,处理这个接口所需要的时间是1s以上的响应时间
// 熔断降级 RT
@GetMapping("/testD")
public String testD() {
// 暂停1秒线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "test DDDDDDD";
}
添加对该接口的一个降级规则,要求平均的响应时间小于200毫秒,如果平均响应时间大于200毫秒且QPS>5,
将触发降级,并且在1秒后的时间窗口后才关闭断路器
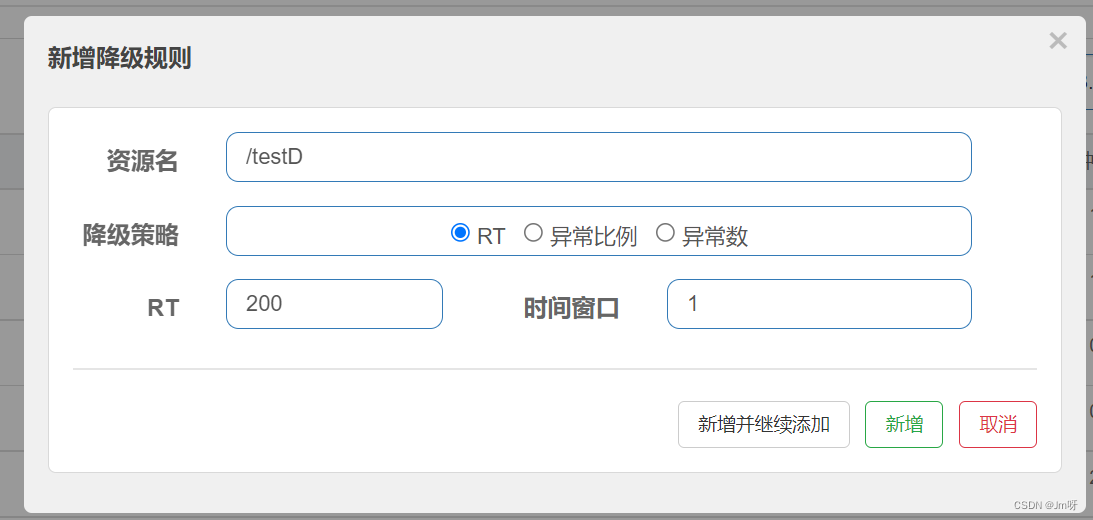
测试:
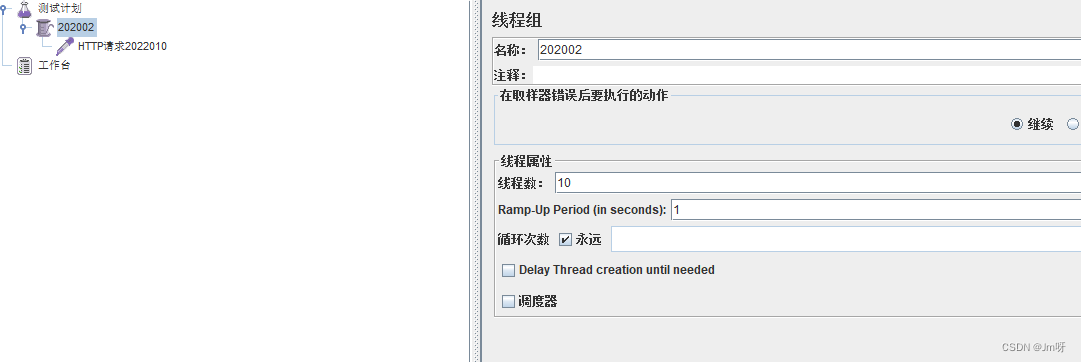
配置JMeter进行高压测试:
结论
按照上述配置,永远一秒钟打进来10个线程(大于5个了)调用testD,我们希望200毫秒处理完本次任务,如果超过200毫秒还没处理完,在未来1秒钟的时间窗口内,断路器打开(保险丝跳闸)微服务不可用,保险丝跳闸断电了后续我停止jmeter,没有这么大的访问量了,断路器关闭(保险丝恢复),微服务恢复OK。
2. 异常比例
异常比例(
DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO):当资源的每秒请求量 >= 5,并且每秒异常总数占通过量的比值超过阈值(DegradeRule中的count)之后,资源进入降级状态,即在接下的时间窗口(DegradeRule中的timeWindow,以s为单位)之内,对这个方法的调用都会自动地返回。异常比率的阈值范围是[0.0, 1.0],代表0% -100%。
注意,与Sentinel 1.8.0相比,有些不同(Sentinel 1.8.0才有的半开状态),Sentinel 1.8.0的如下:
异常比例 (
ERROR_RATIO):当单位统计时长(statIntervalMs)内请求数目大于设置的最小请求数目,并且异常的比例大于阈值,则接下来的熔断时长内请求会自动被熔断。经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求成功完成(没有错误)则结束熔断,否则会再次被熔断。异常比率的阈值范围是 [0.0, 1.0],代表 0% - 100%。link
接下来讲解Sentinel 1.7.0的。
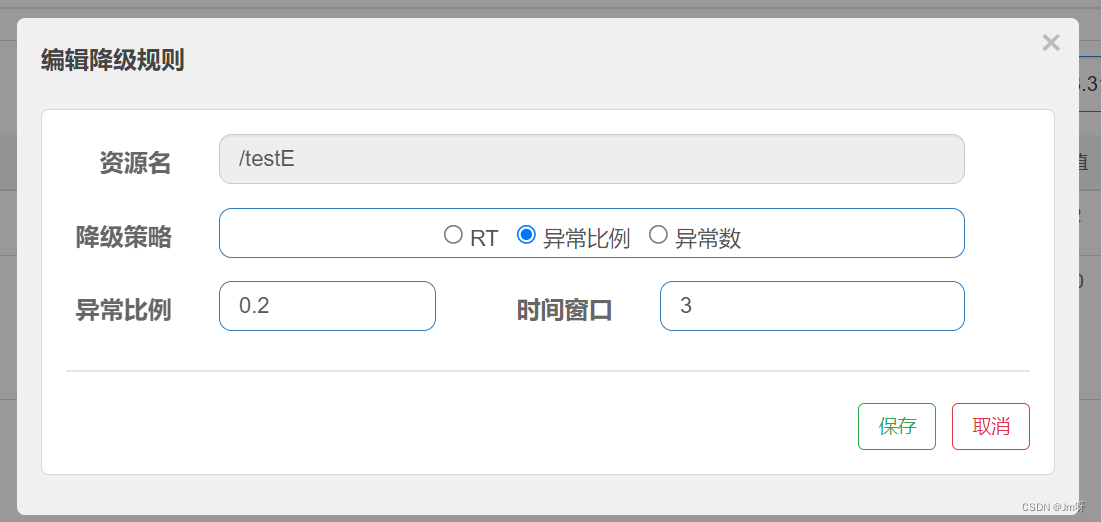
测试:
// 熔断降级 异常比例
@GetMapping("/testE")
public String testE() {
log.info("testE 异常比例");
int age = 1 / 0;
return "test testEtestEtestEtestE";
}
配置:
当QPS>5并且阈值的异常比例超过20%,将触发熔断降级,3秒后恢复熔断
jmeter:
结论
按照上述配置,单独访问一次,必然来一次报错一次(int age = 10/0),调一次错一次。
开启jmeter后,直接高并发发送请求,多次调用达到我们的配置条件了。断路器开启(保险丝跳闸),微服务不可用了,不再报错error而是服务降级了。
3. 异常数
异常数(
DEGRADE_GRADF_EXCEPTION_COUNT):当资源近1分钟的异常数目超过阈值之后会进行熔断。注意由于统计时间窗口是分钟级别的,若timeWindow小于60s,则结束熔断状态后码可能再进入熔断状态。
注意,与Sentinel 1.8.0相比,有些不同(Sentinel 1.8.0才有的半开状态),Sentinel 1.8.0的如下:
异常数 (
ERROR_COUNT):当单位统计时长内的异常数目超过阈值之后会自动进行熔断。经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求成功完成(没有错误)则结束熔断,否则会再次被熔断。
接下来讲解Sentinel 1.7.0的。
异常数是按照分钟统计的,时间窗口一定要大于等于60秒。
测试
// 熔断降级 异常数
@GetMapping("/testF")
public String testF() {
log.info("testF 异常比例");
int age = 1 / 0;
return "test testEtestFtestFtestFtestF";
}
配置:
当在1分钟内,异常数超过5次将触发熔断降级,经过时间窗口后熔断关闭
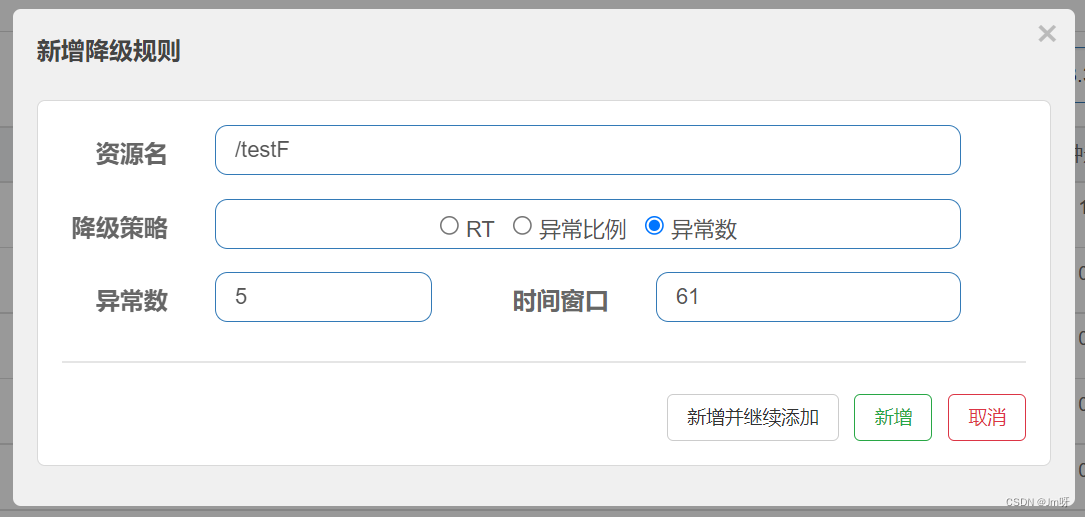
访问http://localhost:8401/testF,第一次访问绝对报错,因为除数不能为零,我们看到error窗口,但是达到5次报错后,进入熔断后降级。
五.Sentinel 热点key
何为热点?热点即经常访问的数据。很多时候我们希望统计某个热点数据中访问频次最高的 Top K 数据,并对其访问进行限制。比如:
- 商品 ID 为参数,统计一段时间内最常购买的商品 ID 并进行限制
- 用户 ID 为参数,针对一段时间内频繁访问的用户 ID 进行限制
热点参数限流会统计传入参数中的热点参数,并根据配置的限流阈值与模式,对包含热点参数的资源调用进行限流。热点参数限流可以看做是一种特殊的流量控制,仅对包含热点参数的资源调用生效。
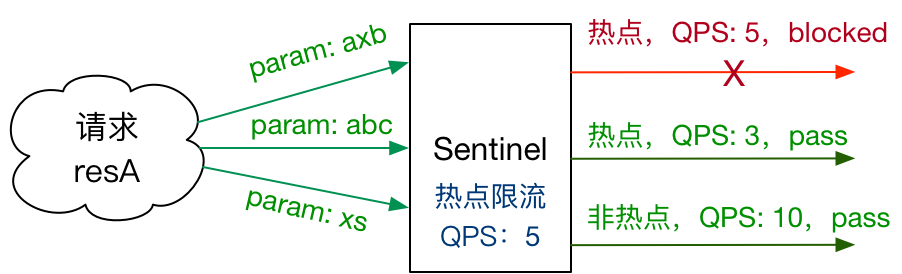
Sentinel 利用 LRU 策略统计最近最常访问的热点参数,结合令牌桶算法来进行参数级别的流控。热点参数限流支持集群模式。
1. 基本使用
创建一个接口,存在两个参数,p1、p2,使用@SentinelResource对该接口进行装饰。
@RestController
public class HotKeyController {
@GetMapping("/testHotKey")
@SentinelResource(value = "testHotkey",blockHandler = "deal_testHotKey")
public String testHotKey(@RequestParam(name = "p1", required = false) String p1,
@RequestParam(name = "p2", required = false) String p2) {
return "----------------------testHotKey";
}
public String deal_testHotKey(String p1, String p2, BlockException blockException) {
return "-----------------------------deal_testHotKey /(ㄒoㄒ)/~~";
}
}
在sentinel客户端中进行对该接口的一热点数据配置:当携带p1(第0个参数)的请求,对其进行限流,阈值为1,统计时长为1秒
测试:
error:
- http://localhost:8401/testHotKey?p1=abc
- http://localhost:8401/testHotKey?p1=abc&p2=33
right:
- http://localhost:8401/testHotKey?p2=abc
2. 参数例外项
- 普通 - 超过1秒钟一个后,达到阈值1后马上被限流
- 我们期望p1参数当它是某个特殊值时,它的限流值和平时不一样
- 特例 - 假如当p1的值等于5时,它的阈值可以达到200
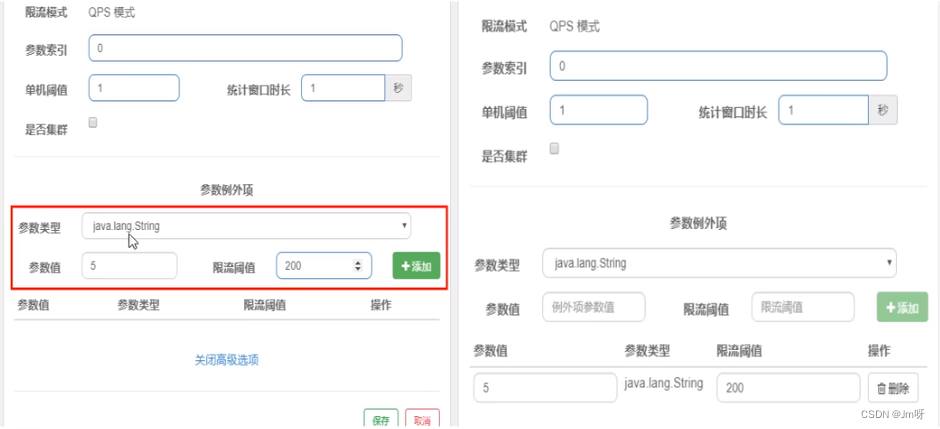
测试
- right - http://localhost:8401/testHotKey?p1=5
- error - http://localhost:8401/testHotKey?p1=3
- 当p1等于5的时候,阈值变为200
- 当p1不等于5的时候,阈值就是平常的1
前提条件 - 热点参数的注意点,参数必须是基本类型或者String
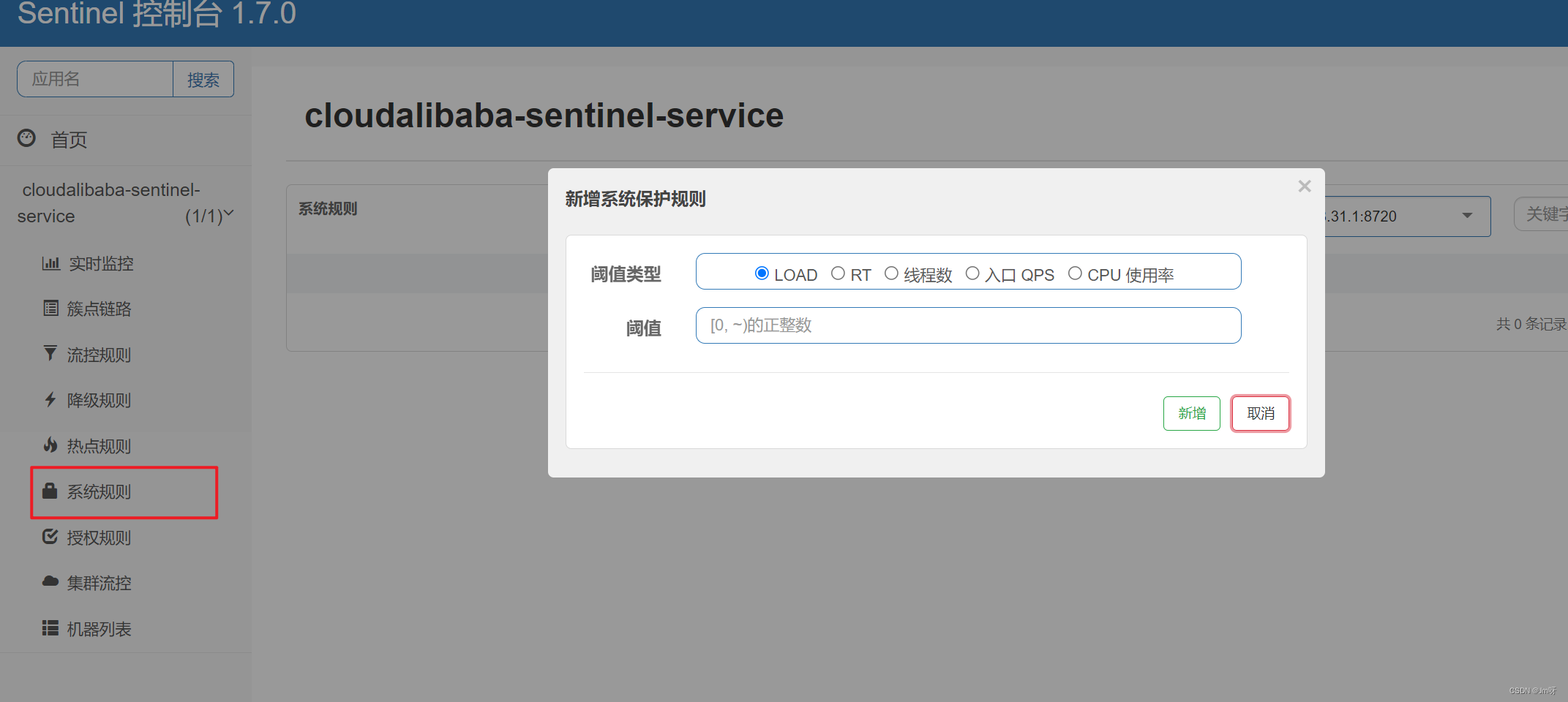
六.Sentinel系统规则
官方文档:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/系统自适应限流
Sentinel 系统自适应限流从整体维度对应用入口流量进行控制,结合应用的 Load、CPU 使用率、总体平均 RT、入口 QPS 和并发线程数等几个维度的监控指标,通过自适应的流控策略,让系统的入口流量和系统的负载达到一个平衡,让系统尽可能跑在最大吞吐量的同时保证系统整体的稳定性。
系统保护规则是应用整体维度的,而不是资源维度的,并且仅对入口流量生效。入口流量指的是进入应用的流量(EntryType.IN),比如 Web 服务或 Dubbo 服务端接收的请求,都属于入口流量。
系统规则支持以下的模式:
- Load 自适应(仅对 Linux/Unix-like 机器生效):系统的 load1 作为启发指标,进行自适应系统保护。当系统 load1 超过设定的启发值,且系统当前的并发线程数超过估算的系统容量时才会触发系统保护(BBR 阶段)。系统容量由系统的 maxQps * minRt 估算得出。设定参考值一般是 CPU cores * 2.5。
- CPU usage(1.5.0+ 版本):当系统 CPU 使用率超过阈值即触发系统保护(取值范围 0.0-1.0),比较灵敏。
- 平均 RT:当单台机器上所有入口流量的平均 RT 达到阈值即触发系统保护,单位是毫秒。
- 并发线程数:当单台机器上所有入口流量的并发线程数达到阈值即触发系统保护。
- 入口 QPS:当单台机器上所有入口流量的 QPS 达到阈值即触发系统保护。
七.@SentinelResource 注解
@SentinelResource 注解
注意:注解方式埋点不支持 private 方法。
@SentinelResource 用于定义资源,并提供可选的异常处理和 fallback 配置项。
@SentinelResource 注解包含以下属性:
value:资源名称,必需项(不能为空)entryType:entry 类型,可选项(默认为 EntryType.OUT)blockHandler / blockHandlerClass: blockHandler 对应处理 BlockException 的函数名称,可选项。blockHandler 函数访问范围需要是 public,返回类型需要与原方法相匹配,参数类型需要和原方法相匹配并且最后加一个额外的参数,类型为 BlockException。blockHandler 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 blockHandlerClass 为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。(blockHandler 一般处理的只是sentinel客户端中配置违规,运行出错该走异常走异常 )fallback /fallbackClass:fallback 函数名称,可选项,用于在抛出异常的时候提供 fallback 处理逻辑。fallback 函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了exceptionsToIgnore里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。fallback 函数签名和位置要求:- 返回值类型必须与原函数返回值类型一致;
- 方法参数列表需要和原函数一致,或者可以额外多一个 Throwable 类型的参数用于接收对应的异常。
- fallback 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 fallbackClass 为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。
defaultFallback(since 1.6.0):默认的 fallback 函数名称,可选项,通常用于通用的 fallback 逻辑(即可以用于很多服务或方法)。fallback 函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了exceptionsToIgnore里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。若同时配置了 fallback 和 defaultFallback,则只有 fallback 会生效。defaultFallback 函数签名要求:- 返回值类型必须与原函数返回值类型一致;
- 方法参数列表需要为空,或者可以额外多一个 Throwable 类型的参数用于接收对应的异常。
- defaultFallback 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 fallbackClass 为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。
exceptionsToIgnore(since 1.6.0):用于指定哪些异常被排除掉,不会计入异常统计中,也不会进入 fallback 逻辑中,而是会原样抛出。
Sentinel主要有三个核心Api:
- SphU定义资源
- Tracer定义统计
- ContextUtil定义了上下文
1. 资源名称限流+后续处理
启动Nacos成功
启动Sentinel成功
修改8401微服务
POM.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.jm.springcloud</groupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
新增一个接口:
@RestController
public class RateLimitController {
@GetMapping("/byResource")
@SentinelResource(value = "byResource", blockHandler = "handleException")
public CommonResult byResource() {
return new CommonResult(200, "按资源名称限流测试OK", new Payment(2020L, "serial001"));
}
public CommonResult handleException(BlockException exception) {
return new CommonResult(400, exception.getClass().getCanonicalName() + "t 服务不可用");
}
}
在Sentinel客户端中通过@SentinelResource的value配置限流信息:
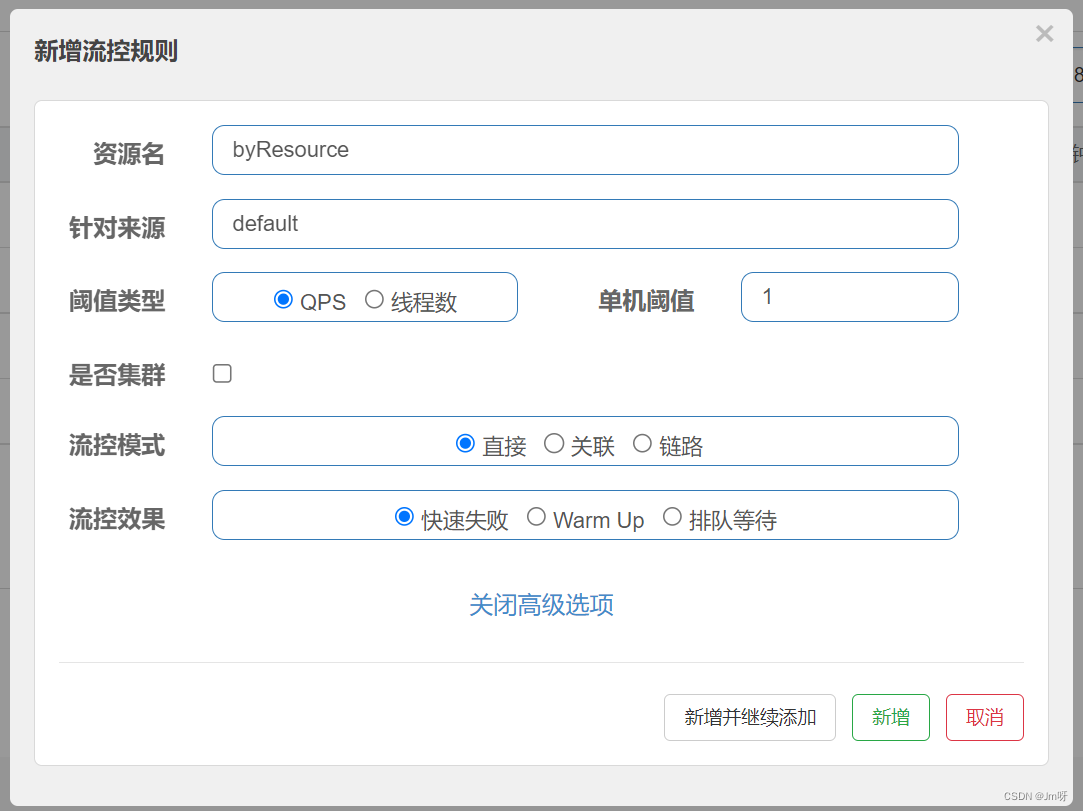
多次快速访问:http://localhost:8401/byResource,可以发现,限流提示不再是系统默认的, 而是我们设置的@SentinelResource 中的blockHandler设置的方法
{"code":444, "message":"com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowExceptiont 服务不可用", "data":null}
2. url地址限流+后续处理
启动Nacos成功
启动Sentinel成功
修改8401微服务
定义接口:
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/byUrl")
@SentinelResource(value = "byUrl")
public CommonResult byUrl() {
return new CommonResult(200, "按url限流测试OK", new Payment(2020L, "serial002"));
}
在Sentinel 客户端中通过 该接口的 路径/rateLimit/byUrl 配置限流
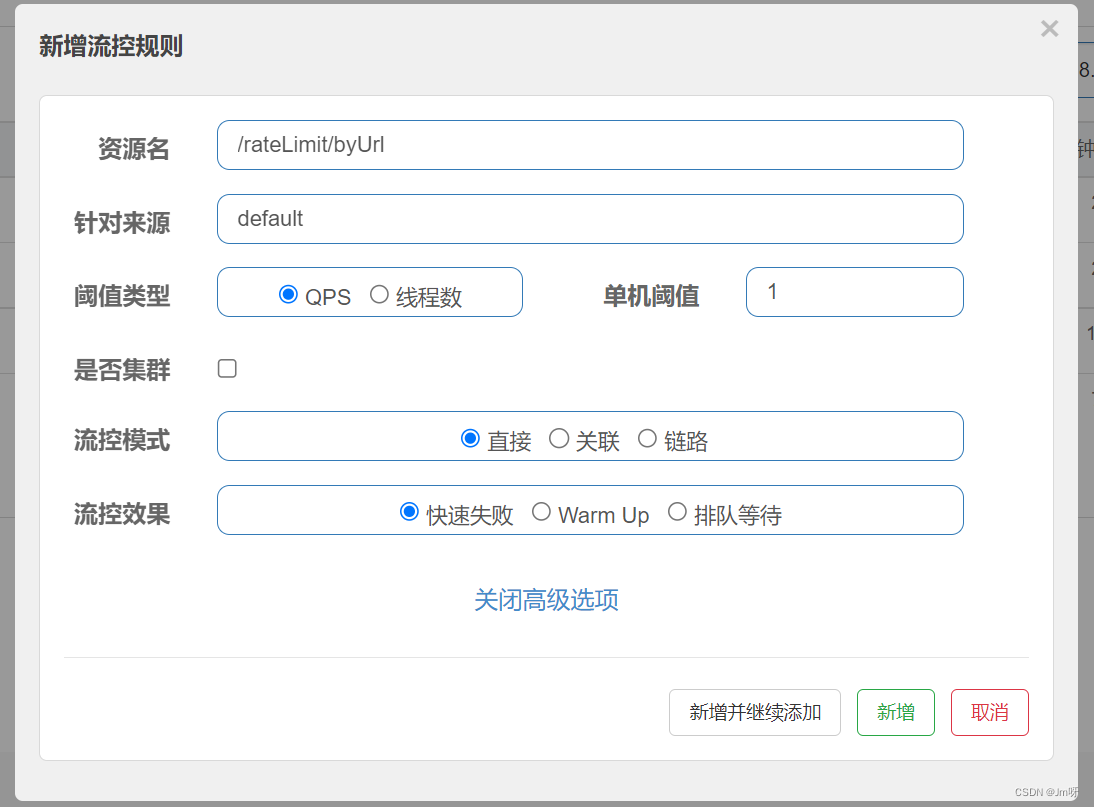
多次快速访问:http://localhost:8401/rateLimit/byUrl,可以发现,限流提示是系统默认的
Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)
以上兜底方案面临的问题
- 系统默认的,没有体现我们自己的业务要求。
- 依照现有条件,我们自定义的处理方法又和业务代码耦合在一块,不直观。
- 每个业务方法都添加—个兜底的,那代码膨胀加剧。
- 全局统—的处理方法没有体现。
- 流控是临时的,不是持久化的。
3. 客户自定义限流处理逻辑
创建CustomerBlockHandler类用于自定义限流处理逻辑,在类中统一的限流提示
public class CustomerBlockHandler {
public static CommonResult handlerException(BlockException exception) {
return new CommonResult(4444, "按客戶自定义,global handlerException----1");
}
public static CommonResult handlerException2(BlockException exception) {
return new CommonResult(4444, "按客戶自定义,global handlerException----2");
}
}
在@SentinelResource 中 blockHandlerClass 指定哪一个类是限流处理类, blockHandler 指定该类中的哪一个方法进行返回,方法必须是静态的
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/customerBlockHandler")
@SentinelResource(value = "customerBlockHandler",
blockHandlerClass = CustomerBlockHandler.class,//<-------- 自定义限流处理类
blockHandler = "handlerException2")//<----------- 限流处理类的哪一个方法进行限流提示返回
public CommonResult customerBlockHandler() {
return new CommonResult(200, "按客戶自定义", new Payment(2020L, "serial003"));
}
测试:
在sentienl 中配置该 customerBlockHandler 的一个限流规则
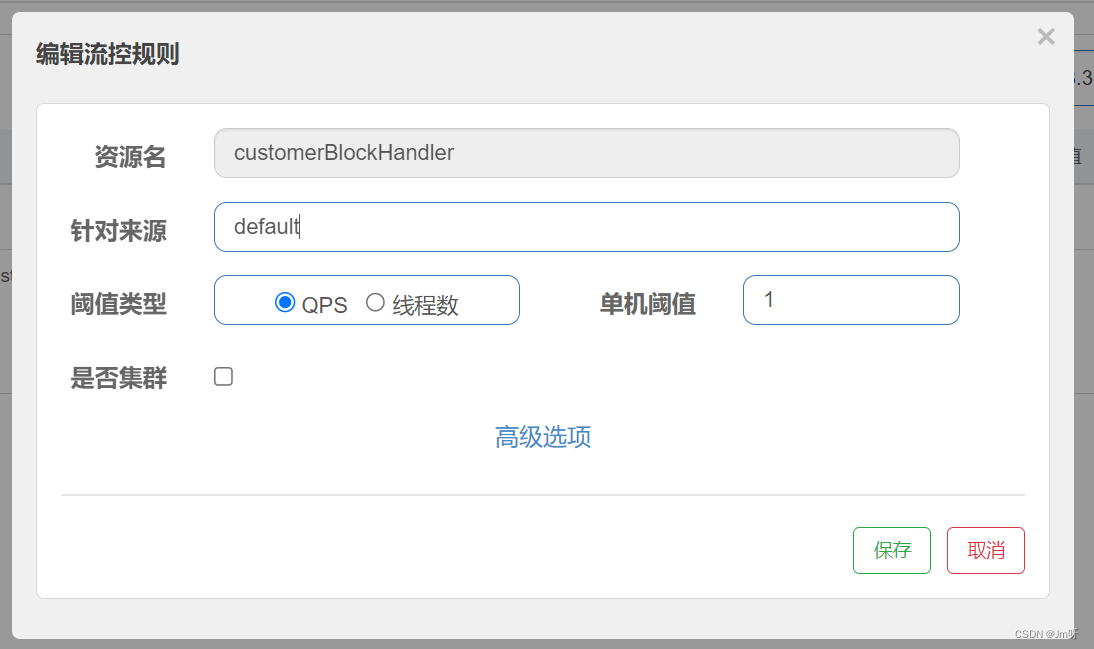
多次访问 http://localhost:8401/rateLimit/customerBlockHandler ,可以发现限流提示返回的正是CustomerBlockHandler.handlerException2中的内容。
八.服务熔断
sentinel整合ribbon+openFeign+fallback
1. 初始化测试环境
- 创建两个消息生产者 :
cloudalibaba-provider-payment9003、cloudalibaba-provider-payment9004 - 创建一个消费者:
cloudalibaba-consumer-nacos-order84
1.1 创建消费者
两个消费者为同样的代码逻辑,故只需要注意端口不同即可
创建模块:cloudalibaba-provider-payment9003
POM.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.jm.springcloud</groupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!-- sentinel -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- nacos -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- SpringBoot整合Web组件+actuator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--日常通用jar包配置-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>4.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Application.yml
server:
port: 9003
spring:
application:
name: nacos-payment-provider
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848 # 配置nacos
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class PaymentApplication9003 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PaymentApplication9003.class, args);
}
}
业务类:
@RestController
public class PaymentController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
//模拟数据库
public static HashMap<Long, Payment> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
static {
hashMap.put(1L, new Payment(1L, "28a8c1e3bc2742d8848569891fb42181"));
hashMap.put(2L, new Payment(2L, "bba8c1e3bc2742d8848569891ac32182"));
hashMap.put(3L, new Payment(3L, "6ua8c1e3bc2742d8848569891xt92183"));
}
@GetMapping(value = "/paymentSQL/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> paymentSQL(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
Payment payment = hashMap.get(id);
CommonResult<Payment> result = new CommonResult(200, "from mysql,serverPort: " + serverPort, payment);
return result;
}
}
1.2 创建消费者
创建模块:cloudalibaba-consumer-nacos-order84
Pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.jm.springcloud</groupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!-- sentinel -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- nacos -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- SpringBoot整合Web组件+actuator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--日常通用jar包配置-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>4.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
application.yml
server:
port: 84
spring:
application:
name: nacos-order-consumer
cloud:
nacos: # nacos 服务注册中心
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: localhost:8080
port: 8719
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
#消费者将要去访问的微服务名称(注册成功进nacos的微服务提供者)
service-url:
nacos-user-service: http://nacos-payment-provider
主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class SentinelConsumerApplication84 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SentinelConsumerApplication84.class, args);
}
}
配置类
@Configuration
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
业务类
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class CircleBreakerController {
@Value("${service-url.nacos-user-service}")
private String SERVICE_URL;
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
}
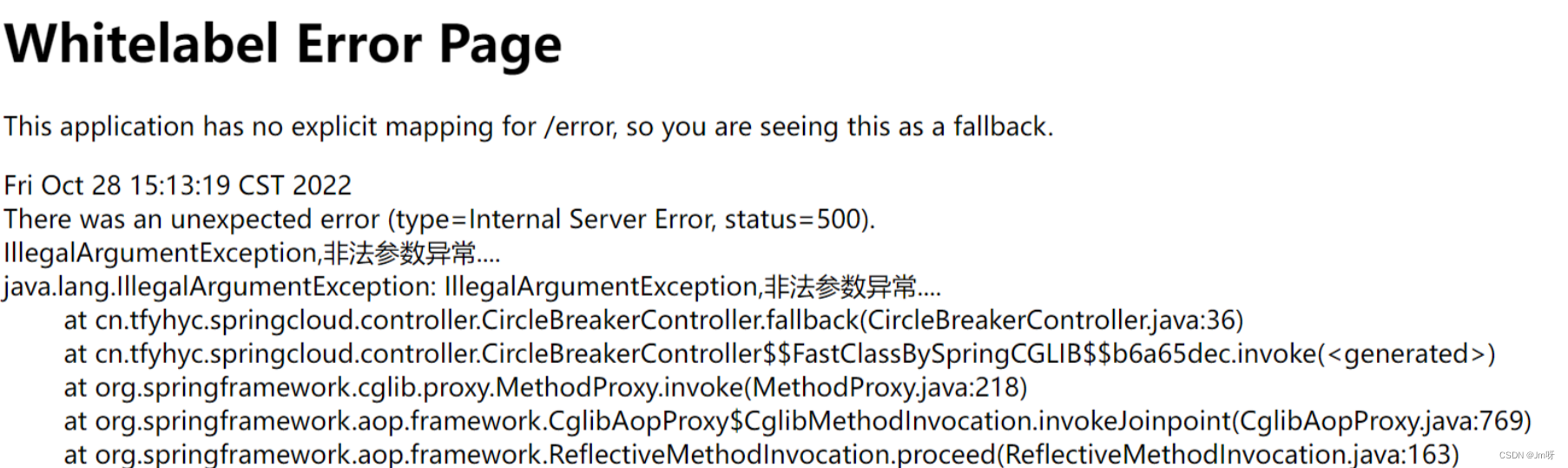
2. 服务熔断无配置
没有任何配置 - 给用户error页面,不友好
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback")
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
3. 服务熔断只配置fallback
fallback只负责业务异常
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback",fallback = "handlerFallBack")
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
public CommonResult handlerFallBack(@PathVariable Long id, Throwable throwable) {
Payment payment = new Payment(id, null);
return new CommonResult(444, "兜底异常handlerFallBack,exeception内容" +
throwable.getMessage(), payment);
}
异常界面:
{"code":444,"message":"兜底异常nandlerFal1back, exception内容illegalkrgumentEBxceptiorn,非法参数异常……","data":{"id":4,"seria:"null"}}
4. 服务熔断只配置blockHandler
blockHandler只负责sentinel控制台配置违规
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback",blockHandler = "blockHandler") //blockHandler只负责sentinel控制台配置违规
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
//本例是blockHandler
public CommonResult blockHandler(@PathVariable Long id, BlockException blockException) {
Payment payment = new Payment(id,"null");
return new CommonResult<>(445,"blockHandler-sentinel限流,无此流水: blockException "+blockException.getMessage(),payment);
}
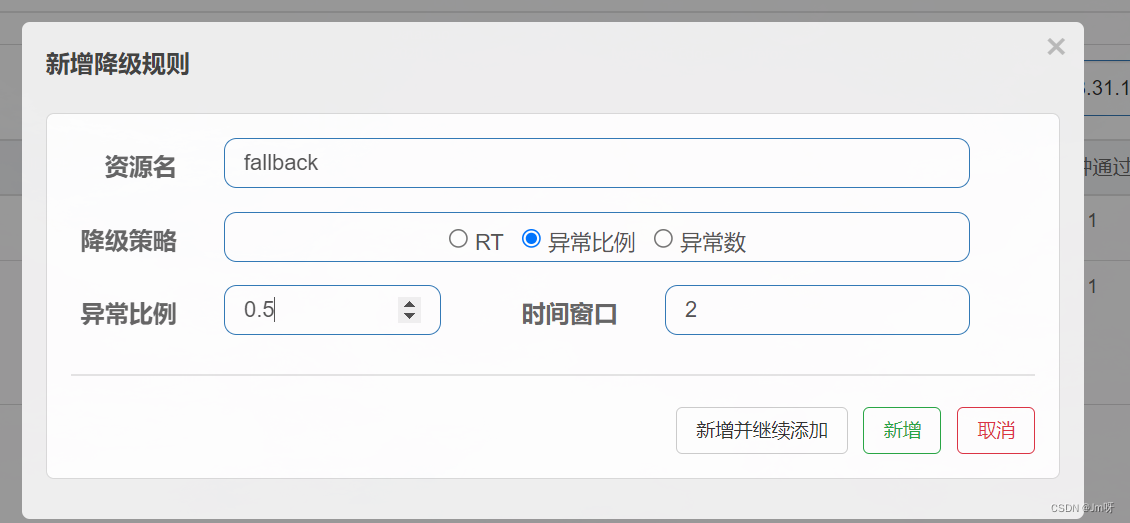
在没有触发降级规则的时候,程序会返回error页面:
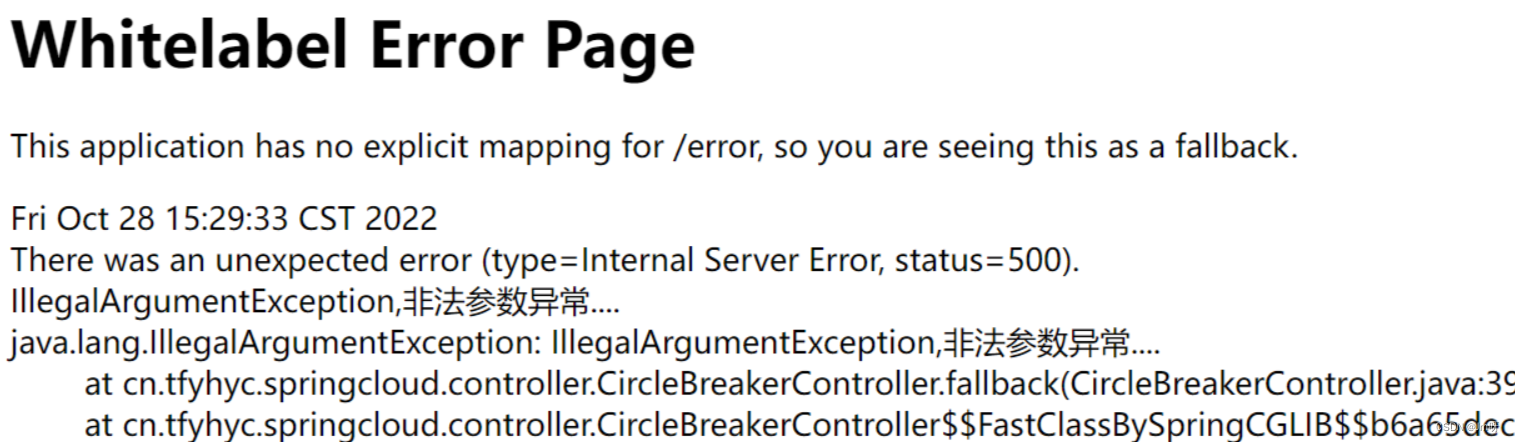
当触发降级规则的时候,将会返回blockHandler定义的方法中的内容
5. fallback和blockHandler都配置
若blockHandler和fallback 都进行了配置,则被限流降级而抛出BlockException时只会进入blockHandler处理逻辑。
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler", fallback = "handlerFallBack")
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
//本例是fallback
public CommonResult handlerFallBack(@PathVariable Long id, Throwable throwable) {
Payment payment = new Payment(id, null);
return new CommonResult(444, "兜底异常handlerFallBack,exeception内容" +
throwable.getMessage(), payment);
}
//本例是blockHandler
public CommonResult blockHandler(@PathVariable Long id, BlockException blockException) {
Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null");
return new CommonResult<>(445, "blockHandler-sentinel限流,无此流水: blockException " + blockException.getMessage(), payment);
}
配置限流策略:

测试:
访问一次:http://localhost:84/consumer/fallback/4的时候,,应为触发了业务异常,所以fallback中的方法执行了
在多次访问:http://localhost:84/consumer/fallback/4时,因为触发了限流策略,所以blockHandler中的方法执行了
6. 忽略异常exceptionsToIgnore
exceptionsToIgnore,忽略指定异常,即这些异常不用兜底方法处理。
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler", fallback = "handlerFallBack",
exceptionsToIgnore = {IllegalArgumentException.class}) // <-----------忽略的异常,不执行 fallback方法
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
访问:http://localhost:84/consumer/fallback/4,发现触发了error页面
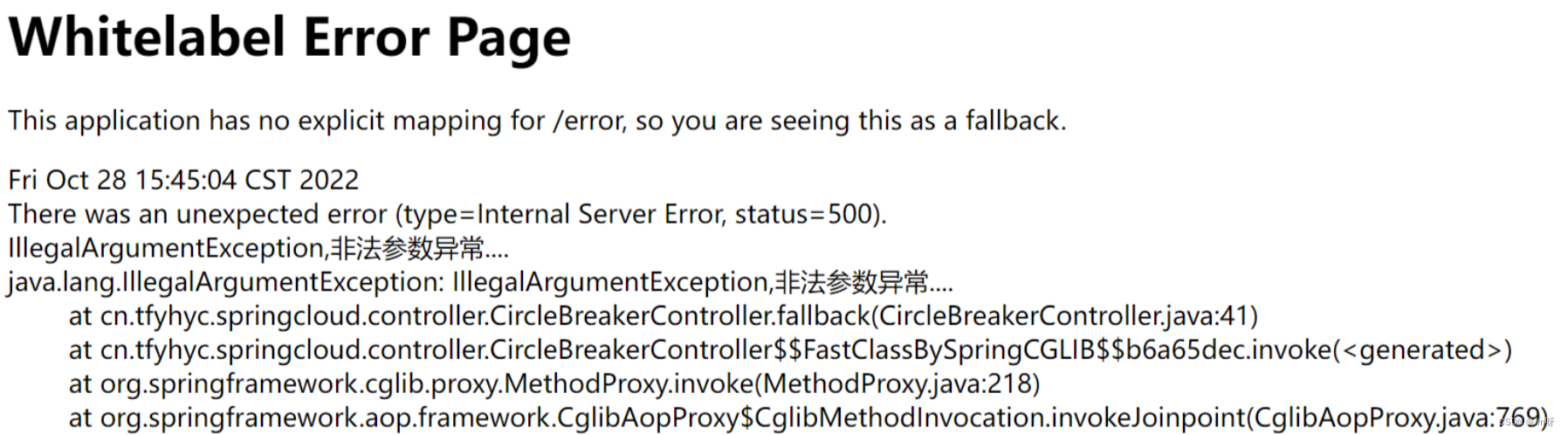
访问:http://localhost:84/consumer/fallback/5, 发现fallback中的方法返回值替代了error页面
7. Sentinel服务熔断OpenFeign
修改84模块
- 84消费者调用提供者9003
- Feign组件一般是消费侧
POM添加openFeign:
<!--SpringCloud openfeign -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
application.yml:开启feign对sentienl的支持
# 开启 Sentinel 对Feign的支持
feign:
sentinel:
enabled: true
业务类:
// fallback: 指定的Feign客户端接口的回退类。回退类必须实现由该注释注释的接口,并且必须是有效的springbean
@FeignClient(name = "nacos-payment-provider", fallback = PaymentServiceImpl.class)
public interface PaymentService {
@GetMapping(value = "/paymentSQL/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> paymentSQL(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
PaymentService的回退类:
@Component
public class PaymentServiceImpl implements PaymentService {
@Override
public CommonResult<Payment> paymentSQL(Long id) {
return new CommonResult<>(44444, "服务降级返回,---PaymentFallbackService", new Payment(id, "errorSerial"));
}
}
controller:
@Resource
private PaymentService paymentService;
@GetMapping(value = "/consumer/paymentSQL/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> paymentSQL(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return paymentService.paymentSQL(id);
}
测试:
正常访问:http://localhost:84/consumer/paymentSQL/1
将消费者payment9003和payment9004停止访问,模拟宕机情况,再次访问:http://localhost:84/consumer/paymentSQL/1,看到已经触发了访问降级
九.熔断框架比较
| - | Sentinel | Hystrix | resilience4j |
|---|---|---|---|
| 隔离策略 | 信号量隔离(并发线程数限流) | 线程池隔商/信号量隔离 | 信号量隔离 |
| 熔断降级策略 | 基于响应时间、异常比率、异常数 | 基于异常比率 | 基于异常比率、响应时间 |
| 实时统计实现 | 滑动窗口(LeapArray) | 滑动窗口(基于RxJava) | Ring Bit Buffer |
| 动态规则配置 | 支持多种数据源 | 支持多种数据源 | 有限支持 |
| 扩展性 | 多个扩展点 | 插件的形式 | 接口的形式 |
| 基于注解的支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 限流 基于QPS,支持基于调用关系的限流 | 有限的支持 | Rate | Limiter |
| 流量整形 | 支持预热模式匀速器模式、预热排队模式 | 不支持 | 简单的Rate Limiter模式 |
| 系统自适应保护 | 支持 | 不支持 | 不支持 |
| 控制台 | 提供开箱即用的控制台,可配置规则、查看秒级监控,机器发观等 | 简单的监控查看 | 不提供控制台,可对接其它监控系统 |
十.规则持久化
一旦我们重启应用,sentinel规则将消失,生产环境需要将配置规则进行持久化。
将限流配置规则持久化进Nacos保存,只要刷新8401某个rest地址,sentinel控制台的流控规则就能看到,只要Nacos里面的配置不删除,针对8401上sentinel上的流控规则持续有效。
步骤
修改:cloudalibaba-sentinel-service8401
POM
<!--SpringCloud ailibaba sentinel-datasource-nacos 后续做持久化用到-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
application.yml
server:
port: 8401
spring:
application:
name: cloudalibaba-sentinel-service
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
# nacos 服务注册中心地址
server-addr: localhost:8848
sentinel:
transport:
# 配置 sentinel dashboard 地址
dashboard: localhost:8080
# 默认8719端口,假如被占用会自动从 8719开始依次加1,直到找到未被占用的端口
port: 8719
datasource: #<---------------------------关注点,添加Nacos数据源配置
ds1:
nacos:
server-addr: localhost:8848 # naocs 服务地址
dataId: cloudalibaba-sentinel-service # 配置项的名称
groupId: SENTINEL_PERSISTENCE # 分组
data-type: json # 数据类型
rule-type: flow # 规则类型
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
Nacos配置:
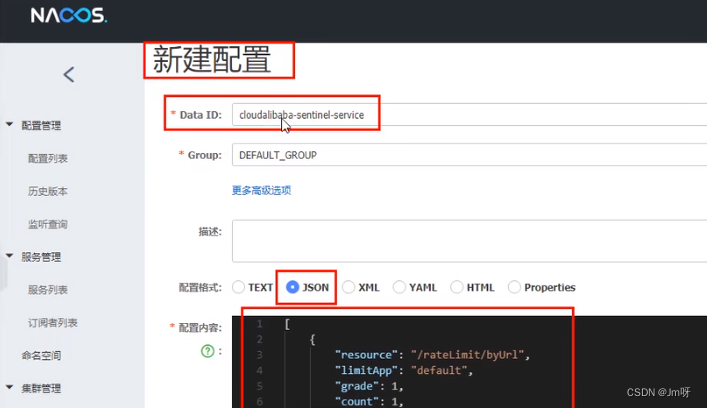
配置内容解析
[{
"resource": "/rateLimit/byUrl",
"limitApp": "default",
"grade": 1,
"count": 1,
"strategy": 0,
"controlBehavior": 0,
"clusterMode": false
}]
- resource:资源名称;
- limitApp:来源应用;
- grade:阈值类型,0表示线程数, 1表示QPS;
- count:单机阈值;
- strategy:流控模式,0表示直接,1表示关联,2表示链路;
- controlBehavior:流控效果,0表示快速失败,1表示Warm Up,2表示排队等待;
- clusterMode:是否集群。
启动8401后刷新sentinel发现业务规则有了
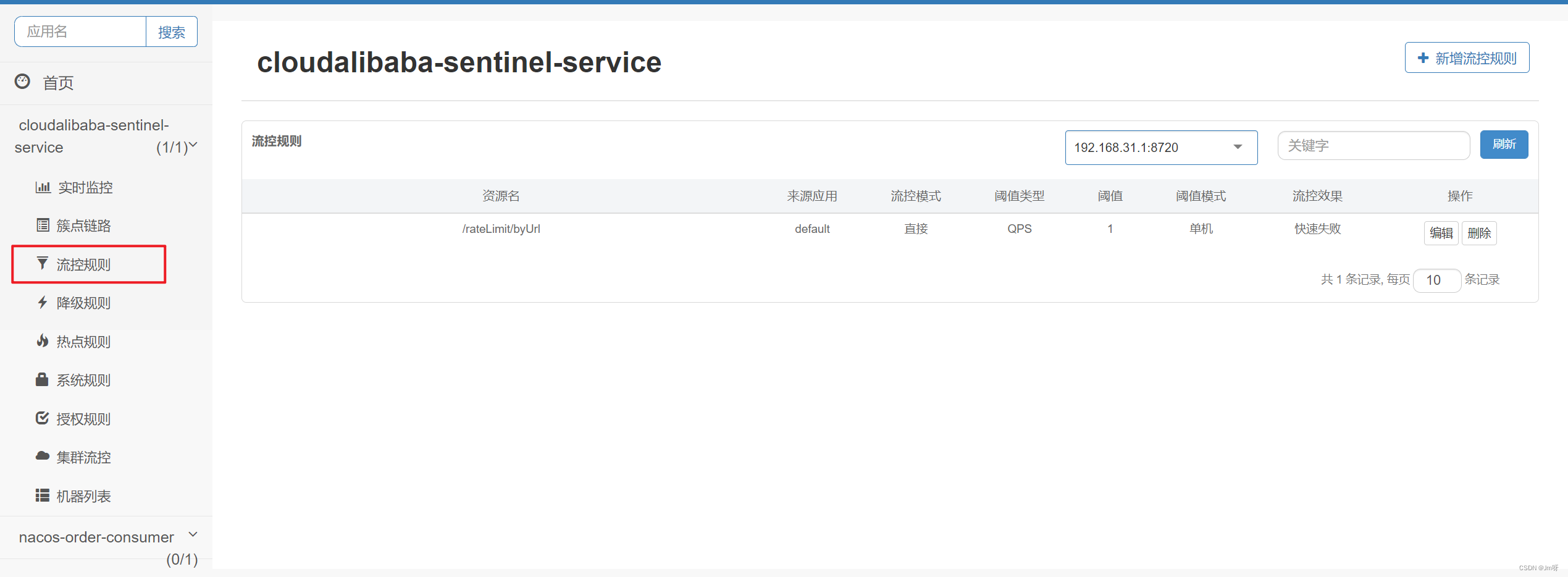
快速访问测试接口 - http://localhost:8401/rateLimit/byUrl- 页面返回Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)
停止8401再看sentinel - 停机后发现流控规则没有了
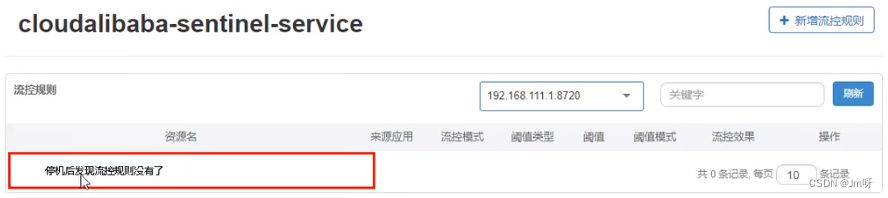
重新启动8401再看sentinel
- 乍一看还是没有,稍等一会儿
- 多次调用 - http://localhost:8401/rateLimit/byUrl
- 重新配置出现了,持久化验证通过
最后
以上就是瘦瘦飞鸟最近收集整理的关于CloudAlibaba - Sentinel熔断与限流一.Sentinel下载安装运行二.Sentinel初始化监控三.流控规则四.降级规则五.Sentinel 热点key六.Sentinel系统规则七.@SentinelResource 注解八.服务熔断九.熔断框架比较十.规则持久化的全部内容,更多相关CloudAlibaba内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复