1 Python 中操作 MySQL 步骤
1.1 安装pymysql命令
sudo pip3 install pymysql
安装软件:sudo apt-get install 软件名称
安装模块:sudo pip3 install 模块名称
1.2 通过pymysql操作数据库的步骤
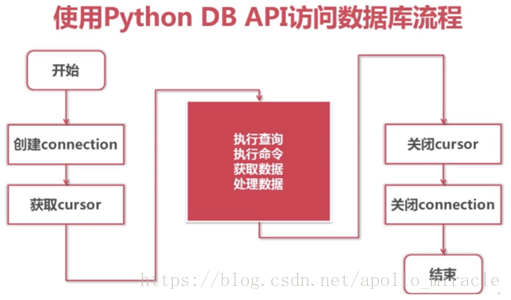
1.3 引入模块
在py文件中引入pymysql模块
from pymysql import *
from pymasql import connect1.4 建立连接对象
1.4.1 Connect 对象
用于建立与数据库的连接
创建对象:调用connect()方法
# conn = connect(参数列表)
conn = connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user="root", password="mysql", database="jing_dong", charset="utf8")参数host:连接的mysql主机,如:本机是”localhost”或”127.0.0.1”
参数port:连接的mysql主机的端口,默认是3306
参数database:数据库的名称
参数user:连接的用户名
参数password:连接的密码
参数charset:通信采用的编码方式,推荐使用utf8
1.4.2 对象的方法
conn.close() # 关闭连接
conn.commit() # 提交
conn.cursor() # 返回Cursor游标对象,用于执行sql语句并获得结果1.5 创建游标对象
1.5.1 Cursor对象
用于执行sql语句,使用频度最高的语句为select、insert、update、delete
获取Cursor对象:调用Connect对象的cursor()方法
cs = conn.cursor()1.5.2 对象的方法
cs.close() # 关闭
# 执行语句,返回受影响的行数,主要用于执行insert、update、delete语句,也可以执行create、alter、drop等语句
cs.execute(operation [, parameters ])
# 执行SQL语句 业务代码 查询操作返回记录数
count = cs.execute("select * from goods")
# 获取查询结果集的下一行数据,返回一个元组
cs.fetchone()
# 获取多条查询结果集,返回是一个元组,默认返回1条
cs.fetchmany(nums)
# 获取结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,再将这些元组装入一个元组返回
cs.fetchall()1.6 对数据表的读操作
# 导入模块
from pymysql import *
# 创建连接对象 连接数据库
conn = connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user="root", password="mysql", database="jing_dong")
# 创建cursor游标对象
cs = conn.cursor()
# 执行SQL语句 业务代码 查询操作返回记录数
count = cs.execute("select * from goods")
# 获取查询结果集的下一行数据,返回一个元组
cs.fetchone()
# 获取多条查询结果集,返回是一个元组,默认返回1条
cs.fetchmany(nums)
# 获取结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,再将这些元组装入一个元组返回
cs.fetchall()
# 最近一次execute返回数据的行数或影响的行数
print(cs.rowcount)
# 使用完毕 先关闭游标
cs.close()
# 再关闭连接
conn.close()
2 增删改查
2.1 增删改
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host="localhost", port=3306, database="jing_dong", user="root", password="mysql", charset="utf8")
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# 执行insert语句,并返回受影响的行数:添加一条数据
# 增加
count = cs1.execute("insert into goods_cates(name) values('硬盘')")
# 打印受影响的行数
print("受影响的行数:%d" % count)
# # 更新
# count = cs1.execute("update goods_cates set name='机械硬盘' where name='硬盘'")
# # 删除
# count = cs1.execute("delete from goods_cates where id=6")
# 提交之前的操作,如果之前已经之执行过多次的execute,那么就都进行提交
conn.commit()
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2.2 查询一行数据
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="root", password="mysql", database="jing_dong", charset="utf8")
# 获得Cursor对象
cs = conn.cursor()
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据
count = cs.execute("select id, name from goods where id>=4")
# 打印受影响的行数
print("查询到%d条数据:" % count)
for i in range(count):
# 获取查询的结果
result = cs.fetchone()
# 打印查询的结果
print(result)
# 获取查询的结果
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2.3 查询多行数据
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="root", password="mysql", database="jing_dong", charset="utf8")
# 获得Cursor对象
cs = conn.cursor()
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据
count = cs.execute("select id,name from goods where id>=4")
# 打印受影响的行数
print("查询到%d条数据:" % count)
result = cs.fetchall()
print(result)
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2.4 用面向对象的思想来实现
from pymysql import *
class JD(object):
def __init__(self):
# 创建Connection连接
self.conn = connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user="root", password="mysql", database="jing_dong",
charset="utf8")
# 获得Cursor对象
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
def __del__(self):
# 关闭Cursor对象, 当程序结束时 python 解释器会自动调用此方法
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()
def execute_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
for temp in self.cursor.fetchall():
print(temp)
def show_all_items(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select * from goods;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def show_cates(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_cates;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def show_brands(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_brands;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
@staticmethod
def print_menu():
print("-----京东------")
print("1:所有的商品")
print("2:所有的商品分类")
print("3:所有的商品品牌分类")
num = input("请输入功能对应的序号:")
return num
def run(self):
while True:
num = JD.print_menu()
if num == "1":
# 查询所有商品
self.show_all_items()
elif num == "2":
# 查询分类
self.show_cates()
elif num == "3":
# 商品品牌分类
self.show_brands()
else:
print("输入有误,重新输入...")
def main():
jd = JD()
jd.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2.5 添加一个商品分类
from pymysql import *
class JD(object):
def __init__(self):
# 创建Connection连接
self.conn = connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='jing_dong',
charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
def __del__(self):
# 关闭Cursor对象, 当程序结束时 python 解释器会自动调用此方法
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()
def execute_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
for temp in self.cursor.fetchall():
print(temp)
def show_all_items(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select * from goods;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def show_cates(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_cates;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def show_brands(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_brands;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def add_brands(self):
item_name = input("输入新商品分类的名称:")
sql = """insert into goods_brands (name) values ("%s")""" % item_name
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
@staticmethod
def print_menu():
print("-----京东------")
print("1:所有的商品")
print("2:所有的商品分类")
print("3:所有的商品品牌分类")
print("4:添加一个商品分类")
num = input("请输入功能对应的序号:")
return num
def run(self):
while True:
num = JD.print_menu()
if num == "1":
# 查询所有商品
self.show_all_items()
elif num == "2":
# 查询分类
self.show_cates()
elif num == "3":
# 商品品牌分类
self.show_brands()
elif num == "4":
# 商品品牌分类
self.add_brands()
else:
print("输入有误,重新输入...")
def main():
jd = JD()
jd.run()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
2.6 根据商品名称查询信息
from pymysql import *
class JD(object):
def __init__(self):
# 创建Connection连接
self.conn = connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='jing_dong',
charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
def __del__(self):
# 关闭Cursor对象, 当程序结束时 python 解释器会自动调用此方法
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()
def execute_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
for temp in self.cursor.fetchall():
print(temp)
def show_all_items(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select * from goods;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def show_cates(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_cates;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def show_brands(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_brands;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def add_brands(self):
item_name = input("输入新商品分类的名称:")
sql = """insert into goods_brands (name) values ("%s")""" % item_name
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
def get_info_by_name(self):
find_name = input("请输入要查询的商品的名字:")
# 对 find_name 进行 判断,验证。
sql = """select * from goods where name='%s';""" % find_name
"""
find_name = ' or 1=1 '; insert into goods ..... ;or '
find_name = 老王牌电脑
select * from goods where name='' or 1=1 or '';
"""
print("---->%s<----" % sql)
self.execute_sql(sql)
@staticmethod
def print_menu():
print("-----京东------")
print("1:所有的商品")
print("2:所有的商品分类")
print("3:所有的商品品牌分类")
print("4:添加一个商品分类")
print("5:根据名字查询一个商品")
num = input("请输入功能对应的序号:")
return num
def run(self):
while True:
num = JD.print_menu()
if num == "1":
# 查询所有商品
self.show_all_items()
elif num == "2":
# 查询分类
self.show_cates()
elif num == "3":
# 商品品牌分类
self.show_brands()
elif num == "4":
# 添加品牌分类
self.add_brands()
elif num == "5":
# 根据名字查询商品
self.get_info_by_name()
else:
print("输入有误,重新输入...")
def main():
jd = JD()
jd.run()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
3 防止SQL注入——参数化
- sql语句的参数化,可以有效防止sql注入
- 注意:此处不同于python的字符串格式化,全部使用%s占位
from pymysql import *
class JD(object):
def __init__(self):
# 创建Connection连接
self.conn = connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='jing_dong',
charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
def __del__(self):
# 关闭Cursor对象, 当程序结束时 python 解释器会自动调用此方法
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()
def execute_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
for temp in self.cursor.fetchall():
print(temp)
def show_all_items(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select * from goods;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def show_cates(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_cates;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def show_brands(self):
"""显示所有的商品"""
sql = "select name from goods_brands;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def add_brands(self):
item_name = input("输入新商品分类的名称:")
sql = """insert into goods_brands (name) values ("%s")""" % item_name
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
def get_info_by_name(self):
find_name = input("请输入要查询的商品的名字:")
# sql = """select * from goods where name='%s';""" % find_name
# print("---->%s<----" % sql)
# self.execute_sql(sql)
sql = "select * from goods where name=%s"
self.cursor.execute(sql, [find_name])
print(self.cursor.fetchall())
@staticmethod
def print_menu():
print("-----京东------")
print("1:所有的商品")
print("2:所有的商品分类")
print("3:所有的商品品牌分类")
print("4:添加一个商品分类")
print("5:根据名字查询一个商品")
num = input("请输入功能对应的序号:")
return num
def run(self):
while True:
num = JD.print_menu()
if num == "1":
# 查询所有商品
self.show_all_items()
elif num == "2":
# 查询分类
self.show_cates()
elif num == "3":
# 商品品牌分类
self.show_brands()
elif num == "4":
# 添加品牌分类
self.add_brands()
elif num == "5":
# 根据名字查询商品
self.get_info_by_name()
else:
print("输入有误,重新输入...")
def main():
jd = JD()
jd.run()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
最后
以上就是粗心金毛最近收集整理的关于MySQL与Python交互1 Python 中操作 MySQL 步骤2 增删改查3 防止SQL注入——参数化 的全部内容,更多相关MySQL与Python交互1内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复