尚硅谷JavaSE笔记合集
| 文章名 | 链接 |
|---|---|
| 【JavaSE】异常 | 文章地址 |
| 【JavaSE】常用类:String、LocalDateTime… | 文章地址 |
| 【JavaSE】枚举 | 文章地址 |
| 【JavaSE】注解 | 文章地址 |
| 【JavaSE】集合框架 | 文章地址 | HashMap源码解析 | List相关实现类源码解析 |
| 【JavaSE】泛型 | 文章地址 |
| 【JavaSE】IO流 | 文章地址 | 字符编码详解 |
| 【JavaSE】网络编程,BIO需求演进 | 文章地址 |
| 【JavaSE】反射 | 文章地址 |
| 【JavaSE】jdk8新特性 | 文章地址 |
一、String
1.1 概述
/**
* String:
* 1.String声明为final,不可被继承
* 2.String实现Serializable接口,表示字符串是支持序列化的
* 实现Comparable接口,表示String是可以比较大小的
* 3.String内部定义了 final char value[] 用于存储字符串数据
* 4.不可变的字符序列,具有不可变性。
*
*/
public class StringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
}
}
1.2 不可变性
/**
* String:
* 4.不可变的字符序列,具有不可变性。
* (1) 重新赋值时,需要重写指定内存区域赋值,不是改变原有的value进行赋值。
* (2) 进行连接时,需要重新指定内存区域赋值,不是改变原有的value完成链接。
* (3) 调用replace()方法时,需要重新指定内存区域赋值,不是改变原有的value进行替换。
* 5.通过字面量的方式(区别于new)给一个字符串赋值,此时的字符串值声明在字符串常量池中。
* 6.字符串常量池中是不会存储相同内容的字符串的。
*
*/
public class StringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
//4.1 重新赋值时,需要重写指定内存区域赋值,不是改变原有的value进行赋值。
String str1=new String("hello");
String str2=str1;
str2="hi";
System.out.println(str1==str2); //false
//4.2 进行连接时,需要重新指定内存区域赋值,不是改变原有的value完成链接。
String str3=new String("hello");
String str4=str3;
str3+=" String";
System.out.println(str3==str4); //false
//4.3 调用replace()方法时,需要重新指定内存区域赋值,不是改变原有的value进行替换。
String str5=new String("hello");
String str6=str5.replace("hello","hi");
System.out.println(str5==str6); //false
//6. 字符串常量池中是不会存储相同内容的字符串的
String str7="abc";
String str8="abc";
System.out.println(str7==str8); //true
}
}
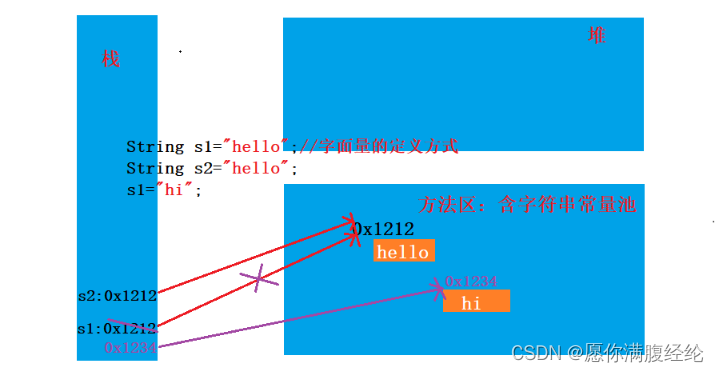
1.3 对象创建内存分析
第二类:堆String对象可以是自定义对象
/**
* 对象创建内存模型:栈变量,堆String对象,堆char数组对象,字符串常量池(不会存在相同内容)
* 第一类:
* 栈变量——>堆String对象——>堆char数组对象
* 第二类:
* 栈变量——>堆String对象——>字符串常量池
* 第三类:
* 栈变量——>字符串常量池
* 第四类:
* 栈变量=null
*/
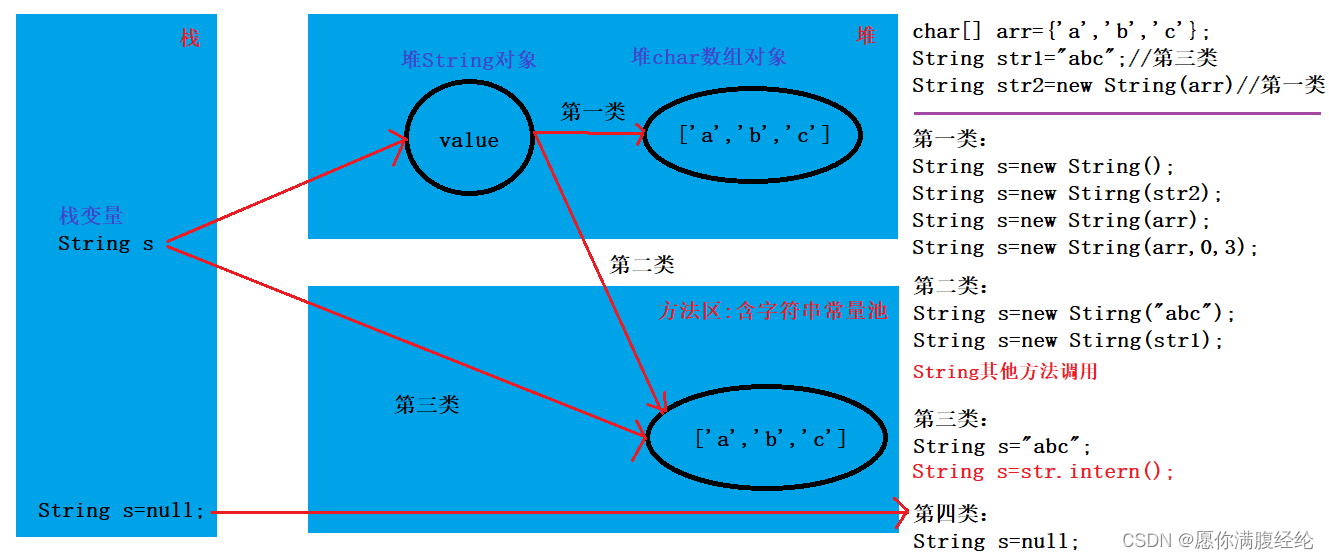
1.4 字符串拼接内存分析
/**
* 常量池:不会存在相同内容
*
* 字符串拼接内存模型:
* 属于第二类情况
* - 其中有一个是变量
* 属于第三类情况
* - 全部都是常量(注意:包括变量名引用常量值)
*/
public class StringTest {
@Test
public void test3(){
String a="a";
String b="b";
final String C="c"; //常量
//1.属于第二类情况
String ab=a+b;
ab=a+"b";
ab="a"+b;
//2.属于第三类情况:注意,包括变量名引用常量值
ab="a"+"b";
ab="a"+C;
}
}
1.5 面试题
/**
* 1.填写程序的输出内容?
* 2.String str=new String("abc")一共创建了多少个对象?
* - 两个。一个为堆内存的String对象,另一个为常量池中的引用
*/
public class StringTest {
String str = new String("good");
char[] ch = { 't', 'e', 's', 't' };
public void change(String str, char ch[]) {
str = "test ok";
ch[0] = 'b';
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringTest ex = new StringTest();
ex.change(ex.str, ex.ch);
System.out.println(ex.str); //good
System.out.println(ex.ch); //best
}
}
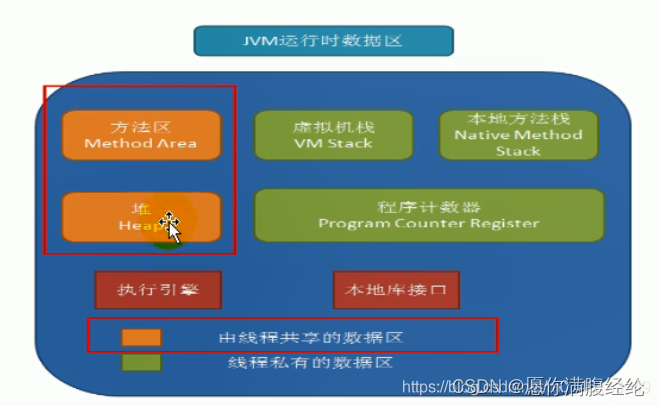
1.6 JVM相关内存结构









1.7 常用方法
1.7.1 返回char
- 获取字符:charAt(int)
@Test
public void test1(){
String str="abc";
System.out.println(str.charAt(0)); //a
}
1.7.2 返回String
- 去掉空白:去掉首尾空白
- 连接:concat(String)
- 转变大小写
- toLowerCase():返回小写字符串,使用默认语言环境
- toUpperCase():返回大写字符串,使用默认语言环境
- 替换
- replace(char , char ):用新字符替换所有旧字符
- replace(CharSequence , CharSequence ):用新字符串替换所有旧字符串
- replaceAll(String regex, String ):用新字符串替换所有正则匹配子字符串
- replaceFirst(String regex, String ):用新字符串替换第一个正则匹配子字符串
- 截取
- substring(int):截取索引到结尾的子字符串
- substring(int ,int ):截取 [int ,int ) 的子字符串
@Test
public void test2(){
String str=" aaa ";
//1.去掉空白
str=str.trim();
System.out.println(str); //aaa
//2.连接
System.out.println(str.concat("AAA")); //aaaAAA
//3.转变大小写
System.out.println(str.toLowerCase()); //aaa
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase()); //AAA
//4.替换
System.out.println(str.replace('a','b')); //bbb
System.out.println(str.replace("aa","bb")); //bba
System.out.println(str.replaceAll(".","b")); //bbb
System.out.println(str.replaceFirst(".","b")); //baa
//5.截取
System.out.println(str.substring(0)); //aaa
System.out.println(str.substring(0,3)); //aaa
}
1.7.3 返回String[]
- 拆分(String[])
- split(String regex):使用正则拆分
- split(String regex, int ):使用正则拆分成有限个数,剩余的为最后字符串元素
@Test
public void test3(){
String str="a-a-a";
//1.拆分
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str.split("-"))); //[a, a, a]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str.split("-",2))); //[a, a-a]
}
1.7.4 返回int
- 获取长度:length()
- 获取索引
- indexOf(String str):返回指定字符串首次出现的索引。未找到返回-1
- indexOf(String , int ):返回指定字符串首次出现的索引,从指定的索引开始。未找到返回-1
- lastIndexOf(String ):返回指定字符串最后出现的索引。未找到返回-1
- lastIndexOf(String , int ):返回指定字符串最后出现的索引,从指定索引结束。未找到返回-1
- 比较
- compareTo(String):比较两个字符串的大小
/**
* 什么情况下,indexOf(str)和lastIndexOf(str)返回值相同?
* - 情况一:存在唯一的一个str。
* - 情况二:不存在str
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
String str="aaa";
//1.获取长度
System.out.println(str.length()); //3
//2.获取索引
System.out.println(str.indexOf("a")); //0
System.out.println(str.indexOf("a",1)); //1
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("a")); //2
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("a",2)); //2
//3.比较
System.out.println(str.compareTo("bbb")); //-1,小于
}
1.7.5 返回boolean
- 判断(boolean)
- isEmpty():判断是否是空字符串
- equalsIgnoreCase(String):判断两个字符串内容是否相同,忽略大小写
- matches(String regex):判断是否与正则匹配
- contains(CharSequence ):判断是否包含指定字符串
- endsWith(String ):判断是否以指定后缀结尾
- startsWith(String ):判断是否以指定后缀开始
- startsWith(String , int ):判断从指定索引开始的子字符串是否以指定后缀开始
@Test
public void test5(){
String str="aaa";
//1.判断
System.out.println(str.isEmpty()); //false
System.out.println(str.equalsIgnoreCase("a")); //false
System.out.println(str.matches("\w+")); //true
System.out.println(str.contains("a")); //true
System.out.println(str.startsWith("aa")); //true
System.out.println(str.startsWith("aa",1)); //true
System.out.println(str.endsWith("aa")); //true
}
1.7.6 其他
- toCharArray():String转换为char[]
- getBytes():String转化为byte[]
- valueOf(Object):Object转换为String
1.8 类型转换
- 基本数据类型包装类
- String——>基本数据类型包装类:包装类.parseXxx(str)、包装类.valueOf(str)
- 基本数据类型包装类——>String:String.valueOf(int)
- char[]
- String——>char[]:str.toCharArray()
- char[]——>String:new String(arr)
- byte[]
- String——>byte[]:编码,str.getBytes()
- byte[]——>String:解码,new String(arr)
- StringBuilder、StringBuffer
- String->StringBuilder、StringBuffer:构造器,StringBuilder(String)、StringBuffer(String)
- StringBuilder、StringBuffer->String:构造器,String(StringBuilder)、String(StringBuffer)或者toString()
/**
* 说明:解码时,要求解码使用的字符集必须与编码时使用的字符集一致,否则会出现乱码。
* utf-8:包含所有国家的字符集,涵盖广 gbk:中国制定的编码标准,涵盖较少
*/
public class StringTypeTurnTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
//1.1 String——>基本数据类型包装类
String str="123";
System.out.println(Integer.valueOf(str)); //123
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt(str)); //123
//1.2 基本数据类型包装类——>String
int i=123;
Integer inte=123;
System.out.println(String.valueOf(i)); //123
System.out.println(String.valueOf(inte)); //123
}
@Test
public void test2(){
//2.1 String——>char[]
String str="123";
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str.toCharArray())); //[1, 2, 3]
//2.2 char[]——>String
char[] arr={'1','2','3'};
System.out.println(new String(arr)); //123
}
@Test
public void test3(){
//3.1 String——>byte[]:编码
String str="abc";
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str.getBytes())); //[97, 98, 99]
//3.2 byte[]——>String:解码
byte[] bt={97,98,99};
System.out.println(new String(bt)); //abc
}
}
1.9 面试题
1、模拟一个trim方法,去除字符串两端的空格。
public String trimTest(String str){
if (str==null){
throw new RuntimeException("字符串为null!");
}
//1.保存头部开始第一个非空索引
int start=0;
//2.保存尾部开始第一个非空索引
int end=str.length()-1;
//3.计算头部开始第一个非空索引
while(start<str.length() && str.startsWith(" ",start)){
start++;
}
//4.计算尾部开始第一个非空索引
while(end>=0 && str.substring(0,end+1).endsWith(" ")){
end--;
}
if (start>end){
return "";
}
return str.substring(start,end+1);
}
2、将一个字符串进行反转。将字符串中指定部分进行反转。比如“abcdefg”反转为”abfedcg”
public String reverseTest(String str,int startIndex,int endIndex){
if (str==null){
throw new RuntimeException("字符串为null!");
}
if (startIndex<0 || endIndex<0 || startIndex>endIndex || startIndex>=str.length() || endIndex>=str.length()){
throw new RuntimeException("整型参数不合法!");
}
//方式一:转换为数组,将元素进行交换
char[] chars1 = str.toCharArray();
char flush=' ';
int time=(endIndex-startIndex)/2;
for (int i = 0; i < time; i++) {
flush=chars1[endIndex-i-1];
chars1[endIndex-i-1]=chars1[startIndex+i];
chars1[startIndex+i]=flush;
}
String way1=new String(chars1);
//方式二:转换为数组,从endIndex开始进行拼接
char[] chars2 = str.toCharArray();
String way2=str.substring(0,startIndex);
for (int i = 0; i < endIndex-startIndex; i++) {
way2+=chars2[endIndex-i-1];
}
way2+=str.substring(endIndex);
//方式三:转换为StringBuilder,从endIndex开始进行添加
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(str.length());
sb.append(str.substring(0,startIndex));
for (int i = 0; i < endIndex-startIndex; i++) {
sb.append(str.charAt(endIndex-i-1));
}
sb.append(str.substring(endIndex));
String way3=sb.toString();
return way1;
}
3、获取一个字符串在另一个字符串中出现的次数
public int counter(String str,String src){
if (str==null || src==null){
throw new RuntimeException("参数值为null!");
}
if(str.length()>=src.length() && str.contains(src)){
//1.定义计数器
int count=0;
int fromIndex=0;
while((fromIndex=str.indexOf(src,fromIndex))!=-1){
count++;
fromIndex+=src.length();
}
return count;
}
return 0;
}
4、获取两个字符串中最大相同子串。
/**
* 注意-其他方式:将小串从大到小进行拆分,然后与大串进行匹配,如果存在则就是最大相同子串
*/
public String sameMax(String src1,String src2){
//判断小串,保证src1为大串,src2为小串
if (src1.length()<src2.length()){
String flush=src1;
src1=src2;
src2=flush;
}
//1.保存最大子串
String result="";
//2.保存最大子串长度
int length=0;
//3.循环遍历src1,在每次循环中遍历匹配src2
char[] chars1 = src1.toCharArray();
char[] chars2 = src2.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars1.length-chars2.length+1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chars2.length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < chars2.length-j; k++) {
if(chars1[i+k]!=chars2[j+k]){
break;
}
if (k+1>length){
length=k+1;
result=src2.substring(j,k+1);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
5、对字符串中字符进行自然顺序排序
public String sort(String src){
char[] chars = src.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(chars);
return new String(chars);
}
二、可变字符序列
2.1 比较
/**
* String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder三者的异同?
*
* 相同点:底层使用char[]存储
*
* 不同点:
* String VS StringBuilder
* - String不可变,效率低。StringBuilder可变,效率高。
* - 都是线程不安全
* StringBuffer VS StringBuilder
* - StringBuffer线程安全,效率低;StringBuilder线程不安全,效率高。
* - 都是可变的字符序列
* - StringBuilder是jdk5.0新增的
*/
2.2 源码分析
/**
* 1.对象创建,底层数组长度
* - new String():new char[0]
* new StringBuffer():new char[16]
* - new String("abc"):new char[]{'a','b','c'};
* new StringBuffer("abc"):new char["abc".length() + 16];
* 2.字符串修改
* - str="a":重新创建对象返回
* - strBuffer.append('a'):value[0] = 'a'
*
* 注意:
* 1.StringBuffer的方法:length(),
* 2.扩容问题:新数组扩容为原来 2倍+2 或 所需容量,并复制到新数组中。消耗性能
*
* 建议:开发中建议大家使用:StringBuffer(int)、StringBuilder(int),减少扩容次数
*
*/
//1.1 StringBuffer():底层数组长度16
public StringBuffer() {
super(16);
}
//1.2 StringBuffer(int):自定义底层数组长度
public StringBuffer(int capacity) {
super(capacity);
}
AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) {
value = new char[capacity];
}
//1.3 StringBuffer(String):底层数组长度 str.length+16
public StringBuffer(String str) {
super(str.length() + 16);
append(str);
}
//2.1添加元素
public synchronized StringBuffer append(String str) {
toStringCache = null;
//2.2 添加元素
super.append(str);
return this;
}
//2.2 添加元素
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
//2.2.1 判断是否为null
if (str == null)
return appendNull();
int len = str.length();
//2.2.2 判断长度是否足够
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
//2.2.3 拷贝元素到数组中
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
//2.2.1 判断是否为null添加"null"
private AbstractStringBuilder appendNull() {
int c = count;
ensureCapacityInternal(c + 4);
final char[] value = this.value;
value[c++] = 'n';
value[c++] = 'u';
value[c++] = 'l';
value[c++] = 'l';
count = c;
return this;
}
//2.2.2 判断长度是否足够
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0) {
//2.2.2.1 扩容
value = Arrays.copyOf(value,
newCapacity(minimumCapacity));
}
}
//2.2.2.1 扩容为原来的2倍+2 或者 为所需长度
private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int newCapacity = (value.length << 1) + 2;
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) {
newCapacity = minCapacity;
}
return (newCapacity <= 0 || MAX_ARRAY_SIZE - newCapacity < 0)
? hugeCapacity(minCapacity)
: newCapacity;
}
//2.2.3 拷贝元素到数组中
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin) {
if (srcBegin < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
}
//判断长度是否足够
if (srcEnd > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
}
if (srcBegin > srcEnd) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
//拷贝元素到数组中
System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
2.3 常用方法
/**
* 常用方法:
* 1.增:append(Object)
* 2.删:delete(int,int)、deleteCharAt(int)
* 3.改:setCharAt(int,char)、replace(int, int, String)
* 4.查:charAt(int)
* 5.插:insert(int,Object)
* 6.长度:length()
* 7.逆序、截取、获取索引下标:reverse()、substring(int,int)、indexOf(char)
*/
public class StringBuildTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(32);
//1.增:append(Object)
System.out.println(sb.append("abc")); //abc
//2.删:delete(int,int)、deleteCharAt(int)
System.out.println(sb.delete(0,1)); //bc
//3.改:setCharAt(int,char)、replace(int, int, String)
sb.setCharAt(0,'a');
System.out.println(sb); //ac
//4.查:charAt(int)
System.out.println(sb.charAt(0)); //a
//5.插:insert(int,Object)
System.out.println(sb.insert(0,'a')); //aac
//6.长度:length()
System.out.println(sb.length()); //3
//7.逆序、截取、获取索引下标
System.out.println(sb.reverse()); //caa
System.out.println(sb.substring(0,1)); //c
System.out.println(sb.indexOf("a")); //1
}
}
2.4 效率对比
public class StringBuildTest {
/**
* 效率对比:String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder,循环拼接20000次
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
String str="";
StringBuilder sbuilder=new StringBuilder();
StringBuffer sbuffer=new StringBuffer();
Long start=0L;
Long end=0L;
//1.String
start=System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {
str+=i;
}
end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("String消耗时间:"+(end-start)); //1299
//2.StringBuffer
start=System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {
sbuffer.append(i);
}
end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("StringBuffer消耗时间:"+(end-start)); //2
//3.StringBuilder
start=System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {
sbuilder.append(i);
}
end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("StringBuilder消耗时间:"+(end-start)); //1
}
}
三、日期时间-jdk8前
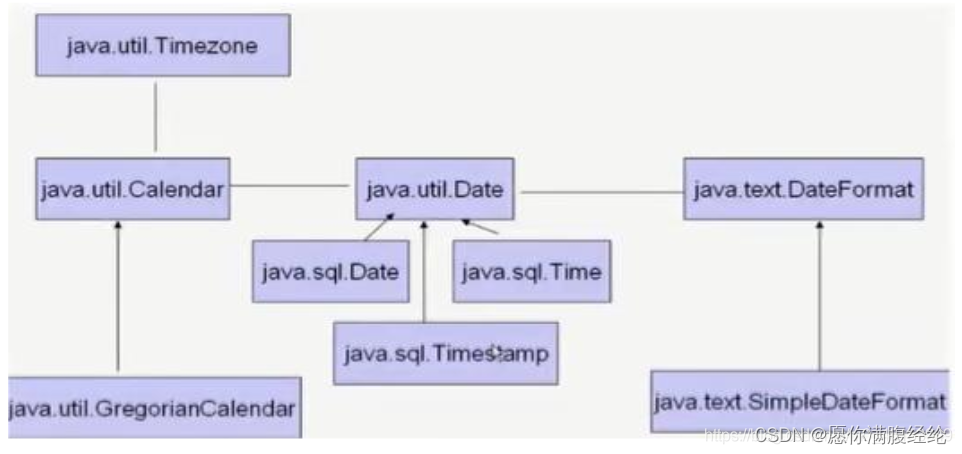
3.1 currentTimeMillis()
System.currentTimeMillis():返回此时与1970年1月1日0时0分0秒的时间差,单位毫秒
- 此方法适于计算时间差。
- 计算世界时间的主要标准有:
- UTC(Coordinated Universal Time)
- GMT(Greenwich Mean Time)
- CST(Central Standard Time)
/**
* System.currentTimeMillis():返回此时与1970年1月1日0时0分0秒的时间差,单位毫秒
*/
public class CurrentTimeTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(l); //1664805955763
}
}
3.2 Date
/**
* jdk8前的时间类测试
* 1.java.util.Date(表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒)
* - Date():实例化当前时间
* - Date(Long):实例化指定时间
* - toString():返回时间内容
* - getTime():返回毫秒数
* 2.java.sql.Date(对应数据库中日期类型的变量)
* - Date(Long):实例化指定时间
* - java.util.Date转换为java.sql.Date?
*/
public class earlyDateTimeTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
//1.实例化当前时间
Date date1=new Date();
//2.实例化指定时间
Date date2=new Date(15643874812627L);
//3.返回时间内容
System.out.println(date1.toString()); //Fri Sep 25 16:46:52 CST 2465
//4.返回毫秒数
System.out.println(date2.getTime()); //15643874812627
}
@Test
public void test2(){
//1.实例化指定时间
java.sql.Date sqlDate=new java.sql.Date(15643874812627L);
System.out.println(sqlDate); //2465-09-25
//2.java.util.Date转换为java.sql.Date
Date date=new Date();
sqlDate=new java.sql.Date(date.getTime());
System.out.println(sqlDate); //2022-10-04
}
}
3.3 SimpleDateFormat
Date类的API不易于国际化,大部分被废弃了,java.text.SimpleDateFormat类是一个不与语言环境有关的方式来格式化和解析日期的具体类。- 它允许进行
- 格式化:日期—>文本
- 解析:文本—>日期
/**
* jdk8前的时间类测试
* 3.SimpleDateFormat(格式化)
* - SimpleDateFormat():默认格式
* - SimpleDateFormat(String):自定义格式
* - 格式化:format(Date)
* - 解析:parse(String)
* 4.Calendar
*/
public class earlyDateTimeTest {
@Test
public void test3() throws ParseException {
//1.默认格式实例化
SimpleDateFormat sdf1=new SimpleDateFormat();
//2.自定义格式实例化
SimpleDateFormat sdf2=new SimpleDateFormat("GGG yyyy-MM-dd aaa hh:mm:ss");
//3.格式化
Date date=new Date();
System.out.println(sdf1.format(date)); //22-10-4 下午4:17
System.out.println(sdf2.format(date)); //公元 2022-10-04 下午 04:17:38
//4.解析
System.out.println(sdf1.parse(sdf1.format(date))); //Tue Oct 04 16:17:00 CST 2022
System.out.println(sdf2.parse(sdf2.format(date))); //Tue Oct 04 16:17:00 CST 2022
}
}
3.4 Calendar日历类
- intfield:YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_WEEK、HOUR_OF_DAY 、MINUTE、SECOND…
- 注意:
- 获取月份时:一月是0,二月是1,以此类推
- 获取星期时:周日是1,周二是2,以此类推
/**
* Calendar:抽象基类,主用用于完成日期字段之间相互操作的功能。
* - getInstance():获取子类GregorianCalendar实例
* - setTime(Date):设置代表的时间
* - getTime():获取代表的时间
* - get(intfield):获取时间信息。
* - set(intfield,intvalue):设置时间信息。
* - add(intfield,intamount):修改时间信息。
*/
public class earlyDateTimeTest {
@Test
public void test4(){
//1.获取子类GregorianCalendar实例
Calendar instance = Calendar.getInstance();
//2.设置代表的时间
instance.setTime(new Date());
//3.获取代表的时间
System.out.println(instance.getTime()); //Tue Oct 04 16:56:31 CST 2022
//4.获取时间信息
System.out.println(instance.get(Calendar.YEAR)); //2022
System.out.println(instance.get(Calendar.MONTH)); //9
System.out.println(instance.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)); //4
//5.设置时间信息
instance.set(Calendar.YEAR,2050);
//6.修改时间信息
instance.add(Calendar.YEAR,1);
System.out.println(instance.getTime()); //Wed Oct 04 16:56:31 CST 2051
}
}
3.5 练习
练习1:字符串"2020-09-08"转换为java.sql.Date
public class earlyDateTimePratise {
@Test
public void test1() throws ParseException {
//1.获得格式化器
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
//2.解析字符串获得毫秒数
long millis = sdf.parse("2022-09-08").getTime();
//3.通过毫秒数创建Date实例
java.sql.Date sqlDate=new java.sql.Date(millis);
System.out.println(sqlDate); //2022-09-08
}
}
练习2:1990-01-01 开始"三天打渔两天晒网", 2020-09-08 是打渔还是晒网?
public class earlyDateTimePratise {
//方式一:通过间隔毫秒数计算花费天数
@Test
public void test2() throws ParseException {
//1.获得格式化器
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
//2.计算花费的毫秒数
Long useMillis=sdf.parse("2020-09-08").getTime()-sdf.parse("1990-01-01").getTime();
//3.计算天数
Long useDay=(useMillis/(1000*60*60*24))+1;
//4.判断结果
switch (String.valueOf (useDay%5)){
case "1":
System.out.println("打渔第一天");break;
case "2":
System.out.println("打渔第二天");break;
case "3":
System.out.println("打渔第三天");break;
case "4":
System.out.println("晒网第一天");break;
case "0":
System.out.println("晒网第二天");break;
}
}
//方式二:1990-01-01 --> 2019-12-31 + 2020-01-01 -->2020-09-08
}
四、日期时间-jdk8中
4.1 概述与转换
jdk1.8之前面临的问题是:
-
可变性:像日期和时间这样的类应该是不可变的。
-
偏移性:Date中的年份是从1900开始的,而月份都从0开始。
Date date2 = new Date(2020 - 1900,9 - 1,8); System.out.println(date2); //Tue Sep 08 00:00:00 CST 2020 -
格式化:格式化只对Date有用,Calendar则不行。
-
此外,它们也不是线程安全的;不能处理闰秒等。
解决
-
java.time API 已经纠正了过去的缺陷,将来很长一段时间内它都会为我们服务。
-
吸收了Joda-Time 的精华,以一个新的开始为Java 创建优秀的API。
java.time–包含值对象的基础包
java.time.chrono–提供对不同的日历系统的访问java.time.format–格式化和解析时间和日期java.time.temporal–包括底层框架和扩展特性java.time.zone–包含时区支持的类
说明:大多数开发者只会用到基础包和format包,也可能会用到temporal包。因此,尽管有68个新的公开类型,大多数开发者,大概将只会用到其中的三分之一。
转换
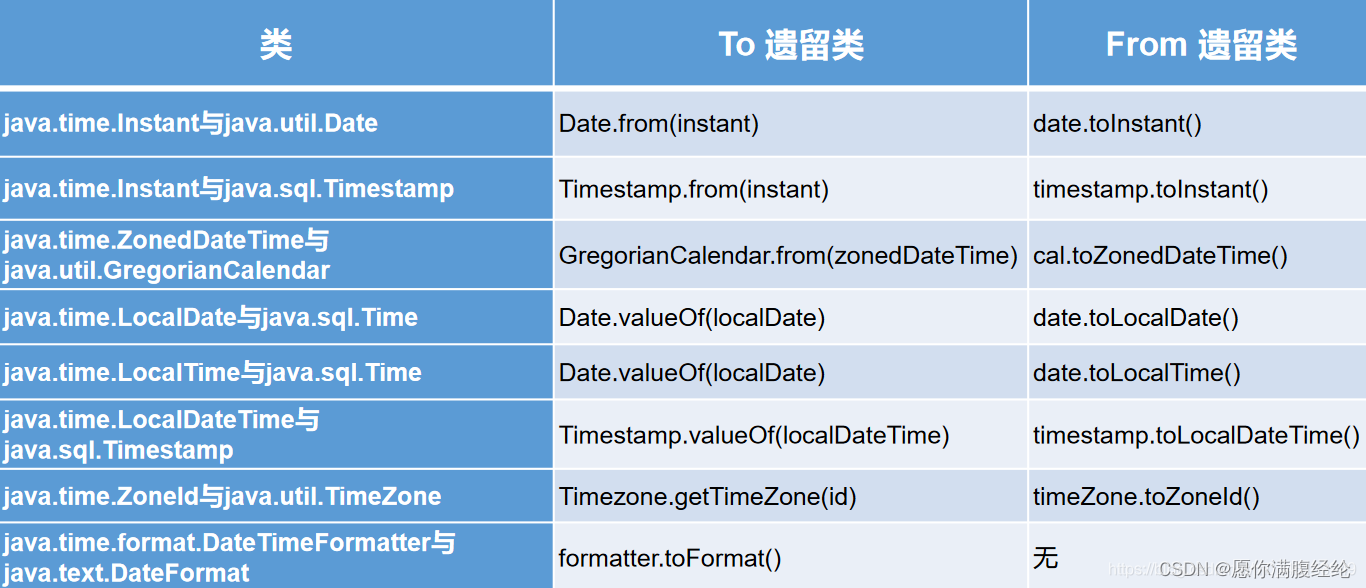
4.2 LocalDateTime
表示公历的日期、时间
- 不可变的对象
- LocalDateTime 为常用类,类似Calendar
/**
* LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime:公历日期、时间。类似于Calendar
* 1.now():获取实例
* 2.of(int,int,int,int,int):获取实例
* 3.getXxx():获取相关属性
* 4.withXxx():设置相关属性
* 5.plusXxx():增加
* 6.minusXxx():减少
* 7.format(DateTimeFormatter):格式化
*/
public class NewDateTimeTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
//1.now():获取实例
LocalDateTime dateTime1 = LocalDateTime.now();
//2.of(int,int,int,int,int):获取实例
LocalDateTime dateTime2 = LocalDateTime.of(2022, 10, 4, 17, 27);
System.out.println(dateTime1); //2022-10-04T17:36:53.914
System.out.println(dateTime2); //2022-10-04T17:27
//3.getXxx():获取相关属性
System.out.println(dateTime1.getYear()); //2022
System.out.println(dateTime1.getMonthValue()); //10
System.out.println(dateTime1.getDayOfMonth()); //4
//体现不可变性
//4.withXxx():设置相关属性
System.out.println(dateTime1.withYear(2023)); //2023-10-04T17:36:53.914
//5.plusXxx():增加
System.out.println(dateTime1.plusYears(1)); //2023-10-04T17:36:53.914
//6.minusXxx():减少
System.out.println(dateTime1.minusYears(1)); //2021-10-04T17:36:53.914
}
}
4.3 Instant类
- 时间线上的一个瞬时点。类似于Date
- 自1970年1月1日0时0分0秒[UTC](北京时间1970年01月01日08时00分00秒)开始的秒数
- 精度可以达到纳秒级:1秒= 1000毫秒=1000*1000微秒=1000*1000*1000
/**
* Instant:
* 1.now:获取当前时间的实例。默认返回UTC时区
* 2.ofEpochMilli(Long):获取指定时间的实例
* 3.atOffset(ZoneOffset):根据时间偏移量创建OffsetDateTime
* 4.toEpochMilli:获取代表的毫秒数
*/
public class NewDateTimeTest {
@Test
public void test2(){
//1.获取当前时间的实例
Instant instant=Instant.now();
System.out.println(instant); //2022-10-04T09:58:01.344Z
//2.获取指定时间的实例
Instant instant1 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(5445454545L);
//3.根据时间偏移量创建OffsetDateTime
//东八区
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = instant.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));
System.out.println(offsetDateTime); //2022-10-04T17:58:01.344+08:00
//4.获取代表的毫秒数
System.out.println(instant.toEpochMilli()); //1664877481344
}
}
4.4 DateTimeFormatter
- 预定义的标准格式的格式化器
- 本地特定时间格式的格式化器
- 自定义的格式的格式化器
/**
* DateTimeFormatter:
* 方式一.ISO_LOCAL_Xxx、ISO_Xxx:预定义的标准格式的格式化器
* 方式二.ofLocalizedXxx:本地特定时间格式的格式化器
* 方式三.ofPattern(String):自定义的格式的格式化器
* 1.格式化:format(LocalDateTime)
* 2.解析:parse(String)
*/
public class NewDateTimeTest {
@Test
public void test3(){
//方式一:预定义的标准格式
DateTimeFormatter dtf1 = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;
//方式二.:本地特定时间格式的格式化器
DateTimeFormatter dtf2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.LONG);
DateTimeFormatter dtf3 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.SHORT);
DateTimeFormatter dtf4 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.MEDIUM);
//方式三:自定义格式的格式化器
DateTimeFormatter dtf5 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
//1.格式化
System.out.println(dtf1.format(LocalDateTime.now())); //2022-10-04T23:43:59.808
System.out.println(dtf2.format(LocalDateTime.now())); //2022年10月4日 下午11时43分59秒
System.out.println(dtf3.format(LocalDateTime.now())); //22-10-4 下午11:43
System.out.println(dtf4.format(LocalDateTime.now())); //2022-10-4 23:43:59
System.out.println(dtf5.format(LocalDateTime.now())); //2022-10-04 11:43:59
//2.解析
//{MinuteOfHour=43, NanoOfSecond=0, MicroOfSecond=0, HourOfAmPm=11, SecondOfMinute=59, MilliOfSecond=0},ISO resolved to 2022-10-04
System.out.println(dtf5.parse(dtf5.format(LocalDateTime.now())));
}
}
4.5 其它
- ZoneId:该类中包含了所有的时区信息,一个时区的ID,如Europe/Paris
- ZonedDateTime:带时区的日期时间(公历)
- 其中每个时区都对应着ID,地区ID都为“{区域}/{城市}”的格式,例如:Asia/Shanghai等
public class OthersTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
//1.ZoneId:类中包含了所有的时区信息
Set<String> zoneIds= ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds(); //获取所有的ZoneId
Object[] objects = zoneIds.toArray();
//[Asia/Aden, America/Cuiaba, Etc/GMT+9,...
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(objects));
//2.ZoneId的of():获取指定时区的时间
LocalDateTime localDateTime= LocalDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Tokyo"));
System.out.println(localDateTime); //2022-10-05T00:53:37.558
//3.ZonedDateTime:带时区的日期时间
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime= ZonedDateTime.now();//获取本时区的ZonedDateTime对象
System.out.println(zonedDateTime); //2022-10-04T23:53:37.605+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]
//4.获取指定时区的ZonedDateTime对象
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime1= ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Tokyo"));
System.out.println(zonedDateTime1);
}
}
- Clock:使用时区提供对当前即时、日期和时间的访问的时钟。
- Duration:时间日期间隔,以天、秒、纳秒为单位
- Period:日期间隔,以年、月、日衡量。只能计算LocalDate
public class OthersTest {
@Test
public void test2(){
//1.Duration:用于计算两个“时间日期”的间隔,以天、秒、纳秒为单位
LocalDateTime localDateTime1= LocalDateTime.of(2022, 10, 5, 8, 0, 0,1);
LocalDateTime localDateTime2= LocalDateTime.of(2022, 10, 6, 8, 0, 1,2);
Duration duration= Duration.between(localDateTime1, localDateTime2);
System.out.println(duration); //PT24H1.000000001S
System.out.println(duration.getSeconds()); //86401
System.out.println(duration.getNano()); //1
System.out.println(duration.toDays()); //1
//2.Period:用于计算两个“时间日期”的间隔,以年、月、日为单位
LocalDate localDate1= LocalDate.now();
LocalDate localDate2= LocalDate.of(2025, 11, 6);
Period period= Period.between(localDate1, localDate2);
System.out.println(period); //P3Y1M1D
System.out.println(period.getYears()); //3
System.out.println(period.getMonths()); //1
System.out.println(period.getDays()); //1
System.out.println(period.withYears(4)); //P4Y1M1D
}
}
- TemporalAdjuster : 时间校正器。有时我们可能需要获取例如:将日期调整到“下一个工作日”等操作。
- TemporalAdjusters : 该类通过静态方法(firstDayOfXxx()/lastDayOfXxx()/nextXxx())提供了大量的常用TemporalAdjuster 的实现。
五、Java比较器
5.1 Comparable自然排序
-
保证实现类的对象在任何位置都可以比较大小。
-
考虑定制排序:
- 没有实现 Comparable接口 且不方便修改代码
- 实现了 Comparable接口 的排序规则不适合当前的操作
/**
* 1.String、包装类等:实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(obj),实现了从小到大的排列
* 2.自定义类:实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(obj)的规则,
* - this > obj,return 正整数
* - this < obj,return 负整数
* - this = obj,return 0
*
*/
public class ComparableTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
//1.String、包装类等:实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(obj),实现了从小到大的排列
String[] strs={"ddd","cc","bbbb","rr","aaa"};
Arrays.sort(strs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strs)); //[aaa, bbbb, cc, ddd, rr]
}
@Test
public void test2(){
//2.自定义类:实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(obj)
Student[] stus=new Student[]{new Student("aa",6),new Student("cc",2),new Student("aa",3)};
Arrays.sort(stus);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(stus)); //[Student{name='aa', age=3}, Student{name='aa', age=6}, Student{name='cc', age=2}]
}
}
//2.自定义类:实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(obj)
class Student implements Comparable{
String name;
int age;
public Student() {}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if(o instanceof Student){
Student s= (Student) o;
int i = this.name.compareTo(s.name);
if(i==0){
return Integer.compare(this.age,s.age);
}
return i;
}
throw new RuntimeException("类型转换错误!");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
5.2 Comparator定制排序
- 属于临时性的比较。
/**
* 定制排序:属于临时性的比较
* - 没有实现 Comparable接口 且不方便修改代码时
* - 实现了 Comparable接口 的排序规则不适合当前的操作时
* 1.重写compare(Object o1,Object o2)方法:
* o1 > o2,return 正整数
* o1 < o2,return 负整数
* o1 = o2,return 0
*
*/
public class ComparatorTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
Student[] stus=new Student[]{new Student("aa",6),new Student("cc",2),new Student("aa",3)};
//1.重写compare(Object o1,Object o2)方法
Arrays.sort(stus, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1.age,o2.age);
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(stus)); //[Student{name='cc', age=2}, Student{name='aa', age=3}, Student{name='aa', age=6}]
}
}
六、System、Math、BigInteger与BigDecimal
6.1 System类
-
位于 java.lang 包。系统级的很多属性和控制方法都放置在该类的内部。
-
构造器私有,无法实例化该类。成员变量和成员方法都是 static 的,很方便进行调用
-
成员变量
- in:标准输入流(键盘输入)
- out:标准输出流(显示器)
- err:标准错误输出流(显示器)
-
成员方法
-
currentTimeMillis():返回当前计算机的GMT(格林威治)时间,1970年1月1号0时0分0秒所差的毫秒数
-
exit(int status):图形界面实现程序的退出功能。
-
status=0:正常退出
- status!=0:异常退出
-
-
gc():请求系统进行垃圾回收
- 是否立刻回收,取决于系统中垃圾回收算法的实现以及系统执行时的情况。
-
getProperty(String key):获得系统中属性名为key的属性对应的值。
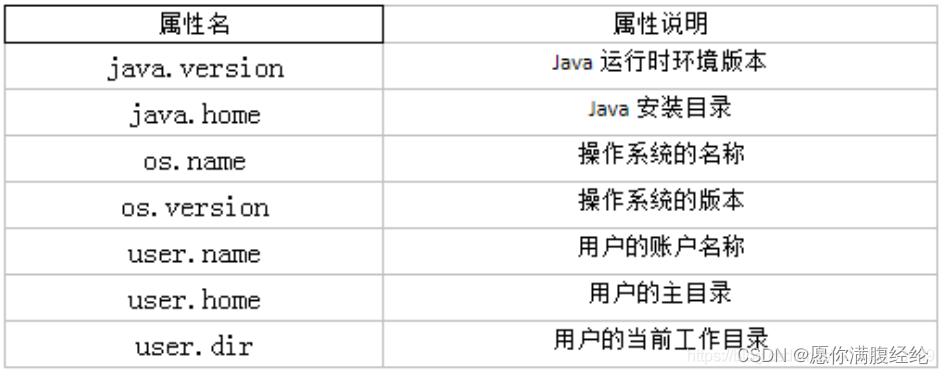
public class OtherTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
//1.java.version=1.8.0_333
System.out.println("java.version=" + System.getProperty("java.version"));
//2.java.home=F:Javajdk1.8.0_333jre
System.out.println("java.home=" + System.getProperty("java.home"));
//3.os.name=Windows 10
System.out.println("os.name=" + System.getProperty("os.name"));
//4.os.version=10.0
System.out.println("os.version=" + System.getProperty("os.version"));
//5.user.name=李泽伟
System.out.println("user.name=" + System.getProperty("user.name"));
//6.user.home=C:Users李泽伟
System.out.println("user.home=" + System.getProperty("user.home"));
//7.user.dir=F:IDEAJavaProjectsJavaseTestCommonClass_Demo
System.out.println("user.dir=" + System.getProperty("user.dir"));
}
}
6.2 Math类
java.lang.Math提供了一系列静态方法用于科学计算。其方法的参数和返回值类型一般为double型。
- abs:绝对值
- acos,asin,atan,cos,sin,tan:三角函数
- sqrt:平方根
- pow(double a,doble b):a的b次幂
- log:自然对数
- exp(double a):e为底数 ,a为对数,返回真数
- max(double a,double b)
- min(double a,double b)
- random():返回0.0到1.0的随机数
- long round(double a):double型数据a转换为long型(四舍五入)
- toDegrees(double angrad):弧度—>角度
- toRadians(double angdeg):角度—>弧度
6.3 BigInteger与BigDecimal
BigInteger
- Integer:最大整型值为 2^31 -1。Long:最大为 2^63 -1
- java.math.BigInteger:不可变的任意精度的整数。
- 提供所有Java 的基本整数操作符的对应物,并提供 java.lang.Math 的所有相关方法。
- 提供以下运算:模算术、GCD 计算、质数测试、素数生成、位操作…
- 构造器
- BigInteger(String val):根据字符串构建
BigInteger对象
- BigInteger(String val):根据字符串构建
- 常用方法

BigDecimal
- java.math.BigDecimal:在商业计算中,要求数字精度比较高
- java.math.BigDecimal:不可变的、任意精度的有符号十进制定点数。
- 构造器
public BigDecimal(double val)public BigDecimal(String val)
- 常用方法
- add(BigDecimal augend):相加
- subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend):相减
- multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand):相乘
- divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, int roundingMode):相除
public class OtherTest {
@Test
public void test2(){
//1.BigInteger
//Integer integer=5465465464321353437737357373867984213213; 编译不通过
BigInteger bi=new BigInteger("5465465464321353437737357373867984213213");
System.out.println(bi); //5465465464321353437737357373867984213213
//2.BigDecimal
BigDecimal bd1=new BigDecimal("56465.5454");
BigDecimal bd2=new BigDecimal("11");
System.out.println(bd1.divide(bd2,8,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP)); //5133.23140000
}
}
最后
以上就是难过硬币最近收集整理的关于【JavaSE】常用类:String、LocalDateTime......一、String二、可变字符序列三、日期时间-jdk8前四、日期时间-jdk8中五、Java比较器六、System、Math、BigInteger与BigDecimal的全部内容,更多相关【JavaSE】常用类:String、LocalDateTime内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。






![[java基础] 比较器.注解.枚举类java比较器枚举类注解](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg8.png)

发表评论 取消回复