前言
Redis作为应用最广泛的K-V数据库,包含了丰富的数据类型。这里所说的数据类型,其实是指V的数据类型。
Redis的数据类型大致分为以下几类:String、Hash、List、Set、Sorted Set、HyperLogLog、Geo。
本篇主要讲解前五种常用的数据类型,在讲解数据类型之前,先看一下Redis相关的帮助命令。学会使用这些命令,能够帮我们快速的了解Redis
前置命令
启动Redis客户端
./redis-cli
启动成功后,测试Redis是否可用
127.0.0.1:6379> ping
PONG
获取帮助
直接输入help指令,会出现如下提示
127.0.0.1:6379> help
redis-cli 5.0.8
To get help about Redis commands type:
"help @<group>" to get a list of commands in <group>
"help <command>" for help on <command>
"help <tab>" to get a list of possible help topics
"quit" to exit
To set redis-cli preferences:
":set hints" enable online hints
":set nohints" disable online hints
Set your preferences in ~/.redisclirc
根据提示可以知道输入help @<group>可以获取group中的命令列表。例如要查询一些通用命令,操作如下(仅列出部分命令)
127.0.0.1:6379> help @generic
DEL key [key ...]
summary: Delete a key
since: 1.0.0
DUMP key
summary: Return a serialized version of the value stored at the specified key.
since: 2.6.0
EXISTS key [key ...]
summary: Determine if a key exists
since: 1.0.0
EXPIRE key seconds
summary: Set a key's time to live in seconds
since: 1.0.0
......
如果不知道有哪些group,可以直接输入help @然后按tab键,就可以自动补全group的名称
输入help <command>可以直接获取对应命令的帮助,例如要获取keys指令的帮助,可以输入
127.0.0.1:6379> help keys
KEYS pattern
summary: Find all keys matching the given pattern
since: 1.0.0
group: generic
查看类型
使用命令
type key
可以查看key对应value的类型
127.0.0.1:6379> set hello world
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> type hello
string
数据类型
string
Redis的string类型是对外的类型,对内会根据不同的值采取不同的编码方式。普通的短字符串会用embstr的方式进行编码,如果是数值类型,会用int进行编码,如果是长字符串(44个字节为界),会采用raw的方式进行编码。
命令OBJECT可以查看Redis内部对数据的处理,例如查看数据的编码
127.0.0.1:6379> set xx abcd
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set yy 1234
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set zz abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklmnopqrs
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> type xx
string
127.0.0.1:6379> type yy
string
127.0.0.1:6379> type zz
string
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding xx
"embstr"
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding yy
"int"
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding zz
"raw"
根据执行结果可以看出xx、yy、zz的类型都是string,但是内部编码不一样。
string最Redis基本的数据类型,Redis没有直接使用C语言传统的字符串表示方法(以空字符结尾的字符数组),而是自己构建了简单动态字符串(Simple Dynamic string, SDS),并将SDS作为Redis默认字符串表示。string是二进制安全的,可以包含任意类型的数据,最大为512MB。定义的结构体如下:
struct sdshdr {
int len; // 记录buf数组大小
int free; // 记录buf数组还有多少可用空间
char buf[]; // 字符串实体,保存字符串的内容
};
因为有了对字符串长度定义len,所以在处理字符串时候不会以零值字节(�)为字符串结尾标志。
二进制安全就是输入任何字节都能正确处理,即使包含零值字节。
由于string类型的数据都是按照二进制存储的,所以Redis还提供了一些按位(bit)来操作string数据的命令,如下所示(仅列出与bit操作相关命令)
127.0.0.1:6379> help @string
BITCOUNT key [start end]
summary: Count set bits in a string
since: 2.6.0
BITFIELD key [GET type offset] [SET type offset value] [INCRBY type offset increment] [OVERFLOW WRAP|SAT|FAIL]
summary: Perform arbitrary bitfield integer operations on strings
since: 3.2.0
BITOP operation destkey key [key ...]
summary: Perform bitwise operations between strings
since: 2.6.0
BITPOS key bit [start] [end]
summary: Find first bit set or clear in a string
since: 2.8.7
GETBIT key offset
summary: Returns the bit value at offset in the string value stored at key
since: 2.2.0
SETBIT key offset value
summary: Sets or clears the bit at offset in the string value stored at key
since: 2.2.0
首先看下SETBIT命令,该命令的作用是给key对应的值的偏移(offset)设置一个bit的值,先来看下使用方式
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit hello 1 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> get hello
"@"
127.0.0.1:6379> strlen hello
(integer) 1
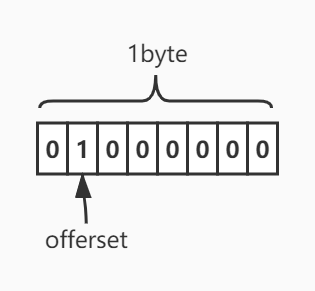
setbit hello 1 1命令就是在offerset为1的bit处,把值设置成1(因为是二进制,所以只能设置成0或者1)。01000000转换成10进制是64,64是ASCII码,对应的字符正是@符号(Linux命令man ascii可以查看ascii码表)
接着继续操作
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit hello 9 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit hello 14 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> get hello
"@B"
127.0.0.1:6379> strlen hello
(integer) 2

setbit hello 9 1
setbit hello 14 1
这两条命令分别在offerset为9和14的地方把值改成了1,由于超过了一个byte的位数,所以需要两个byte。两个byte分别代表ASCII值的64和66,也就是@和B。
理解了setbit,自然就理解了getbit,此处不再赘述。
再看下BITPOS命令,该命令描述如下
BITPOS key bit [start] [end]
summary: Find first bit set or clear in a string
since: 2.8.7
这个命令的作用是查找二进制的某个值(只能是0或者1),在[start, end]区间第一次出现的位置,这个start和end都是以字节为单位(比如[1, 2]是指在第二个字节和第三个字节中查找,从0开始计数),具体使用方式如下(继续上面的操作)
127.0.0.1:6379> bitpos hello 1 0 0
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> bitpos hello 1 1 1
(integer) 9
bitpos hello 1 0 0表示在hello这个key对应的value中的第0个字节到第0个字节(也就是只查找第0个字节)查找二进制数1。还是看这张图

第0个字节就是01000000,查找1所在的位置,偏移量就是1(从0开始)。而bitpos hello 1 1 1是在第1个字节中查找二进制1,偏移量就是9。
接着再看BITCOUNT命令,该命令描述如下
BITCOUNT key [start end]
summary: Count set bits in a string
since: 2.6.0
这个命令的作用就是统计某个key对应的value的指定字节范围内,二进制1出现的次数,start和end都是以字节(byte)为单位。具体使用如下(继续上面的操作)
127.0.0.1:6379> bitcount hello 0 0
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> bitcount hello 0 1
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> bitcount hello 1 1
(integer) 2

二进制1,在第0个字节出现了1次,在第0个和第1个字节出现了3次,在第1个字节出现了2次。所以结果分别是1、3、2。
以上几个关于bit操作的命令都是操作一个key的,接下来再看可以操作多个key的BITOP,该命令描述如下
BITOP operation destkey key [key ...]
summary: Perform bitwise operations between strings
since: 2.6.0
改命令的作用就是在多个key之间进行位运算
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit xx 1 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit xx 2 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit yy 1 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit yy 3 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> get xx
"`"
127.0.0.1:6379> get yy
"P"
127.0.0.1:6379> bitop and andkey xx yy
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> get andkey
"@"
127.0.0.1:6379> bitop or orkey xx yy
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> get orkey
"p"
首先根据前面关于SETBIT的知识可以知道,四条SETBIT命令执行完成后,xx和yy对应的值的二进制分别可以表示成如下形式
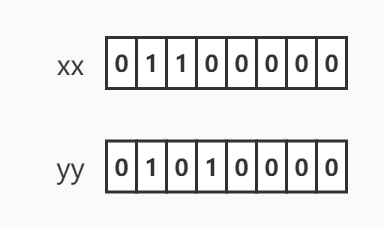
bitop and andkey xx yy命令会把这两个值进行按位与操作,并把结果赋值给andkey。
bitop or orkey xx yy命令会把这两个值进行按位或操作,并把结果赋值给orkey。
图解过程如下

根据图示可以知道addkey和orkey的值分别为01000000和01110000,转换成十进制分别是64和112。再根据ASCII码表就可以知道分别代表@和小写字母p。
list
list是有序可重复列表的意思,底层采用双向链表实现,结构如下

了解了内部结构,再来看list相关的命令就简单了。list相关的命令可以分为几类,利用这些命令,可以用list来实现栈(stack)、队列(queue)、阻塞队列(blocking queue)、数组(array)等结构
首先来实现栈
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush hello a b c d
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hello 0 -1
1) "d"
2) "c"
3) "b"
4) "a"
127.0.0.1:6379> lpop hello
"d"
127.0.0.1:6379> lpop hello
"c"
127.0.0.1:6379> lpop hello
"b"
127.0.0.1:6379> lpop hello
"a"
lpush hello a b c d表示向以hello为key的list中依次放入a、b、c、d四个元素。
lrange hello 0 -1表示打印出hello中的所有元素,0表示从第一个元素开始,-1表示最后一个元素。因为Redis是支持负索引的,-1表示最后一个元素,-2表示倒数第二个元素,依次类推。放入元素的顺序是a、b、c、d,四个元素均是从左边放入,相当于都是用的头插法。四个元素插入完成后,结构应该如图所示
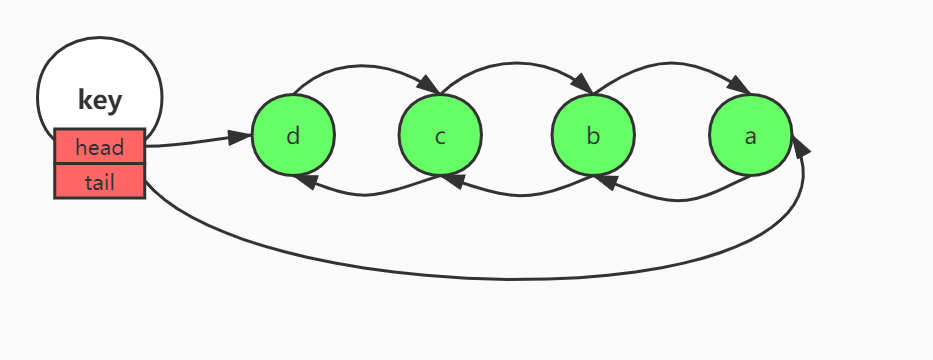
lpop hello表示弹出hello左边的第一个元素,所以弹出的顺序依次为d、c、b、a。因为插入的顺序是abcd,而弹出的顺序是dcba,这样就实现了栈(stack)的功能。利用rpush和rpop也是同理,不过rpush使用的是尾插法。
接下来实现队列(queue)的功能
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hello 0 -1
(empty list or set)
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush hello a b c d
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hello 0 -1
1) "d"
2) "c"
3) "b"
4) "a"
127.0.0.1:6379> rpop hello
"a"
127.0.0.1:6379> rpop hello
"b"
127.0.0.1:6379> rpop hello
"c"
127.0.0.1:6379> rpop hello
"d"
可以看到元素进入的顺序是abcd,弹出的顺序也是abcd。利用lpush和rpop就实现了类似队列先进先出(FIFO)的功能,同理利用rpush和lpop也能实现先进先出(FIFO)的功能。
另外,list还提供了三个阻塞式的命令
127.0.0.1:6379> help @list
BLPOP key [key ...] timeout
summary: Remove and get the first element in a list, or block until one is available
since: 2.0.0
BRPOP key [key ...] timeout
summary: Remove and get the last element in a list, or block until one is available
since: 2.0.0
BRPOPLPUSH source destination timeout
summary: Pop a value from a list, push it to another list and return it; or block until one is available
since: 2.2.0
操作和之前的命令一样,只是当没有可用元素时,会被阻塞。
除此之外,list还提供了一系列关于索引的操作
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hello 0 -1
(empty list or set)
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush hello a b c d
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hello 0 -1
1) "d"
2) "c"
3) "b"
4) "a"
127.0.0.1:6379> lindex hello 1
"c"
127.0.0.1:6379> lset hello 0 x
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hello 0 -1
1) "x"
2) "c"
3) "b"
4) "a"
127.0.0.1:6379> linsert hello after c y
(integer) 5
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hello 0 -1
1) "x"
2) "c"
3) "y"
4) "b"
5) "a"
127.0.0.1:6379> llen hello
(integer) 5
lindex hello 1查看下标为1的值
lset hello 0 x把下标为0的值改为x
linsert hello after c y在元素c的后面插入元素y
llen hello查看list的长度
除此之外,list还提供了删除命令lrem和ltrim
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush hello a b a c a b
(integer) 6
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hello 0 -1
1) "b"
2) "a"
3) "c"
4) "a"
5) "b"
6) "a"
127.0.0.1:6379> lrem hello 2 a
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hello 0 -1
1) "b"
2) "c"
3) "b"
4) "a"
127.0.0.1:6379> ltrim hello 1 -2
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange hello 0 -1
1) "c"
2) "b"
lrem hello 2 a是从左向右删除2个a元素
ltrim hello 1 -2是删除索引小于1或者索引大于-2的所有元素,即只保留中间部分,删除首尾数据。
hash
redis中的hash类型主要用来存储一些类似对象的结构,常用操作如下
127.0.0.1:6379> hset student name sicimike
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> hmset student id 1001 age 18
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> hget student id
"1001"
127.0.0.1:6379> hmget student name age
1) "sicimike"
2) "18"
hset指令用于往key对应的value(student对象)插入一个属性和值,hmset用于同时插入多个
hget用于获取student对象中的某个属性值,hmget表示同时获取多个
127.0.0.1:6379> hkeys student
1) "name"
2) "id"
3) "age"
127.0.0.1:6379> hvals student
1) "sicimike"
2) "1001"
3) "18"
127.0.0.1:6379> hgetall student
1) "name"
2) "sicimike"
3) "id"
4) "1001"
5) "age"
6) "18"
hkeys、hvals和hgetall分别表示获取student对象的所有属性名称、所有属性的值、所以属性名称和值。
127.0.0.1:6379> hincrby student age 2
(integer) 20
127.0.0.1:6379> hget student age
"20"
127.0.0.1:6379> hincrby student age -2
(integer) 18
127.0.0.1:6379> hget student age
"18"
hincrby用来给student对象的某个属性值加上指定的值,如果加上的是负数,相当于减法。
set
set是无序不重复的集合,和java集合中的Set差不多,常用操作如下
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key1 a b a c d
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS key1
1) "d"
2) "b"
3) "a"
4) "c"
sadd用于往集合中添加元素,支持同时添加多个
smembers用于返回集合中的所有元素
127.0.0.1:6379> srem key1 a c
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS key1
1) "d"
2) "b"
srem用于从集合中删除指定元素
以上的操作都是针对一个set集合的,下面是关于多个集合的求交集、并集、差集。
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key2 a b c d e
(integer) 5
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key3 c d e f g
(integer) 5
127.0.0.1:6379> SINTER key2 key3
1) "d"
2) "c"
3) "e"
127.0.0.1:6379> SINTERSTORE destkey key2 key3
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS destkey
1) "d"
2) "c"
3) "e"
127.0.0.1:6379> SUNION key2 key3
1) "b"
2) "c"
3) "g"
4) "e"
5) "d"
6) "a"
7) "f"
SINTER、SINTERSTORE两个指令都是求多个集合的交集,不同的是前者会把结果集直接返回给客户端,后者会把结果集存入指定的key。
SUNION是求多个集合的并集
127.0.0.1:6379> sdiff key2 key3
1) "a"
2) "b"
127.0.0.1:6379> sdiff key3 key2
1) "f"
2) "g"
sdiff命令用于求多个集合的差集,差集是有方向的,key的顺序就代表了方向。所以sdiff key2 key3和sdiff key3 key2结果不一样。
除了以上的命令,set还提供了两个获取随机元素的命令SRANDMEMBER和SPOP
先看SRANDMEMBER的命令描述
127.0.0.1:6379> help SRANDMEMBER
SRANDMEMBER key [count]
summary: Get one or multiple random members from a set
since: 1.0.0
group: set
命令的作用是从set中获取一个或多个随机元素,先来看下相关的操作
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key4 a b c d e f g
(integer) 7
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS key4
1) "b"
2) "c"
3) "g"
4) "e"
5) "a"
6) "d"
7) "f"
往set中放入7个元素。
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER key4 5
1) "c"
2) "g"
3) "d"
4) "a"
5) "f"
SRANDMEMBER key4 5表示从7个元素中随机取出5个,不允许重复。
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER key4 10
1) "e"
2) "g"
3) "b"
4) "c"
5) "d"
6) "a"
7) "f"
SRANDMEMBER key4 10表示从7个元素中取出10个,不允许重复。因为set中只有7个元素,所以结果只能取出7个。
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER key4 -5
1) "b"
2) "b"
3) "a"
4) "b"
5) "d"
SRANDMEMBER key4 -5表示从7个元素中随机取出5个,允许重复,也就说负数代表允许重复。
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER key4 -10
1) "c"
2) "d"
3) "f"
4) "e"
5) "d"
6) "f"
7) "b"
8) "c"
9) "b"
10) "f"
SRANDMEMBER key4 -10表示从7个元素中取出10个,允许重复。因为允许重复,所以可以取出10个。
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER key4 0
(empty list or set)
SRANDMEMBER key4 0表示从set中取出0个元素
再来看SPOP命令,先看SPOP的命令描述
127.0.0.1:6379> help spop
SPOP key [count]
summary: Remove and return one or multiple random members from a set
since: 1.0.0
group: set
SPOP命令可以从set中删除并返回一个或多个随机元素
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key4 a b c d e f g
(integer) 7
127.0.0.1:6379> spop key4
"b"
127.0.0.1:6379> spop key4 2
1) "f"
2) "c"
127.0.0.1:6379> spop key4 0
(empty list or set)
127.0.0.1:6379> spop key4 -2
(error) ERR index out of range
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS key4
1) "g"
2) "e"
3) "a"
4) "d"
从执行结果来看,确实可以删除并返回一个或多个随机元素,并且不支持负数。
sorted_set
除了无序不重复的集合set外,redis还提供了有序不重复的集合sorted_set。sorted_set在添加元素的时候,需要给每个元素设置一个score,这个数值的大小就是元素的排序的依据。下面是关于sorted_set的操作
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd key1 9 zhangsan 4 lisi 7 wangwu
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange key1 0 -1
1) "lisi"
2) "wangwu"
3) "zhangsan"
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange key1 0 -1 withscores
1) "lisi"
2) "4"
3) "wangwu"
4) "7"
5) "zhangsan"
6) "9"
zadd用于往sorted_set中添加元素
zrange key1 0 -1表示查看所有元素(按照score升序)
zrange key1 0 -1 withscores表示查看所有元素,并且显示对应的score
127.0.0.1:6379> ZREVRANGE key1 0 1
1) "zhangsan"
2) "wangwu"
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGEBYSCORE key1 7 9
1) "wangwu"
2) "zhangsan"
ZREVRANGE key1 0 1命令用于输出score最高的两个元素,是按照score降序的。因为ZREVRANGE是反向遍历的,且不会改变sorted_set的结构。
ZRANGEBYSCORE key1 7 9命令用于输出score大于等于7,且小于等于9的元素
127.0.0.1:6379> zscore key1 lisi
"4"
127.0.0.1:6379> zrank key1 lisi
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> ZINCRBY key1 2 lisi
"6"
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange key1 0 -1 withscores
1) "lisi"
2) "6"
3) "wangwu"
4) "7"
5) "zhangsan"
6) "9"
zscore命令获取元素的score
zrank命令获取元素的排名(score递增的排名)
ZINCRBY命令给某个元素的score加上指定的值。
以上的命令都是操作单个的sorted_set,除此之外redis还提供了操作多个sorted_set的命令ZUNIONSTORE,先看下命令描述
127.0.0.1:6379> help ZUNIONSTORE
ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key [key ...] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]
summary: Add multiple sorted sets and store the resulting sorted set in a new key
since: 2.0.0
group: sorted_set
这个命令就是给多个sorted_set求并集。set的并集很好理解,但是sorted_set涉及到score,求并集时应该怎么处理呢?先看具体的操作
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd key2 30 zhangsan 70 lisi 40 wangwu
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd key3 40 zhangsan 60 lisi 50 zhaoliu
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> ZUNIONSTORE destkey 2 key2 key3
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange destkey 0 -1 withscores
1) "wangwu"
2) "40"
3) "zhaoliu"
4) "50"
5) "zhangsan"
6) "70"
7) "lisi"
8) "130"
wangwu在key4中没有,zhaoliu在key3中没有,求并集之后会直接放入并集destkey中。对于两个集合都有的zhangsan和lisi,求并集之后,是把他们的score的和放入并集destkey中。
127.0.0.1:6379> ZUNIONSTORE destkey 2 key2 key3 weights 2 0.5 aggregate sum
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange destkey 0 -1 withscores
1) "zhaoliu"
2) "25"
3) "wangwu"
4) "80"
5) "zhangsan"
6) "80"
7) "lisi"
8) "170"
此处求交集,相比上一条命令,多个weights 2 0.5和aggregate sum。其中aggregate sum就是把两个集合中相同元素的score相加,只是第一条指令省略了aggregate sum。

该条命令的含义如图所示。
127.0.0.1:6379> ZUNIONSTORE destkey 2 key2 key3 aggregate min
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange destkey 0 -1 withscores
1) "zhangsan"
2) "30"
3) "wangwu"
4) "40"
5) "zhaoliu"
6) "50"
7) "lisi"
8) "60"
理解了上面那条指令,这条也就不难理解了,只是把score求和变成了取最小的score。
sorted_set常用于各种排行榜的实现,无论是排序还是查找sorted_set都非常高效。这种高效得益于底层的数据结构。
sorted_set底层采用跳表(skip list)实现。跳表插入、删除、查找操作的时间复杂度是O(logN)。跳表的基本结构如图所示
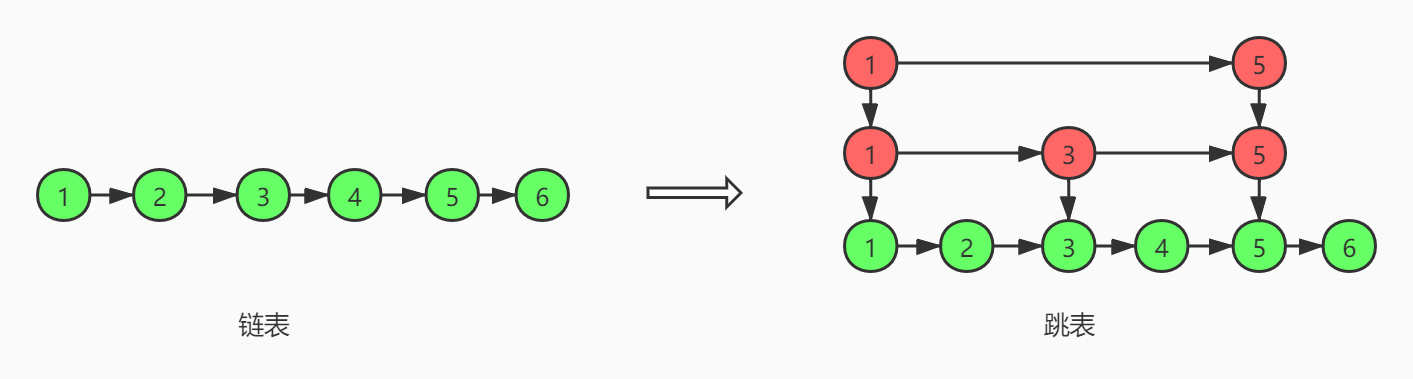
跳表的实现是基于有序链表,改进的地方在于跳表除了保存了原始的链表,还在链表上加了多层类似索引的结构。这样使得对链表的操作不需要一个节点一个节点的遍历。
总结
本篇主要讲解了redis五种常用的数据类型,以及部分类型的底层结构。理解redis数据类型,是用好redis的必要条件。
除了常用的五种类型外,redis还提供了hyperloglog和geo两种类型,分别用来做基数统计和地理信息相关的操作。
参考
- https://www.zhihu.com/question/28705562
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/53975333
最后
以上就是贤惠糖豆最近收集整理的关于Redis:数据类型的全部内容,更多相关Redis内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复