Java8时间与日期API
- API设计原因
- 时间日期常用类概述
- 创建方法(now)
- 生成自定义的日期时间对象(of)
- 为LocalDateTime添加时区信息
- ZoneId类
- 获取系统时区
- 获取其他时区的时间
- 关于Month枚举
- 根据现有时间进行时间推断(plus,minus)
- 采用period对plus方法设置自定义一段时间
- 直接修改日期(with)
- 调节器
- TemporalAdjusters实例
- DayOfWeek
- 自定义TemporalAdjuster调节器
- 日期查询TemporalQuery
- 实例
- 时间转换
- java.util.Date转LocalDate方法一
- java.util.Date转LocalDate方法二
- java.sql.Date转换LocalDate
- java.sql.Timestamp时间戳转换LocalDate
- Calendar转换ZonedDateTime
- Calendar直接转化LocalDateTime
- 日期解析与格式化DateTimeFormatter
- format格式化
- parse解析
- ofLocalizedDate格式化时区常用显示格式
- 自定义格式化
- 格式化参考表
API设计原因
在Java面世之初,标准库中就引入了两种用于处理日期和时间的类,但是由于很多问题,很多方法都已经弃用,在3avaSE 8中引入java.time包解决了长久以来存在的诸多弊端,java.time包基于Joda-Time库构件,是一种免费的开源解决方法,多年来一直作为处理]ava日其期和时间的事实标准
Java原本自带的java.util.Date和java.util.calendar类
但是这两个类:
- 有线程不安全的风险
- 使用繁杂
- 官方废弃
- 设计烂
故Date类和Calendar早早就被废弃
时间日期常用类概述
- Instant类
Instanit类对时间轴上的单一瞬时点建模,可以用于记录应用程序中的事件时间戳,在之后学习的类型转换中,均可以使用Instant类作为中间类完成转换. - Duration类
Duration类表示秒或纳秒时间间隔,适合处理较短的时间,需要更高的精确性 - Period类
period类表示一段时间的年、月、日 - LocalDate类
LocalDate是一个不可变的日期时间对象,表示日期,通常被视为年月日 - LocalTime类
LocalTime是一个不可变的日期时间对象,代表一个时间,通常被看作是小时-秒,时间表示为纳秒精度 - LocalDateTime类
LocalDateTime是一个不可变的日期时间对象,代表日期时间,通常被视为年-月-日-时-分-秒 - ZonedDateTime类
ZonedDateTime类具有时区的日期时间的不可变表示,此类储存所有日期时间字段,精度为纳秒,时区为区域偏移量,用于处理模糊的本地日期时间 - Year类:表示年
- YearMonth类:表示年月
- MonthDay类:表示月日
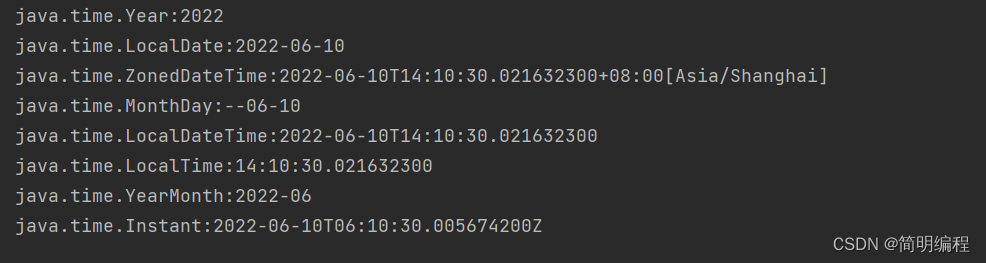
创建方法(now)
上述所有类都是线程安全的,并且这些类不提供公共构造函数,即无法用new直接创建而是要使用工厂法实例化
例:
package demo;
import java.time.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class TimeDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Instant now = Instant.now();
LocalDateTime now1 = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalTime now2 = LocalTime.now();
LocalDate now3 = LocalDate.now();
ZonedDateTime now4 = ZonedDateTime.now();
Year now5 = Year.now();
YearMonth now6 = YearMonth.now();
MonthDay now7 = MonthDay.now();
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(now.getClass().getName(),now.toString());
hashMap.put(now1.getClass().getName(),now1.toString());
hashMap.put(now2.getClass().getName(),now2.toString());
hashMap.put(now3.getClass().getName(),now3.toString());
hashMap.put(now4.getClass().getName(),now4.toString());
hashMap.put(now5.getClass().getName(),now5.toString());
hashMap.put(now6.getClass().getName(),now6.toString());
hashMap.put(now7.getClass().getName(),now7.toString());
hashMap.forEach((x,y)->{
System.out.println(x+":"+y);
});
}
}
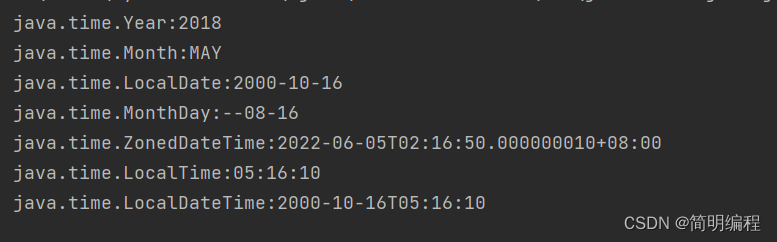
生成自定义的日期时间对象(of)
这里注意ZoneDateTime的of()方法最后传入的是一个ZoneId类的地区偏移量,写法如下:
ZonedDateTime.of(2022, 6, 5, 2, 16, 50,10,ZoneId.of(“+8”));
package demo;
import java.time.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class TimeDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate of = LocalDate.of(2000, 10, 16);
LocalTime of1 = LocalTime.of(5, 16, 10);
LocalDateTime of2 = LocalDateTime.of(of, of1);
Year of3 = Year.of(2018);
Month of4 = Month.of(5);
MonthDay of5 = MonthDay.of(8, 16);
ZonedDateTime of6 = ZonedDateTime.of(2022, 6, 5, 2, 16, 50,10,ZoneId.of("+8"));
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(of.getClass().getName(),of.toString());
hashMap.put(of1.getClass().getName(),of1.toString());
hashMap.put(of2.getClass().getName(),of2.toString());
hashMap.put(of3.getClass().getName(),of3.toString());
hashMap.put(of4.getClass().getName(),of4.toString());
hashMap.put(of5.getClass().getName(),of5.toString());
hashMap.put(of6.getClass().getName(),of6.toString());
hashMap.forEach((x,y)->{
System.out.println(x+":"+y);
});
}
}
为LocalDateTime添加时区信息
其实就是我们上面提到的ZoneId!
两种简单常用的方法
- 使用of自定义时区
- 使用systemDefault()设置当前时区
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class TimeDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//设置时间
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1);
//设置地区
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = localDateTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
System.out.println(zonedDateTime);
}
}
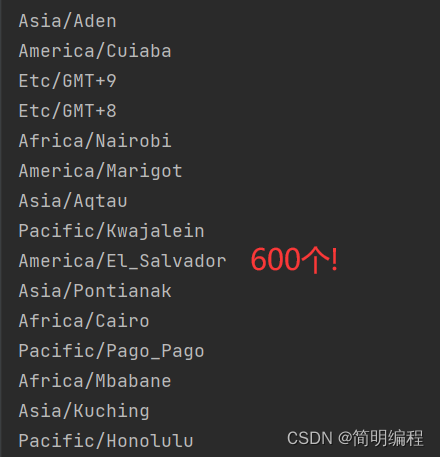
ZoneId类
用于获取时区信息,其中的getAvailableZoneIds()方法可以获取600个可用时区
package demo;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.Set;
public class TimeDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> availableZoneIds = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();
availableZoneIds.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
获取系统时区
package demo;
import java.time.ZoneId;
public class TimeDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault();
System.out.println(zoneId);
}
}

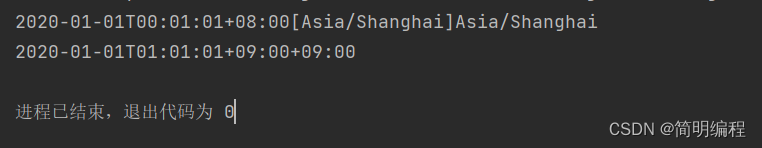
获取其他时区的时间
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class TimeDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//设置时间
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1);
//设置地区
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = localDateTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
System.out.println(zonedDateTime);
//设置时区获取,也可以设置地点
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime1 = zonedDateTime.withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId.of("+9"));
System.out.println(zonedDateTime1+""+zonedDateTime1.getZone());
}
}
关于Month枚举
在初始化LocalDate和LocalDateTime对象时使用月份枚举传入,这样更不易出错!更简单!!
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.Month;
public class TimeDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
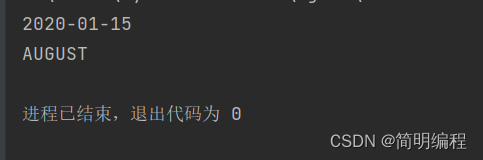
LocalDate of = LocalDate.of(2020, Month.JANUARY, 15);
System.out.println(of);
//验证
Month of1 = Month.of(8);
System.out.println(of1);
}
}
根据现有时间进行时间推断(plus,minus)
可选方法:(minus:- , plus: +)
- plusDays(1);
- plusMonths(1);
- plusWeeks(1);
- plusYears(1);
- plusNanos() : 在涉及纳秒级别的类中有
当然minus也一样
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.Month;
import java.time.MonthDay;
import java.time.Year;
public class TimeDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
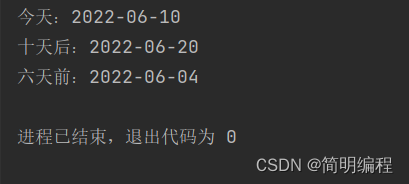
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate localDate = now.plusDays(10);
LocalDate localDate1 = now.minusDays(6);
System.out.println("今天:"+now);
System.out.println("十天后:"+localDate);
System.out.println("六天前:"+localDate1);
}
}
采用period对plus方法设置自定义一段时间
如下:获取2年1个月16天后的时间
plus的另一个重载则是以ChronoUnit枚举方式对事件进行计算
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.Period;
public class TimeDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
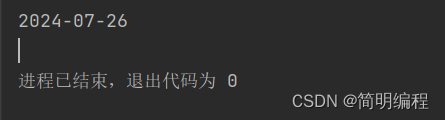
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
//采用period
Period of = Period.of(2, 1, 16);
LocalDate plus = now.plus(of);
System.out.println(plus);
}
}
直接修改日期(with)
对时间直接进行修改,其中with()类似plus()
其中with(TemporalAdjuster adjuster)下有多个实现类,如下:
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.Period;
public class TimeDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate localDate = now.withDayOfMonth(16);
LocalDate localDate1 = now.withMonth(5);
LocalDate localDate2 = now.withYear(2021);
LocalDate of = LocalDate.of(2000, 10, 13);
LocalDate with = now.with(of);
System.out.println(now);
System.out.println(localDate);
System.out.println(localDate1);
System.out.println(localDate2);
System.out.println(with);
}
}
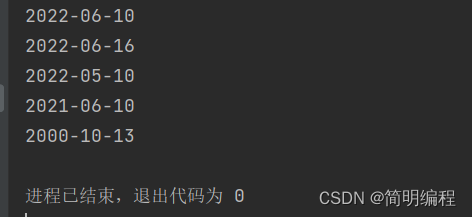
调节器
TemporalAdjusters实例
其中有很多方法如下:
- firstDayOfMonth():本月第一天
- lastDayOfMonth():本月最后一天
- firstDayOfNextMonth():下个月第一天
- firstDayOfYear():本年第一天
- lastDayOfYear():本年最后一天
- firstDayOfNextYear():下一年第一天
- firstInMonth(DayOfWeek dayOfWeek):第一个月的第N天
- 等
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjusters;
public class TimeDemo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
//本月最后一天
LocalDate with = now.with(TemporalAdjusters.lastDayOfMonth());
System.out.println(with);
}
}

DayOfWeek
本类是个枚举,封装了周一到周日
那么在哪里可以用到呢?
其实就在上面的TemporalAdjusters中搭配previous和next方法使用
注意:这里previous虽然说是上周但是实际得出的是本周
package demo;
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjusters;
public class TimeDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
//上一个周1
LocalDate with = now.with(TemporalAdjusters.previous(DayOfWeek.MONDAY));
//下一个周五
LocalDate with1 = now.with(TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.FRIDAY));
System.out.println(with);
System.out.println(with1);
}
}
自定义TemporalAdjuster调节器
从源码中看出,TemporalAdjuster是个函数式接口,仅有:
Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal);
由这个接口可以看出Temporal是所有日期时间类的总接口之一
并且我们可以使用from方法进行转换
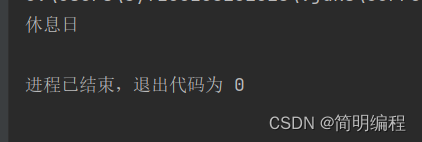
需求: 获取当前日期,判断是否是周末,不是则输出工作日,是则休息日
package demo;
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.MonthDay;
import java.time.temporal.Temporal;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class SelfDefineTimeAdjuster implements TemporalAdjuster {
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
//获取当前日期,判断是否是周末,不是则输出工作日,是则休息日
LocalDate now = LocalDate.from(temporal);
// LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
DayOfWeek from = DayOfWeek.from(now);
if (from.getValue() <= 5) {
System.out.println("工作日");
} else {
System.out.println("休息日");
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
SelfDefineTimeAdjuster self = new SelfDefineTimeAdjuster();
self.adjustInto(now);
}
}
日期查询TemporalQuery
TemporalQuery接口同样是个函数式接口,下设R queryFrom(TemporalAccessor temporal);方法
其中TemporalAccessor是Temporal的父接口
实例
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAccessor;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalQuery;
public class SelfTimeQuery implements TemporalQuery<Long> {
@Override
public Long queryFrom(TemporalAccessor temporal) {
//查询国庆节是否到了,返回差值
LocalDate now = LocalDate.from(temporal);
LocalDate festival = LocalDate.of(now.getYear(), 10, 1);
//使用ChronoUnit进行计算
long between = ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(now, festival);
return between;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SelfTimeQuery selfTimeQuery = new SelfTimeQuery();
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
Long aLong = selfTimeQuery.queryFrom(now);
System.out.println(aLong);
}
}

时间转换
java.util.Date转LocalDate方法一
我们常使用Instant类和ZoneDateTime类帮助进行转换
package demo;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.util.Date;
public class TimeDemo13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();
Instant instant = date.toInstant();
//使用instant类中的atZone添加时区信息
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = instant.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
//通过ZoneDateTime的toLocalDate进行转化
LocalDate localDate = zonedDateTime.toLocalDate();
System.out.println(localDate.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(localDate);
}
}
java.util.Date转LocalDate方法二
第二种方法就是应用java.sql.Date类帮助 java.util.Date进行转化 ,应用getTime()方法直接转为毫秒值让sql.Date接收
java.sql.Date转换LocalDate
可以使用其自带的.toLocalDate()方法进行直接转换
package demo;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class TimeDemo14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
LocalDate localDate = date.toLocalDate();
System.out.println(localDate);
System.out.println(localDate.getClass().getName());
}
}
java.sql.Timestamp时间戳转换LocalDate
其实Timestamp无法直接转化LocalDate而是可以直接转化为LocalDateTime使用其toLocalDateTime()方法即可
借助LocalDateTime帮助进行再转化就可以转换为LocalDate
package demo;
import java.sql.Timestamp;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class TimeDemo15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timestamp timestamp = new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
LocalDateTime localDateTime = timestamp.toLocalDateTime();
LocalDate localDate = localDateTime.toLocalDate();
System.out.println(localDate);
}
}
Calendar转换ZonedDateTime
通过ZonedDateTime.ofInstant()方法进行转化
步骤:
- 获取时区
- 获取ZoneId
- 获取instant
- 传入ZoneId和instant到ofInstant()方法
package demo;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.TimeZone;
public class TimeDemo16 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar instance = Calendar.getInstance();
//获取时区
TimeZone timeZone = instance.getTimeZone();
//获取ZoneId
ZoneId zoneId = timeZone.toZoneId();
//获取instant
Instant instant = instance.toInstant();
//转换
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.ofInstant(instant, zoneId);
System.out.println(zonedDateTime.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(zonedDateTime);
}
}
Calendar直接转化LocalDateTime
package demo;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class TimeDemo17 {
//注意month要加1
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar instance = Calendar.getInstance();
int year = instance.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = instance.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1;
int day = instance.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
int hour = instance.get(Calendar.HOUR);
int min = instance.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
int sec = instance.get(Calendar.SECOND);
LocalDateTime of = LocalDateTime.of(year, month, day, hour, min, sec);
System.out.println(of);
}
}
日期解析与格式化DateTimeFormatter
SimpleDateFormat类是线程不安全的,所以Java8出现了新的格式化类
DateTimeFormatter
并且其不需要创建转换器对象而是直接使用后parse和format方法
format格式化
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class TimeDemo18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
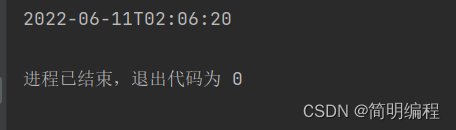
String format = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE);
String format1 = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
String format2 = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_TIME);
System.out.println(format);
System.out.println(format1);
System.out.println(format2);
}
}
parse解析
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
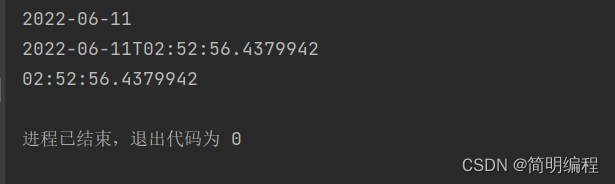
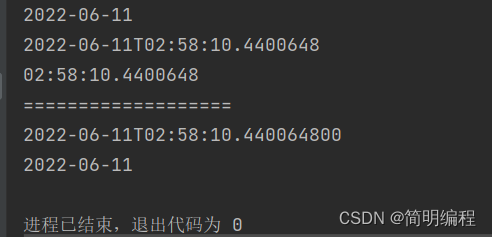
public class TimeDemo18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
String format = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE);
String format1 = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
String format2 = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_TIME);
System.out.println(format);
System.out.println(format1);
System.out.println(format2);
System.out.println("===================");
LocalDateTime parse = LocalDateTime.parse(format1);
LocalDate parse1 = LocalDate.parse(format);
System.out.println(parse);
System.out.println(parse1);
}
}
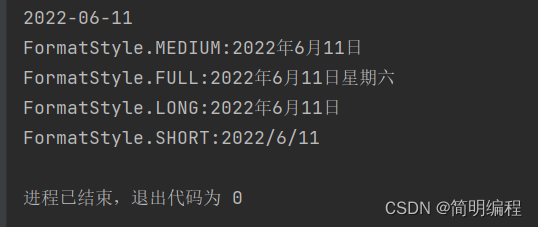
ofLocalizedDate格式化时区常用显示格式
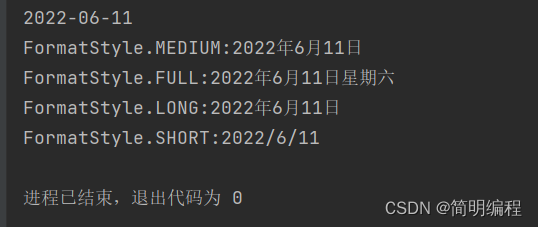
该方法DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.MEDIUM)参数为FormatStyle枚举类包含四个属性:
- FULL
- LONG
- MEDIUM
- SHORT
实例如下:
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.format.FormatStyle;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class TimeDemo19 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
String format = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE);
String format2 = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.MEDIUM));
String format1 = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.FULL));
String format3 = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.LONG));
String format4 = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.SHORT));
HashMap<String, String> data = new HashMap<>();
data.put("FormatStyle.FULL",format1);
data.put("FormatStyle.MEDIUM",format2);
data.put("FormatStyle.LONG",format3);
data.put("FormatStyle.SHORT",format4);
System.out.println(format);
data.forEach((x,y)->{
System.out.println(x+":"+y);
});
}
}
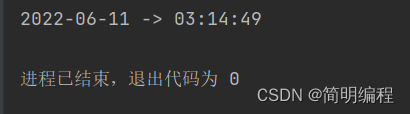
自定义格式化
使用DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern方法进行自定义格式化方式
package demo;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class SelfTimeFormat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
//使用DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern方法进行自定义格式化方式
String format = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd -> HH:mm:ss"));
System.out.println(format);
}
}
格式化参考表
格式化字符:
| 字母 | 日期或时间元素 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| G | Era 标识符 | Text |
| y | 年 | Year |
| M | 年中的月份 | Month |
| w | 年中的周数 | Number |
| W | 月中的周数 | Number |
| D | 年中的天数 | Number |
| d | 月份中的天数 | Number |
| F | 月份中的星期 | Number |
| E | 星期中的天数 | Text |
| a | AM,PM标记 | Text |
| H | 一天中的小时数(0~23) | Number |
| h | AM,PM中的小时数(1~12) | Number |
| k | 一天中的小时数(1~24) | Number |
| K | AM,PM中的小时数 (0~11) | Number |
| m | 小时中的分钟数 | Number |
| s | 分钟中的秒数 | Number |
| S | 毫秒数 | Number |
| z | 时区 | General time zone |
| Z | 时区 | RFC 822 time zone |
常用时间格式:
| 日期时间 | 对应的格式 |
|---|---|
| 2021/01/01 | yyyy/MM/dd |
| 2021.01.01 | yyyy.MM.dd |
| 2021-01-01 01:01:01 | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss |
| 2021年01月01日 01时01分01秒 星期一 | yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒 EEEE |
| 下午3时 | ah时 |
| 今年已过去了1天 | 今年已过去了D天 |
最后
以上就是无限香烟最近收集整理的关于Java8时间与日期API(别再使用Date和Calendar了)API设计原因时间日期常用类概述创建方法(now)生成自定义的日期时间对象(of)关于Month枚举根据现有时间进行时间推断(plus,minus)直接修改日期(with)调节器日期查询TemporalQuery时间转换日期解析与格式化DateTimeFormatter的全部内容,更多相关Java8时间与日期API(别再使用Date和Calendar了)API设计原因时间日期常用类概述创建方法(now)生成自定义内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复