Android-图片加载Gilde
- Android-图片加载Gilde
- 介绍
- 活动缓存
- 内存缓存
- 三和四:磁盘缓存
- 简单使用
- 源码浅析
- Glide.with(context)方法
- with方法调用的小结
- RequestManager.load(url)方法
- load(url)方法的小结
- RequestBuilder.apply()方法
- RequestBuilder.into()方法
- into()方法小结
- 来看看这个LruCache
- 磁盘缓存
- 生命周期
- RequestManagerRetriever类中
- ActivityFragmentLifecycle
- LifecycleListener 接口
- RequestManager
- requestTracker.clearRequests()
- 小结
- 流程图
Android-图片加载Gilde
Gilde-github
介绍
Glide会在开始一个新的图片请求之前检查多级缓存;
调用into之后,会依次按这个顺序查找:
1、活动缓存(Active Resources):如果当前对应的图片资源正在使用,则这个图片会被Glide放入活动缓存。
2、内存缓存(Memory Cache):如果图片最近被加载过,并且当前没有使用这个图片,则会被放入内存中
3、资源类型(Resoures Disk Cache):被解码后的图片写入磁盘文件中,解码的过程可能修改了图片的参数(如:inSampleSize、inPreferredConfig)
4、原始缓存(Data Disk Cache):图片原始数据在磁盘中的缓存(从网络、文件中直接获得的原始数据)
活动缓存
当需要加载某张图片能够从内存缓存中获得的时候,在图片加载时主动将对应图片从内存缓存中移除,加入到活动资源中;
活动资源中是一个”引用计数"的图片资源的弱引用集合。
因为同一张图片可能在多个地方被同时使用,每一次使用都会将引用计数+1,而当引用计数为0时候,则表示这个图片没有被使用也就是没有强引用了。这样则会将图片从活动资源中移除,并加入内存缓存。
内存缓存
内存缓存默认使用LRU(缓存淘汰算法/最近最少使用算法),当资源从活动资源移除的时候,会加入此缓存。使用图片的时候会主动从此缓存移除,加入活动资源。
LRU缓存:就是一个个的节点用双向链表缓存起来,原队列大小已满,如果要新加,那么就会把最后一个(最近最少使用)删了,把新加的放在最前面(链表的头部),如果需要使用的在里面存在,那么就把那个放到最前面。
三和四:磁盘缓存
Resource 缓存的是经过解码后的图片,如果再使用就不需要再去进行解码配置(BitmapFactory.Options),加快获得图片速度。比如原图是一个100x100的ARGB_8888图片,在首次使用的时候需要的是50x50的RGB_565图片,那么Resource将50x50 RGB_565缓存下来,再次使用此图片的时候就可以从 Resource 获得。不需要去计算inSampleSize(缩放因子)。
Data 缓存的则是图像原始数据。
简单使用
1、导入依赖
implementation 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:4.9.0'
annotationProcessor 'com.github.bumptech.glide:compiler:4.9.0'
2、代码中使用
String url = "https://smh5api.suandashi.cn/image/52445a94-300c-4532-927e-bcd80c033da7.jpg";
RequestOptions options = new RequestOptions()
.circleCrop();
Glide.with(MainActivity.this)
.load(url)
.apply(options)
.into(new DrawableImageViewTarget(imageView) {
@Override
public void onResourceReady(@NonNull Drawable resource, @Nullable Transition<? super Drawable> transition) {
super.onResourceReady(resource, transition);
}
});
Glide.with(MainActivity.this)
.load(url)
.apply(options)
.into(imageView);
源码浅析
Glide.with(context)方法
一步步的跟进到Glide类中的get方法;
单例的方式去创建了唯一的Glide对象,调用checkAndInitializeGlide方法中的initializeGlide方法去创建对象
在initializeGilde方法中调用了builder(GlideBuilder).build(applicationContext)方法构建出的局部变量Gilde对象,最终赋值到全局静态的Gilde对象中, Glide.glide = glide;
RequestManagerRetriever: 这个对象通过Glide.get(context).getRequestManagerRetriever()的调用获取到;
通过这个RequestManagerRetriever对象调用了get方法获取到了一个RequestManager 对象;
RequestManager的作用主要是用来与Fragment的生命周期绑定;
public class Glide implements ComponentCallbacks2 {
private static volatile Glide glide;
private final RequestManagerRetriever requestManagerRetriever;
......
@NonNull
public static RequestManager with(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity) {
//通过调用RequestManagerRetriever 对象的get方法返回了一个RequestManager 对象
return getRetriever(activity).get(activity);
}
......
@NonNull
public RequestManagerRetriever getRequestManagerRetriever() {
return requestManagerRetriever;
}
......
@NonNull
private static RequestManagerRetriever getRetriever(@Nullable Context context) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(context, "You cannot start a load on a not yet attached View or a Fragment where getActivity() returns null (which usually occurs when getActivity() is called before the Fragment is attached or after the Fragment is destroyed).");
//返回了一个RequestManagerRetriever 对象
return Glide.get(context).getRequestManagerRetriever();
}
......
//单例模式创建了Glide对象
@NonNull
public static Glide get(@NonNull Context context) {
if (glide == null) {
Class var1 = Glide.class;
synchronized(Glide.class) {
if (glide == null) {
//这里做初始化工作,初始化Glide对象
checkAndInitializeGlide(context);
}
}
}
return glide;
}
......
private static void checkAndInitializeGlide(@NonNull Context context) {
if (isInitializing) {
throw new IllegalStateException("You cannot call Glide.get() in registerComponents(), use the provided Glide instance instead");
} else {
isInitializing = true;
initializeGlide(context);
isInitializing = false;
}
}
......
private static void initializeGlide(@NonNull Context context) {
initializeGlide(context, new GlideBuilder());
}
private static void initializeGlide(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull GlideBuilder builder) {
//获取到Application中的上下文
Context applicationContext = context.getApplicationContext();
......
//通过GlideBuilder 对象的build方法构建出Glide对象
Glide glide = builder.build(applicationContext);
......
//在这里赋值个了全局中的静态的gilde对象身上
Glide.glide = glide;
}
}
一起来看看这个构建GlideBuilder.build方法
在这个方法中,初始化了各种对象,关于缓存的:内存大小计算的对象、LruBitmapPool(复用池)、LruResourceCache(Lru的内存缓存)、InternalCacheDiskCacheFactory(磁盘缓存)等等
看到里面的一些对象的初始化,大概就知道是创建出了最大的一些缓存和复用池
public final class GlideBuilder {
......
//磁盘缓存
private DiskCache.Factory diskCacheFactory;
//复用池
private BitmapPool bitmapPool;
//内存缓存
private MemoryCache memoryCache;
//计算内存大小的对象
private MemorySizeCalculator memorySizeCalculator;
private final ArrayPool arrayPool;
......
......
@NonNull
Glide build(@NonNull Context context) {
if (sourceExecutor == null) {
sourceExecutor = GlideExecutor.newSourceExecutor();
}
if (diskCacheExecutor == null) {
diskCacheExecutor = GlideExecutor.newDiskCacheExecutor();
}
if (animationExecutor == null) {
animationExecutor = GlideExecutor.newAnimationExecutor();
}
//内存大小的计算
if (memorySizeCalculator == null) {
memorySizeCalculator = new MemorySizeCalculator.Builder(context).build();
}
if (connectivityMonitorFactory == null) {
connectivityMonitorFactory = new DefaultConnectivityMonitorFactory();
}
//Bitmap复用池
if (bitmapPool == null) {
int size = memorySizeCalculator.getBitmapPoolSize();
if (size > 0) {
bitmapPool = new LruBitmapPool(size);
} else {
bitmapPool = new BitmapPoolAdapter();
}
}
//数组复用池
if (arrayPool == null) {
arrayPool = new LruArrayPool(memorySizeCalculator.getArrayPoolSizeInBytes());
}
//内存缓存
if (memoryCache == null) {
memoryCache = new LruResourceCache(memorySizeCalculator.getMemoryCacheSize());
}
//磁盘缓存
if (diskCacheFactory == null) {
diskCacheFactory = new InternalCacheDiskCacheFactory(context);
}
if (engine == null) {
engine =
new Engine(
memoryCache,
diskCacheFactory,
diskCacheExecutor,
sourceExecutor,
GlideExecutor.newUnlimitedSourceExecutor(),
GlideExecutor.newAnimationExecutor(),
isActiveResourceRetentionAllowed);
}
if (defaultRequestListeners == null) {
defaultRequestListeners = Collections.emptyList();
} else {
defaultRequestListeners = Collections.unmodifiableList(defaultRequestListeners);
}
RequestManagerRetriever requestManagerRetriever =
new RequestManagerRetriever(requestManagerFactory);
//最终用这些缓存的对象去new了一个Glide对象返回出去了
return new Glide(
context,
engine,
memoryCache,
bitmapPool,
arrayPool,
requestManagerRetriever,
connectivityMonitorFactory,
logLevel,
defaultRequestOptions.lock(),
defaultTransitionOptions,
defaultRequestListeners,
isLoggingRequestOriginsEnabled);
}
......
}
RequestManagerRetriever 类中调用get方法后,相关联调用的方法
RequestManagerRetriever实现了Handler.Callback接口,在构造方法中,通过主线程的Looper对象去创建了一个主线程的handler,然后将回调传入的是this,也就是说handler的消息处理都会在自己实现的handlerMessage回调方法中;
通过getSupportFragmentManager得到了一个FragmentManager;
然后在supportFragmentGet方法中通过getSupportRequestManagerFragment方法的调用,获取到一个SupportRequestManagerFragment,值得一提的就是第一次进来的时候,fragmentManage中不存在,回去从缓存Map中去取,如果还没有就会去new一个;
new的时候,在这个Fragment的构造方法中,会new出一个Lifecycle,这个应该不陌生吧?生命周期绑定回调的;
然后将创建出来的fragment存入到了缓存的Map中,添加事务后给handler发了一条what为2的消息,在handler中将这个fragment从缓存的map中移除掉,然后将这个fragment返回出去;
得到这个fragment之后,通过fragment获取RequestManager对象,如果没有获取到才会通过RequestManagerFactory工厂build出RequestManager对象,并存入到fragment当中,最后返回出去;
看到这也就是走完了Glide.with(context)这个方法的调用
最终得到的RequestManager对象:是一个请求管理类,包含生命周期的回调;
public class RequestManagerRetriever implements Handler.Callback {
final Map<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager, SupportRequestManagerFragment> pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments = new HashMap();
private final Handler handler;
public RequestManagerRetriever(@Nullable RequestManagerFactory factory) {
this.factory = factory != null ? factory : DEFAULT_FACTORY;
//Handler的创建吧?传入的回调是this吧? 也就是说后面handler处理消息都会在内部的handlerMessage中吧?
//注意这类创建Handler的时候,是用的主线程的Looper对象,也就是说不管是不是在子线程中new的这个类对象,最终Hanlder的消息处理都是在主线程中
handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper(), this /* Callback */);
}
......
@NonNull
public RequestManager get(@NonNull Context context) {
if (context == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You cannot start a load on a null Context");
} else if (Util.isOnMainThread() && !(context instanceof Application)) {
if (context instanceof FragmentActivity) {
return get((FragmentActivity) context);
} else if (context instanceof Activity) {
return get((Activity) context);
} else if (context instanceof ContextWrapper) {
return get(((ContextWrapper) context).getBaseContext());
}
}
return getApplicationManager(context);
}
......
@NonNull
public RequestManager get(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity) {
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
return get(activity.getApplicationContext());
} else {
//盘点当前activity是否已经销毁了
assertNotDestroyed(activity);
//创建了FragmentManager
FragmentManager fm = activity.getSupportFragmentManager();
return supportFragmentGet(
activity, fm, /*parentHint=*/ null, isActivityVisible(activity));
}
}
......
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR1)
private static void assertNotDestroyed(@NonNull Activity activity) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR1 && activity.isDestroyed()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You cannot start a load for a destroyed activity");
}
}
......
@Deprecated
@NonNull
private RequestManager fragmentGet(@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull android.app.FragmentManager fm,
@Nullable android.app.Fragment parentHint,
boolean isParentVisible) {
RequestManagerFragment current = getRequestManagerFragment(fm, parentHint, isParentVisible);
RequestManager requestManager = current.getRequestManager();
if (requestManager == null) {
// TODO(b/27524013): Factor out this Glide.get() call.
Glide glide = Glide.get(context);
requestManager =
factory.build(
glide, current.getGlideLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode(), context);
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);
}
return requestManager;
}
......
@NonNull
private RequestManager supportFragmentGet(
@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull FragmentManager fm,
@Nullable Fragment parentHint,
boolean isParentVisible) {
//创建出Fragment
SupportRequestManagerFragment current =
getSupportRequestManagerFragment(fm, parentHint, isParentVisible);
RequestManager requestManager = current.getRequestManager();
if (requestManager == null) {
// TODO(b/27524013): Factor out this Glide.get() call.
Glide glide = Glide.get(context);
requestManager =
factory.build(
glide, current.getGlideLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode(), context);
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);
}
return requestManager;
}
......
//创建出Fragment
@NonNull
private SupportRequestManagerFragment getSupportRequestManagerFragment(
@NonNull final FragmentManager fm, @Nullable Fragment parentHint, boolean isParentVisible) {
//第一次进来的时候,从FragmentManager这里肯定是找不到这个Tag的fragment吧
SupportRequestManagerFragment current =
(SupportRequestManagerFragment) fm.findFragmentByTag(FRAGMENT_TAG);
if (current == null) {
//如果上面FragmentManager中没找到,就从缓存的Map中去找
current = pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments.get(fm);
if (current == null) {
//如果缓存的map中也没有的话,就直接new了一个出来
//注意这个fragment的构造方法中,new出来一个Lifecycle对象
current = new SupportRequestManagerFragment();
current.setParentFragmentHint(parentHint);
if (isParentVisible) {
//Lifecycle 这个不陌生吧?
//fragment创建好之后,立马就调用了onStart生命周期
current.getGlideLifecycle().onStart();
}
//存入到缓存的Map中
pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments.put(fm, current);
//添加事务
fm.beginTransaction().add(current, FRAGMENT_TAG).commitAllowingStateLoss();
//给handler发了个what为2的消息,最终进入到下面这个handleMessage中
//为什么是进入到下面这个handleMessage中?
//注意看这个Handler的创建,以及这个类实现的接口Handler.Callback
handler.obtainMessage(ID_REMOVE_SUPPORT_FRAGMENT_MANAGER, fm).sendToTarget();
}
}
return current;
}
......
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message message) {
boolean handled = true;
Object removed = null;
Object key = null;
switch (message.what) {
case ID_REMOVE_FRAGMENT_MANAGER:
android.app.FragmentManager fm = (android.app.FragmentManager) message.obj;
key = fm;
removed = pendingRequestManagerFragments.remove(fm);
break;
case ID_REMOVE_SUPPORT_FRAGMENT_MANAGER:
//最终在这个handler里面讲这个fragment从缓存的Map当中移除掉
FragmentManager supportFm = (FragmentManager) message.obj;
key = supportFm;
removed = pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments.remove(supportFm);
break;
default:
handled = false;
break;
}
if (handled && removed == null && Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.WARN)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to remove expected request manager fragment, manager: " + key);
}
return handled;
}
......
@NonNull
private RequestManager getApplicationManager(@NonNull Context context) {
// Either an application context or we're on a background thread.
if (applicationManager == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (applicationManager == null) {
// Normally pause/resume is taken care of by the fragment we add to the fragment or
// activity. However, in this case since the manager attached to the application will not
// receive lifecycle events, we must force the manager to start resumed using
// ApplicationLifecycle.
// TODO(b/27524013): Factor out this Glide.get() call.
Glide glide = Glide.get(context.getApplicationContext());
applicationManager =
factory.build(
glide,
new ApplicationLifecycle(),
new EmptyRequestManagerTreeNode(),
context.getApplicationContext());
}
}
}
return applicationManager;
}
......
}
with方法调用的小结
看到上面Glide的构建:
1、大概明白Glide.with()方法是获取Glide缓存的最大内存(用来存储图片)创建出内存缓存、磁盘缓存、复用池对象,最后new出来一个单例的Glide对象;并且创建出了一个RequestManagerRetriever对象,通过调用这个对象的get方法获取到一个RequestManager对象;
2、这个get方法的调用,第一次会创建出一个fragment,在fragment创建的构造方法中,会创建出这个Fragment的Lifecycle对象,用来和生命周期做绑定,创建完fragment后会添加到缓存Map中,然后添加事务,最后再通过handler将这个fragment从缓存Map中移除掉;
3、然后用这个创建出来的fragment获取RequestManager对象,如果没有获取到才会通过RequestManagerFactory工厂build出RequestManager对象,并存入到fragment当中,最后返回出去,也就是走完了Glide.with(context)这个方法的调用;
RequestManager:是一个请求管理类,包含生命周期的回调;
RequestManager.load(url)方法
load方法的调用最终会返回一个泛型的RequestBuilder对象
RequestBuilder这个是用来构建请求的对象;
可以看到这个load方法,有很多重载的方法,处理各种不同的参数请求;
最终是调用到RequestBuilder这个类中的load方法,
public class RequestManager implements LifecycleListener,
ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<Drawable>> {
......
@NonNull
@CheckResult
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> asDrawable() {
return as(Drawable.class);
}
......
@NonNull
@CheckResult
public <ResourceType> RequestBuilder<ResourceType> as(
@NonNull Class<ResourceType> resourceClass) {
return new RequestBuilder<>(glide, this, resourceClass, context);
}
......
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable Bitmap bitmap) {
return asDrawable().load(bitmap);
}
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable Drawable drawable) {
return asDrawable().load(drawable);
}
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable String string) {
return asDrawable().load(string);
}
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable Uri uri) {
return asDrawable().load(uri);
}
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable File file) {
return asDrawable().load(file);
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@RawRes @DrawableRes @Nullable Integer resourceId) {
return asDrawable().load(resourceId);
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@CheckResult
@Override
@Deprecated
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable URL url) {
return asDrawable().load(url);
}
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable byte[] model) {
return asDrawable().load(model);
}
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable Object model) {
return asDrawable().load(model);
}
......
}
来看看这个RequestBuilder类里面的load方法
这个RequestBuilder类里面也有很多load的重载方法,我这里就不全贴出来了;
这里这么多重载,是因为有很多中请求图片的方式吧?
比如:网址、文件、Uri等等;
重载方法最终是调用到loadGeneric方法,这里我理解为这个RequestBuilder对象中存放标识请求方式(model);
大致知道这里RequestManager.load(url)方法调用后会得到一个RequestBuilder对象;
public class RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> extends BaseRequestOptions<RequestBuilder<TranscodeType>>
implements Cloneable,
ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<TranscodeType>> {
......
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable String string) {
return asDrawable().load(string);
}
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable Uri uri) {
return asDrawable().load(uri);
}
@NonNull
@Override
@CheckResult
public RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> load(@Nullable String string) {
return loadGeneric(string);
}
//将RequestBuilder类中的model(请求方式)保存起来;
@NonNull
private RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> loadGeneric(@Nullable Object model) {
this.model = model;
isModelSet = true;
return this;
}
......
}
load(url)方法的小结
load方法的调用,各种不同请求方式的重载,最终是调用到RequestBuilder类中的loadGeneric方法,然后将请求方式复制到RequestBuilder对象身上的全局变量model中,然后将这个RequestBuilder对象返回出去;
RequestBuilder.apply()方法
这方法中基本就是做一些配置设置,最终还是会返回当前RequestBuilder对象
sorry,有兴趣的童鞋,可以自己去看看这个方法,跟着一步步去看看
RequestBuilder.into()方法
来看看这个比较重要的方法 into方法
这里我们看看上面简单使用的第一种into
一路跟进去,看到这个Request对象的创建,buildRequest方法调用;
这里省略掉一些代码,一些判断和赋值,都是为了创建这个Request对象时传入的参数,以及一些缩略图的判断;
最终第一次是调用到obtainRequest这个方法,通过Request的实现类SingleRequest.obtain静态方法,创建出这个实现类SingleRequest;
这个Request是一个接口,SingleRequest是这个接口的实现类,所以最终做事的会是这个SingleRequest请求处理;
得到这个SingleRequest实现类之后,判断中调用了实现类中的begin()方法 也就是开始请求,童鞋们继续往下看↓;
public class RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> extends BaseRequestOptions<RequestBuilder<TranscodeType>>
implements Cloneable,
ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<TranscodeType>> {
......
@NonNull
public <Y extends Target<TranscodeType>> Y into(@NonNull Y target) {
return into(target, /*targetListener=*/ null, Executors.mainThreadExecutor());
}
......
@NonNull
@Synthetic
<Y extends Target<TranscodeType>> Y into(
@NonNull Y target,
@Nullable RequestListener<TranscodeType> targetListener,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
return into(target, targetListener, /*options=*/ this, callbackExecutor);
}
......
private <Y extends Target<TranscodeType>> Y into(
@NonNull Y target,
@Nullable RequestListener<TranscodeType> targetListener,
BaseRequestOptions<?> options,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(target);
if (!isModelSet) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must call #load() before calling #into()");
}
//这里得到的是Request的实现类SingleRequest
Request request = buildRequest(target, targetListener, options, callbackExecutor);
Request previous = target.getRequest();
if (request.isEquivalentTo(previous)
&& !isSkipMemoryCacheWithCompletePreviousRequest(options, previous)) {
request.recycle();
if (!Preconditions.checkNotNull(previous).isRunning()) {
//开始请求
previous.begin();
}
return target;
}
requestManager.clear(target);
target.setRequest(request);
requestManager.track(target, request);
return target;
}
......
//这个方法调用完之后得到的是Request的实现类SingleRequest
private Request buildRequest(
Target<TranscodeType> target,
@Nullable RequestListener<TranscodeType> targetListener,
BaseRequestOptions<?> requestOptions,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
return buildRequestRecursive(
target,
targetListener,
/*parentCoordinator=*/ null,
transitionOptions,
requestOptions.getPriority(),
requestOptions.getOverrideWidth(),
requestOptions.getOverrideHeight(),
requestOptions,
callbackExecutor);
}
......
private Request buildRequestRecursive(
Target<TranscodeType> target,
@Nullable RequestListener<TranscodeType> targetListener,
@Nullable RequestCoordinator parentCoordinator,
TransitionOptions<?, ? super TranscodeType> transitionOptions,
Priority priority,
int overrideWidth,
int overrideHeight,
BaseRequestOptions<?> requestOptions,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
......
Request mainRequest =
buildThumbnailRequestRecursive(
target,
targetListener,
parentCoordinator,
transitionOptions,
priority,
overrideWidth,
overrideHeight,
requestOptions,
callbackExecutor);
if (errorRequestCoordinator == null) {
return mainRequest;
}
......
Request errorRequest =
errorBuilder.buildRequestRecursive(
target,
targetListener,
errorRequestCoordinator,
errorBuilder.transitionOptions,
errorBuilder.getPriority(),
errorOverrideWidth,
errorOverrideHeight,
errorBuilder,
callbackExecutor);
errorRequestCoordinator.setRequests(mainRequest, errorRequest);
return errorRequestCoordinator;
}
private Request buildThumbnailRequestRecursive(
Target<TranscodeType> target,
RequestListener<TranscodeType> targetListener,
@Nullable RequestCoordinator parentCoordinator,
TransitionOptions<?, ? super TranscodeType> transitionOptions,
Priority priority,
int overrideWidth,
int overrideHeight,
BaseRequestOptions<?> requestOptions,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
if (thumbnailBuilder != null) {
// Recursive case: contains a potentially recursive thumbnail request builder.
if (isThumbnailBuilt) {
throw new IllegalStateException("You cannot use a request as both the main request and a "
+ "thumbnail, consider using clone() on the request(s) passed to thumbnail()");
}
TransitionOptions<?, ? super TranscodeType> thumbTransitionOptions =
thumbnailBuilder.transitionOptions;
// Apply our transition by default to thumbnail requests but avoid overriding custom options
// that may have been applied on the thumbnail request explicitly.
if (thumbnailBuilder.isDefaultTransitionOptionsSet) {
thumbTransitionOptions = transitionOptions;
}
Priority thumbPriority = thumbnailBuilder.isPrioritySet()
? thumbnailBuilder.getPriority() : getThumbnailPriority(priority);
int thumbOverrideWidth = thumbnailBuilder.getOverrideWidth();
int thumbOverrideHeight = thumbnailBuilder.getOverrideHeight();
if (Util.isValidDimensions(overrideWidth, overrideHeight)
&& !thumbnailBuilder.isValidOverride()) {
thumbOverrideWidth = requestOptions.getOverrideWidth();
thumbOverrideHeight = requestOptions.getOverrideHeight();
}
ThumbnailRequestCoordinator coordinator = new ThumbnailRequestCoordinator(parentCoordinator);
Request fullRequest =
obtainRequest(
target,
targetListener,
requestOptions,
coordinator,
transitionOptions,
priority,
overrideWidth,
overrideHeight,
callbackExecutor);
isThumbnailBuilt = true;
// Recursively generate thumbnail requests.
Request thumbRequest =
thumbnailBuilder.buildRequestRecursive(
target,
targetListener,
coordinator,
thumbTransitionOptions,
thumbPriority,
thumbOverrideWidth,
thumbOverrideHeight,
thumbnailBuilder,
callbackExecutor);
isThumbnailBuilt = false;
coordinator.setRequests(fullRequest, thumbRequest);
return coordinator;
} else if (thumbSizeMultiplier != null) {
// Base case: thumbnail multiplier generates a thumbnail request, but cannot recurse.
ThumbnailRequestCoordinator coordinator = new ThumbnailRequestCoordinator(parentCoordinator);
Request fullRequest =
obtainRequest(
target,
targetListener,
requestOptions,
coordinator,
transitionOptions,
priority,
overrideWidth,
overrideHeight,
callbackExecutor);
BaseRequestOptions<?> thumbnailOptions =
requestOptions.clone().sizeMultiplier(thumbSizeMultiplier);
Request thumbnailRequest =
obtainRequest(
target,
targetListener,
thumbnailOptions,
coordinator,
transitionOptions,
getThumbnailPriority(priority),
overrideWidth,
overrideHeight,
callbackExecutor);
coordinator.setRequests(fullRequest, thumbnailRequest);
return coordinator;
} else {
// Base case: no thumbnail.
return obtainRequest(
target,
targetListener,
requestOptions,
parentCoordinator,
transitionOptions,
priority,
overrideWidth,
overrideHeight,
callbackExecutor);
}
}
......
private Request obtainRequest(
Target<TranscodeType> target,
RequestListener<TranscodeType> targetListener,
BaseRequestOptions<?> requestOptions,
RequestCoordinator requestCoordinator,
TransitionOptions<?, ? super TranscodeType> transitionOptions,
Priority priority,
int overrideWidth,
int overrideHeight,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
//
return SingleRequest.obtain(
context,
glideContext,
model,
transcodeClass,
requestOptions,
overrideWidth,
overrideHeight,
priority,
target,
targetListener,
requestListeners,
requestCoordinator,
glideContext.getEngine(),
transitionOptions.getTransitionFactory(),
callbackExecutor);
}
}
大致看看这个Requset接口里面定义的方法
package com.bumptech.glide.request;
public interface Request {
//开始加载
void begin();
//清理
void clear();
//请求是否正在运行
boolean isRunning();
//请求是否完成
boolean isComplete();
//是否设置了占位符资源
boolean isResourceSet();
//请求是否被清理了
boolean isCleared();
//请求是否失败了
boolean isFailed();
//释放
void recycle();
boolean isEquivalentTo(Request other);
}
接着上面来看这个实现类中的begin方法调用
判断加载方式(model)如果为空,直接结束请求,因为请求方式都没有…
接着下面是一些状态的判断处理;
接着看看这个onSizeReady方法里面
onSizeReady:
1、将当前这个请求设置为正在请求的状态;
2、计算出宽高尺寸
3、engine.load()方法的调用,返回一个Engine.LoadStatus对象
public final class SingleRequest<R> implements Request,
SizeReadyCallback,
ResourceCallback,
FactoryPools.Poolable {
......
private Engine engine;
private Engine.LoadStatus loadStatus;
......
//创建出Request实现类,也就是自己这个类
public static <R> SingleRequest<R> obtain(
Context context,
GlideContext glideContext,
Object model,
Class<R> transcodeClass,
BaseRequestOptions<?> requestOptions,
int overrideWidth,
int overrideHeight,
Priority priority,
Target<R> target,
RequestListener<R> targetListener,
@Nullable List<RequestListener<R>> requestListeners,
RequestCoordinator requestCoordinator,
Engine engine,
TransitionFactory<? super R> animationFactory,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") SingleRequest<R> request =
(SingleRequest<R>) POOL.acquire();
if (request == null) {
//new 构建出实现类自己
request = new SingleRequest<>();
}
//做一些数据的初始化
request.init(
context,
glideContext,
model,
transcodeClass,
requestOptions,
overrideWidth,
overrideHeight,
priority,
target,
targetListener,
requestListeners,
requestCoordinator,
engine,
animationFactory,
callbackExecutor);
return request;
}
......
@Override
public synchronized void begin() {
assertNotCallingCallbacks();
stateVerifier.throwIfRecycled();
startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
if (model == null) {
if (Util.isValidDimensions(overrideWidth, overrideHeight)) {
width = overrideWidth;
height = overrideHeight;
}
int logLevel = getFallbackDrawable() == null ? Log.WARN : Log.DEBUG;
//加载失败调用onLoadFailed方法,这里失败原因是加载的方式没有;
//还记得前面load()方法吗,那里是会返回一个RequestBuilder对象,里面成员变量中有个model(加载方式),在创建这个对象时进行赋值;
onLoadFailed(new GlideException("Received null model"), logLevel);
return;
}
//如果该请求已经正在执行,那么在开启的话就抛出异常
if (status == Status.RUNNING) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot restart a running request");
}
//该请求是已经完成的状态下
if (status == Status.COMPLETE) {
onResourceReady(resource, DataSource.MEMORY_CACHE);
return;
}
status = Status.WAITING_FOR_SIZE;
if (Util.isValidDimensions(overrideWidth, overrideHeight)) {
//这里计算好宽高尺寸,并将这个请求的状态设置成了正在请求的状态
onSizeReady(overrideWidth, overrideHeight);
} else {
target.getSize(this);
}
if ((status == Status.RUNNING || status == Status.WAITING_FOR_SIZE)
&& canNotifyStatusChanged()) {
target.onLoadStarted(getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
if (IS_VERBOSE_LOGGABLE) {
logV("finished run method in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
}
......
@Override
public synchronized void onSizeReady(int width, int height) {
stateVerifier.throwIfRecycled();
if (IS_VERBOSE_LOGGABLE) {
logV("Got onSizeReady in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
if (status != Status.WAITING_FOR_SIZE) {
return;
}
//设置该请求状态为正在请求的状态
status = Status.RUNNING;
//计算出宽高
float sizeMultiplier = requestOptions.getSizeMultiplier();
this.width = maybeApplySizeMultiplier(width, sizeMultiplier);
this.height = maybeApplySizeMultiplier(height, sizeMultiplier);
if (IS_VERBOSE_LOGGABLE) {
logV("finished setup for calling load in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
loadStatus =
engine.load(
glideContext,
model,
requestOptions.getSignature(),
this.width,
this.height,
requestOptions.getResourceClass(),
transcodeClass,
priority,
requestOptions.getDiskCacheStrategy(),
requestOptions.getTransformations(),
requestOptions.isTransformationRequired(),
requestOptions.isScaleOnlyOrNoTransform(),
requestOptions.getOptions(),
requestOptions.isMemoryCacheable(),
requestOptions.getUseUnlimitedSourceGeneratorsPool(),
requestOptions.getUseAnimationPool(),
requestOptions.getOnlyRetrieveFromCache(),
this,
callbackExecutor);
if (status != Status.RUNNING) {
loadStatus = null;
}
if (IS_VERBOSE_LOGGABLE) {
logV("finished onSizeReady in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
}
......
//记载失败时调用的方法
private synchronized void onLoadFailed(GlideException e, int maxLogLevel) {
stateVerifier.throwIfRecycled();
e.setOrigin(requestOrigin);
int logLevel = glideContext.getLogLevel();
if (logLevel <= maxLogLevel) {
Log.w(GLIDE_TAG, "Load failed for " + model + " with size [" + width + "x" + height + "]", e);
if (logLevel <= Log.INFO) {
e.logRootCauses(GLIDE_TAG);
}
}
loadStatus = null;
status = Status.FAILED;
isCallingCallbacks = true;
try {
//TODO: what if this is a thumbnail request?
boolean anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget = false;
if (requestListeners != null) {
for (RequestListener<R> listener : requestListeners) {
anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget |=
listener.onLoadFailed(e, model, target, isFirstReadyResource());
}
}
anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget |=
targetListener != null
&& targetListener.onLoadFailed(e, model, target, isFirstReadyResource());
if (!anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget) {
setErrorPlaceholder();
}
} finally {
isCallingCallbacks = false;
}
notifyLoadFailed();
}
}
loadStatus=engine.load(),我们就去Engine这个类里面去看看
这里面才会是真正的加载
这里我们可以看到读取活动缓存、内存缓存;
这里面的意思就是:
1、先根据宽高加载方式等等信息去拿到Key;
2、通过这个key,先去活动缓存中去查找调用loadFromActiveResources这个方法,如果活动缓存里面找到了,那么就拿出来onResourceReady回调出去,并且将这个图片资源的引用计数+1,然后停止,不在往下走;
3、如果活动缓存中没有找到这个图片资源,就调用loadFromCache这个方法,去内存中查找,通过remove方法,将这个key对应的图片资源从Lru内存缓存的双向链表中移除,返回出来,如果有这个图片资源的话,就讲这个图片资源的引用计数器+1,然后把这个图片资源添加到活动资源当中去,然后onResourceReady回调出去,停止,不在往下走;
4、如果内存缓存也没有的话,就会进入jobs这个缓存中,里面是两个HashMap;
5、如果以上缓存中都不存在的话,就会构建出EngineJob、DecodeJob这两个对象,然后添加到jobs缓存中,然后EngineJob对象调用start方法传入了DecodeJob对象,DecodeJob对象是一个Runable,最终传入到线程池当中,这个时候DecodeJob对象中的run方法就会被执行;
往下面下面看↓
public class Engine implements EngineJobListener,
MemoryCache.ResourceRemovedListener,
EngineResource.ResourceListener {
......
private final MemoryCache cache; //内存缓存
private final ActiveResources activeResources; //活动缓存
......
public synchronized <R> LoadStatus load(
GlideContext glideContext,
Object model,
Key signature,
int width,
int height,
Class<?> resourceClass,
Class<R> transcodeClass,
Priority priority,
DiskCacheStrategy diskCacheStrategy,
Map<Class<?>, Transformation<?>> transformations,
boolean isTransformationRequired,
boolean isScaleOnlyOrNoTransform,
Options options,
boolean isMemoryCacheable,
boolean useUnlimitedSourceExecutorPool,
boolean useAnimationPool,
boolean onlyRetrieveFromCache,
ResourceCallback cb,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
long startTime = VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE ? LogTime.getLogTime() : 0;
//取出对应的key
EngineKey key = keyFactory.buildKey(model, signature, width, height, transformations,
resourceClass, transcodeClass, options);
//从活动缓存中去查找对应key的资源吧
EngineResource<?> active = loadFromActiveResources(key, isMemoryCacheable);
if (active != null) {
cb.onResourceReady(active, DataSource.MEMORY_CACHE);
if (VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Loaded resource from active resources", startTime, key);
}
return null;
}
//从根据key到Lru内存缓存中去取
EngineResource<?> cached = loadFromCache(key, isMemoryCacheable);
if (cached != null) {
cb.onResourceReady(cached, DataSource.MEMORY_CACHE);
if (VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Loaded resource from cache", startTime, key);
}
return null;
}
//jobs缓存
EngineJob<?> current = jobs.get(key, onlyRetrieveFromCache);
if (current != null) {
current.addCallback(cb, callbackExecutor);
if (VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Added to existing load", startTime, key);
}
return new LoadStatus(cb, current);
}
EngineJob<R> engineJob =
engineJobFactory.build(
key,
isMemoryCacheable,
useUnlimitedSourceExecutorPool,
useAnimationPool,
onlyRetrieveFromCache);
DecodeJob<R> decodeJob =
decodeJobFactory.build(
glideContext,
model,
key,
signature,
width,
height,
resourceClass,
transcodeClass,
priority,
diskCacheStrategy,
transformations,
isTransformationRequired,
isScaleOnlyOrNoTransform,
onlyRetrieveFromCache,
options,
engineJob);
jobs.put(key, engineJob);
engineJob.addCallback(cb, callbackExecutor);
engineJob.start(decodeJob);
if (VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Started new load", startTime, key);
}
return new LoadStatus(cb, engineJob);
}
......
//从活动缓存中去取图片资源
@Nullable
private EngineResource<?> loadFromActiveResources(Key key, boolean isMemoryCacheable) {
if (!isMemoryCacheable) {
return null;
}
EngineResource<?> active = activeResources.get(key);
if (active != null) {
active.acquire();
}
return active;
}
......
//读取内存缓存中对应key的图片资源
private EngineResource<?> loadFromCache(Key key, boolean isMemoryCacheable) {
if (!isMemoryCacheable) {
return null;
}
EngineResource<?> cached = getEngineResourceFromCache(key);
//如果在内存缓存中找到了这个图片资源的话
if (cached != null) {
//引用计数器+1
cached.acquire();
//添加到活动缓存中
activeResources.activate(key, cached);
}
return cached;
}
......
private EngineResource<?> getEngineResourceFromCache(Key key) {
//内存缓存中试图去remove,如果能remove掉的话,就会返回被remove的图片资源
Resource<?> cached = cache.remove(key);
final EngineResource<?> result;
if (cached == null) {
result = null;
} else if (cached instanceof EngineResource) {
// Save an object allocation if we've cached an EngineResource (the typical case).
result = (EngineResource<?>) cached;
} else {
result = new EngineResource<>(cached, true /*isMemoryCacheable*/, true /*isRecyclable*/);
}
//将图片资源返回出去,也有可能是个null
return result;
}
......
}
这个run方法中,我们看runWrapped这个方法的调用
runGenerators跟进这个方法里面,开启了一个无限循环;
通过DataFetcherGenerator 这个对象调用startNext方法;
往下看↓,我们跟进这个startNext方法中;
class DecodeJob<R> implements DataFetcherGenerator.FetcherReadyCallback,
Runnable,
Comparable<DecodeJob<?>>,
Poolable {
private volatile DataFetcherGenerator currentGenerator;
......
@Override
public void run() {
GlideTrace.beginSectionFormat("DecodeJob#run(model=%s)", model);
DataFetcher<?> localFetcher = currentFetcher;
try {
if (isCancelled) {
notifyFailed();
return;
}
runWrapped();
} catch (CallbackException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "DecodeJob threw unexpectedly"
+ ", isCancelled: " + isCancelled
+ ", stage: " + stage, t);
}
if (stage != Stage.ENCODE) {
throwables.add(t);
notifyFailed();
}
if (!isCancelled) {
throw t;
}
throw t;
} finally {
if (localFetcher != null) {
localFetcher.cleanup();
}
GlideTrace.endSection();
}
}
......
private void runWrapped() {
switch (runReason) {
case INITIALIZE:
stage = getNextStage(Stage.INITIALIZE);
currentGenerator = getNextGenerator();
runGenerators();
break;
case SWITCH_TO_SOURCE_SERVICE:
runGenerators();
break;
case DECODE_DATA:
decodeFromRetrievedData();
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized run reason: " + runReason);
}
}
......
private void runGenerators() {
currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
startFetchTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
boolean isStarted = false;
while (!isCancelled && currentGenerator != null
&& !(isStarted = currentGenerator.startNext())) {
stage = getNextStage(stage);
currentGenerator = getNextGenerator();
if (stage == Stage.SOURCE) {
reschedule();
return;
}
}
// We've run out of stages and generators, give up.
if ((stage == Stage.FINISHED || isCancelled) && !isStarted) {
notifyFailed();
}
}
......
}
发现上面startNext方法是个接口定义的方法
package com.bumptech.glide.load.engine;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import com.bumptech.glide.load.DataSource;
import com.bumptech.glide.load.Key;
import com.bumptech.glide.load.data.DataFetcher;
interface DataFetcherGenerator {
interface FetcherReadyCallback {
......
}
boolean startNext();
void cancel();
}
我们直接去看这个实现类
startNext方法:磁盘中通过key获取缓存文件
通过loadData.fetcher.loadData(helper.getPriority(), this);去获取这个图片资源
package com.bumptech.glide.load.engine;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import com.bumptech.glide.load.DataSource;
import com.bumptech.glide.load.Key;
import com.bumptech.glide.load.data.DataFetcher;
import com.bumptech.glide.load.model.ModelLoader;
import com.bumptech.glide.load.model.ModelLoader.LoadData;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
class DataCacheGenerator implements DataFetcherGenerator,
DataFetcher.DataCallback<Object> {
private final List<Key> cacheKeys;
private final DecodeHelper<?> helper;
private final FetcherReadyCallback cb;
private int sourceIdIndex = -1;
private Key sourceKey;
private List<ModelLoader<File, ?>> modelLoaders;
private int modelLoaderIndex;
private volatile LoadData<?> loadData;
@SuppressWarnings("PMD.SingularField")
private File cacheFile;
DataCacheGenerator(DecodeHelper<?> helper, FetcherReadyCallback cb) {
this(helper.getCacheKeys(), helper, cb);
}
DataCacheGenerator(List<Key> cacheKeys, DecodeHelper<?> helper, FetcherReadyCallback cb) {
this.cacheKeys = cacheKeys;
this.helper = helper;
this.cb = cb;
}
@Override
public boolean startNext() {
while (modelLoaders == null || !hasNextModelLoader()) {
sourceIdIndex++;
if (sourceIdIndex >= cacheKeys.size()) {
return false;
}
Key sourceId = cacheKeys.get(sourceIdIndex);
@SuppressWarnings("PMD.AvoidInstantiatingObjectsInLoops")
Key originalKey = new DataCacheKey(sourceId, helper.getSignature());
//从磁盘当中去查找
cacheFile = helper.getDiskCache().get(originalKey);
if (cacheFile != null) {
this.sourceKey = sourceId;
modelLoaders = helper.getModelLoaders(cacheFile);
modelLoaderIndex = 0;
}
}
loadData = null;
boolean started = false;
while (!started && hasNextModelLoader()) {
ModelLoader<File, ?> modelLoader = modelLoaders.get(modelLoaderIndex++);
//加载读取文件
loadData =
modelLoader.buildLoadData(cacheFile, helper.getWidth(), helper.getHeight(),
helper.getOptions());
if (loadData != null && helper.hasLoadPath(loadData.fetcher.getDataClass())) {
started = true;
loadData.fetcher.loadData(helper.getPriority(), this);
}
}
return started;
}
private boolean hasNextModelLoader() {
return modelLoaderIndex < modelLoaders.size();
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
LoadData<?> local = loadData;
if (local != null) {
local.fetcher.cancel();
}
}
@Override
public void onDataReady(Object data) {
cb.onDataFetcherReady(sourceKey, data, loadData.fetcher, DataSource.DATA_DISK_CACHE, sourceKey);
}
@Override
public void onLoadFailed(@NonNull Exception e) {
cb.onDataFetcherFailed(sourceKey, e, loadData.fetcher, DataSource.DATA_DISK_CACHE);
}
}
看看DecodeHelper的这些实现类,也就是很多获取图片资源的方式

大概来看看这个HttpUrlFetcher这个网络加载的方式
loadData 读取图片吧,这里是个网络请求的方式读取,来看看loadDataWithRedirects这个方法;
loadDataWithRedirects这个方法里面使用了HttpURLConnection 网络请求,
状态码200成功的状态下,获取输入流InputStream,然后通过callback.onDataReady(result);回调出去;
public class HttpUrlFetcher implements DataFetcher<InputStream> {
private final HttpUrlConnectionFactory connectionFactory;
private HttpURLConnection urlConnection;
private InputStream stream;
......
@Override
public void loadData(@NonNull Priority priority,
@NonNull DataCallback<? super InputStream> callback) {
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
try {
//获取到输入流
InputStream result = loadDataWithRedirects(glideUrl.toURL(), 0, null, glideUrl.getHeaders());
//回调出去
callback.onDataReady(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "Failed to load data for url", e);
}
callback.onLoadFailed(e);
} finally {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Finished http url fetcher fetch in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
}
}
......
private InputStream loadDataWithRedirects(URL url, int redirects, URL lastUrl,
Map<String, String> headers) throws IOException {
if (redirects >= MAXIMUM_REDIRECTS) {
throw new HttpException("Too many (> " + MAXIMUM_REDIRECTS + ") redirects!");
} else {
// Comparing the URLs using .equals performs additional network I/O and is generally broken.
// See http://michaelscharf.blogspot.com/2006/11/javaneturlequals-and-hashcode-make.html.
try {
if (lastUrl != null && url.toURI().equals(lastUrl.toURI())) {
throw new HttpException("In re-direct loop");
}
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
// Do nothing, this is best effort.
}
}
urlConnection = connectionFactory.build(url);
for (Map.Entry<String, String> headerEntry : headers.entrySet()) {
urlConnection.addRequestProperty(headerEntry.getKey(), headerEntry.getValue());
}
urlConnection.setConnectTimeout(timeout);
urlConnection.setReadTimeout(timeout);
urlConnection.setUseCaches(false);
urlConnection.setDoInput(true);
// Stop the urlConnection instance of HttpUrlConnection from following redirects so that
// redirects will be handled by recursive calls to this method, loadDataWithRedirects.
urlConnection.setInstanceFollowRedirects(false);
// Connect explicitly to avoid errors in decoders if connection fails.
urlConnection.connect();
// Set the stream so that it's closed in cleanup to avoid resource leaks. See #2352.
stream = urlConnection.getInputStream();
if (isCancelled) {
return null;
}
final int statusCode = urlConnection.getResponseCode();
if (isHttpOk(statusCode)) {
return getStreamForSuccessfulRequest(urlConnection);
} else if (isHttpRedirect(statusCode)) {
String redirectUrlString = urlConnection.getHeaderField("Location");
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(redirectUrlString)) {
throw new HttpException("Received empty or null redirect url");
}
URL redirectUrl = new URL(url, redirectUrlString);
// Closing the stream specifically is required to avoid leaking ResponseBodys in addition
// to disconnecting the url connection below. See #2352.
cleanup();
return loadDataWithRedirects(redirectUrl, redirects + 1, url, headers);
} else if (statusCode == INVALID_STATUS_CODE) {
throw new HttpException(statusCode);
} else {
throw new HttpException(urlConnection.getResponseMessage(), statusCode);
}
}
// Referencing constants is less clear than a simple static method.
private static boolean isHttpOk(int statusCode) {
return statusCode / 100 == 2;
}
// Referencing constants is less clear than a simple static method.
private static boolean isHttpRedirect(int statusCode) {
return statusCode / 100 == 3;
}
//这里是请求成功后 获取到InputStream输入流
private InputStream getStreamForSuccessfulRequest(HttpURLConnection urlConnection)
throws IOException {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(urlConnection.getContentEncoding())) {
int contentLength = urlConnection.getContentLength();
stream = ContentLengthInputStream.obtain(urlConnection.getInputStream(), contentLength);
} else {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "Got non empty content encoding: " + urlConnection.getContentEncoding());
}
stream = urlConnection.getInputStream();
}
return stream;
}
......
}
into()方法小结
1、load和apply方法都是返回一个RequestBuilder对象;
load方法里面的各种重载主要是用来区分各种加载方式,比如http、Uri、File等等;apply方法里面基本就是一些配置;
2、inot方法才是个重点,里面是用来加载图片资源,还有各种缓存,以及去用不同的方式做图片输入流的获取;
活动缓存:是一个Map集合,value是一个弱引用的资源对象,资源对象中有一个引用计数器,当引用计数器等于0的时候,就会回调出去,在Engine类中的onResourceReleased回调方法中,调用活动缓存的清理方法,将这个图片资源从活动缓存的弱引用中remove掉,同时将这个图片资源添加到内存缓存当中;
内存缓存:是一个Lru算法,Lru里面是一个双向链表,也是个最不常用移除算法,也就是在最开始的是设定最大缓存空间,当新增加图片资源时,重新计算剩余内存,当内存超过时,会将最后一个(也就是最不常用)的图片资源remove掉;
磁盘缓存:里面也是一个Lru算法双向链表,这个磁盘缓存是在同步不同方式下载图片资源的时候,通过一个线程池进行数据的存储;
into读取加载图片资源的顺序是:先通过Key去活动缓存中查找图片资源,如果活动资源中存在,就直接进行使用,并将资源对象的引用计数器+1;如果活动缓存中不存在的话,就进行内存缓存中去查找,如果内存缓存中存在的话,就直接将内存缓存的双向链表中移除并拿出来,将资源对象的引用计数器+1,然后添加到活动缓存当中,并将这个资源直接拿着使用;如果内存缓存中没找到的话,会去一个jobs对象的Map集合中去查找EngineJob对象,如果找到直接通过线程池执行将图片资源进行读取或者进行下载处理,反之继续往下走;下面会有创建两个Job对象,一个是存有线程池,并实现了另一个DecodeJob的接口回调,另一个DecodeJob对象是一个Runable对象,创建完成后将EngineJob添加到jobs对象中,并执行EngineJob中的线程池,运行DecodeJob中的run方法,去进行磁盘的读取,如果没读到会去进行图片资源的下载,然后添加到内存缓存中;
值得一提的是:当当前界面关闭的时候,会将活动缓存中的图片资源都存入到内存缓存的双向链表当中去~~ 这个在我们下面看生命周期的时候去看看
来看看这个LruCache
put方法:先判断键值不为空,同步锁后:
1、计算出所有存入的缓存总大小;
2、保存到双向链表中,并返回了值;
3、根据这个值是否存在去决定是否需要从总缓存中减去响应的大小;
4、如果这个对象已经存在双向链表中,就去做移除(entryRemoved这个方法自己去重写);
5、再去计算大小以及计算出是否超出了最大内存,超出的话就移除掉双向链表中最不常用的(最后一个)对象;
sizeOf方法:需要重写,也就是重写计算出存入对象的所占缓存大小;
trimToSize:无限循环,在里面去比对当前缓存中的总大小和我们设置的最大缓存,如果超出了最大缓存,就将双向链表中的最不常用(最后一个)进行移除,直到当前缓存大小没有超过最大缓存的时候,才会结束掉这个循环,也就是会不断的去移除最后一个;
LinkedHashMap双向链表:先进先出的原则!!!
public class LruCache<K, V> {
//双向链表:先进先出的原则
private final LinkedHashMap<K, V> map;
/** Size of this cache in units. Not necessarily the number of elements. */
private int size;
private int maxSize;
......
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
//计算出所有存入的总大小
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
//存入到双向链表当中
previous = map.put(key, value);
//这里可以理解为这种图片已经存在了
if (previous != null) {
//那么这里就会将这个已经存在的图片的缓存大小从总缓存中减去
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
//将这个已经存在的图片移除掉,这个方法是个需要我们去重写的,也就是通知到我们这里删除的是哪个对象
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
//这个方法中去做移除,并且重新计算总大小
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
......
//获取当前这个需要缓存的对象的缓存大小
private int safeSizeOf(K key, V value) {
int result = sizeOf(key, value);
if (result < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Negative size: " + key + "=" + value);
}
return result;
}
......
//这个方法是需要重写的,这里是重写每个存入对象的大小
protected int sizeOf(K key, V value) {
return 1;
}
......
//我们自己去重写
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {}
......
//移除不常用的对象,并且重新计算总大小
private void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
//无限循环
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
//这类是退出这个无限循环的触发条件
//如果总缓存小于了我们设置的最大缓存就会退出这个无限循环
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
//如果缓存的总大小已经超过了我们设置的最大缓存的话
//下面可以理解为去删除最后一个,并且将缓存的总大小减去这个需要被删除的对象的缓存大小
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = null;
//遍历,最终这里的toEvict会是最后一个
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : map.entrySet()) {
toEvict = entry;
}
// END LAYOUTLIB CHANGE
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
//拿到最后一个的key 和 value
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
//从双向链表中移除掉这个key的对象(图片)
map.remove(key);
//减去这个大小
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
//调用我们需要重写的删除方法,也就是通知到我们这里删除的是哪个对象
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
......
//移除的方法
public final V remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
//将对应key的对象从双向链表中移除掉
previous = map.remove(key);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
//最终会调用到entryRemoved这个抽象方法,也就是通知到我们这里删除的是哪个对象
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}
......
}
磁盘缓存
磁盘缓存:内部也是个自己做的lru算法类似的方式去管理磁盘缓存空间;
大致的看下里面的内容
**lruEntries :**也是一个双向链表
open方法:
1、判断了下maxsize;
2、创建文件;
3、创建了自己这个对象,注意opne这个方法是个静态的;
4、调用readJournal读取文件的内容(一行一行的进行读取相应的内容);
readJournal方法:
1、一行一行读取信息(版本号、app版本号等等信息);
2、根据关键字做去lru双向链表中的数据移除;
public final class DiskLruCache implements Closeable {
static final String JOURNAL_FILE = "journal";
static final String JOURNAL_FILE_TEMP = "journal.tmp";
static final String JOURNAL_FILE_BACKUP = "journal.bkp";
......
private long maxSize;
private long size = 0;
private Writer journalWriter;
private final LinkedHashMap<String, Entry> lruEntries =
new LinkedHashMap<String, Entry>(0, 0.75f, true);
private static final String REMOVE = "REMOVE";
......
public static DiskLruCache open(File directory, int appVersion, int valueCount, long maxSize)
throws IOException {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
if (valueCount <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("valueCount <= 0");
}
// 创建文件
File backupFile = new File(directory, JOURNAL_FILE_BACKUP);
if (backupFile.exists()) {
File journalFile = new File(directory, JOURNAL_FILE);
// If journal file also exists just delete backup file.
if (journalFile.exists()) {
backupFile.delete();
} else {
renameTo(backupFile, journalFile, false);
}
}
// 创建了自己这个对象,注意opne这个方法是个静态的
DiskLruCache cache = new DiskLruCache(directory, appVersion, valueCount, maxSize);
//文件存在的情况下
if (cache.journalFile.exists()) {
try {
//读取文件
cache.readJournal();
cache.processJournal();
return cache;
} catch (IOException journalIsCorrupt) {
System.out
.println("DiskLruCache "
+ directory
+ " is corrupt: "
+ journalIsCorrupt.getMessage()
+ ", removing");
cache.delete();
}
}
......
private static void renameTo(File from, File to, boolean deleteDestination) throws IOException {
if (deleteDestination) {
deleteIfExists(to);
}
if (!from.renameTo(to)) {
throw new IOException();
}
}
.......
private static void deleteIfExists(File file) throws IOException {
if (file.exists() && !file.delete()) {
throw new IOException();
}
}
......
private void readJournal() throws IOException {
StrictLineReader reader = new StrictLineReader(new FileInputStream(journalFile), Util.US_ASCII);
try {
//读取各种信息
String magic = reader.readLine();
//版本号
String version = reader.readLine();
//app的版本号
String appVersionString = reader.readLine();
String valueCountString = reader.readLine();
String blank = reader.readLine();
if (!MAGIC.equals(magic)
|| !VERSION_1.equals(version)
|| !Integer.toString(appVersion).equals(appVersionString)
|| !Integer.toString(valueCount).equals(valueCountString)
|| !"".equals(blank)) {
throw new IOException("unexpected journal header: [" + magic + ", " + version + ", "
+ valueCountString + ", " + blank + "]");
}
int lineCount = 0;
while (true) {
try {
//一行一行进行内容的读取,并根据判断做缓存的移除
readJournalLine(reader.readLine());
lineCount++;
} catch (EOFException endOfJournal) {
break;
}
}
redundantOpCount = lineCount - lruEntries.size();
// If we ended on a truncated line, rebuild the journal before appending to it.
if (reader.hasUnterminatedLine()) {
rebuildJournal();
} else {
journalWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream(journalFile, true), Util.US_ASCII));
}
} finally {
Util.closeQuietly(reader);
}
}
......
private void readJournalLine(String line) throws IOException {
int firstSpace = line.indexOf(' ');
if (firstSpace == -1) {
throw new IOException("unexpected journal line: " + line);
}
int keyBegin = firstSpace + 1;
int secondSpace = line.indexOf(' ', keyBegin);
final String key;
if (secondSpace == -1) {
key = line.substring(keyBegin);
//当前这一行是不是有REMOVE这个关键字
if (firstSpace == REMOVE.length() && line.startsWith(REMOVE)) {
//如果有的话,就在这个lru双向链表中移除
lruEntries.remove(key);
return;
}
} else {
key = line.substring(keyBegin, secondSpace);
}
Entry entry = lruEntries.get(key);
if (entry == null) {
entry = new Entry(key);
lruEntries.put(key, entry);
}
if (secondSpace != -1 && firstSpace == CLEAN.length() && line.startsWith(CLEAN)) {
String[] parts = line.substring(secondSpace + 1).split(" ");
entry.readable = true;
entry.currentEditor = null;
entry.setLengths(parts);
} else if (secondSpace == -1 && firstSpace == DIRTY.length() && line.startsWith(DIRTY)) {
entry.currentEditor = new Editor(entry);
} else if (secondSpace == -1 && firstSpace == READ.length() && line.startsWith(READ)) {
// This work was already done by calling lruEntries.get().
} else {
throw new IOException("unexpected journal line: " + line);
}
}
......
private void processJournal() throws IOException {
deleteIfExists(journalFileTmp);
for (Iterator<Entry> i = lruEntries.values().iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
Entry entry = i.next();
if (entry.currentEditor == null) {
for (int t = 0; t < valueCount; t++) {
size += entry.lengths[t];
}
} else {
entry.currentEditor = null;
for (int t = 0; t < valueCount; t++) {
deleteIfExists(entry.getCleanFile(t));
deleteIfExists(entry.getDirtyFile(t));
}
i.remove();
}
}
}
......
}
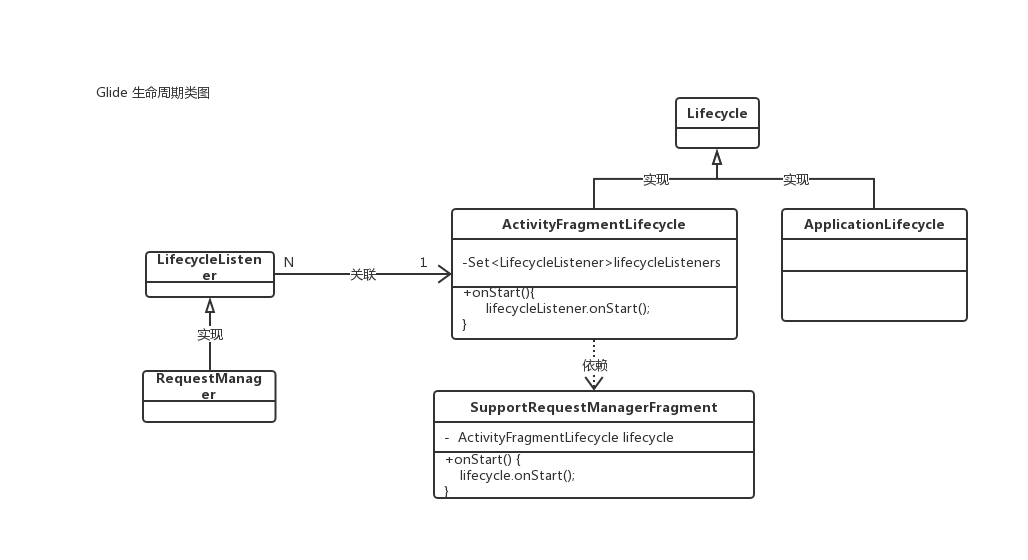
生命周期
RequestManagerRetriever类中
通过Activity创建出一个FragmentManager对象;
在通过getSupportRequestManagerFragment方法去查找或者创建一个Fragment,这个Fragment是使用在当前的activity中,用来监听管理生命周期,并且给RequestManager分发生命周期回调的;
在new SupportRequestManagerFragment的时候,创建了一个Lifecycle对象进行了生命周期的绑定;
这里为什么要移除?
为了保证这个Activity当中只存在一个super顶级的一个fragment;保证唯一性,避免重复创建fragment;
@NonNull
public RequestManager get(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity) {
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
return this.get(activity.getApplicationContext());
} else {
assertNotDestroyed(activity);
//通过Activity获取到FragmentManager
androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager fm = activity.getSupportFragmentManager();
//调用supportFragmentGet方法;
return this.supportFragmentGet(activity, fm, (Fragment)null, isActivityVisible(activity));
}
}
@NonNull
private RequestManager supportFragmentGet(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager fm, @Nullable Fragment parentHint, boolean isParentVisible) {
//创建出一个Fragment SupportRequestManagerFragment 是继承了Fragment
SupportRequestManagerFragment current = this.getSupportRequestManagerFragment(fm, parentHint, isParentVisible);
RequestManager requestManager = current.getRequestManager();
if (requestManager == null) {
Glide glide = Glide.get(context);
requestManager = this.factory.build(glide, current.getGlideLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode(), context);
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);
}
return requestManager;
}
//获取或者创建出Fragment
@NonNull
private SupportRequestManagerFragment getSupportRequestManagerFragment(
@NonNull final FragmentManager fm, @Nullable Fragment parentHint, boolean isParentVisible) {
//先从FragmentManager中去找
SupportRequestManagerFragment current =
(SupportRequestManagerFragment) fm.findFragmentByTag(FRAGMENT_TAG);
if (current == null) {
//没有找到就去缓存容器Map当中去找
current = pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments.get(fm);
if (current == null) {
//如果还是没找到,就new 了一个SupportRequestManagerFragment对象
current = new SupportRequestManagerFragment();
current.setParentFragmentHint(parentHint);
if (isParentVisible) {
current.getGlideLifecycle().onStart();
}
//添加到缓存Map中
pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments.put(fm, current);
//事务添加 commitAllowingStateLoss添加事务 是允许丢失状态,也就是允许添加事务失败
fm.beginTransaction().add(current, FRAGMENT_TAG).commitAllowingStateLoss();
//在handler当中把Map中这个创建的fragment移除了
handler.obtainMessage(ID_REMOVE_SUPPORT_FRAGMENT_MANAGER, fm).sendToTarget();
}
}
return current;
}
ActivityFragmentLifecycle
这个Fragment创建的时候里面创建的ActivityFragmentLifecycle类,实现了生命周期管理的Lifecycle接口;
类中有个集合变量Set,里面存放着监听,也就是外层通过添加监听,来接收这个LifecycleListener监听的回调,这个结合中是存放着弱引用的集合监听;
那就是在创建这个对象的时候,将RequestManager这个实现了LifecycleListener监听的对象传了进来,实现了这个接听里面的方法,然后通过这个类分发出来的界面生命周期而且对请求进行处理;
注意看这个生命周期回调至回调了:onStart、onStop、onDestroy这三个生命周期
package com.bumptech.glide.manager;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import com.bumptech.glide.util.Util;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.WeakHashMap;
/**
* A {@link com.bumptech.glide.manager.Lifecycle} implementation for tracking and notifying
* listeners of {@link android.app.Fragment} and {@link android.app.Activity} lifecycle events.
*/
class ActivityFragmentLifecycle implements Lifecycle {
private final Set<LifecycleListener> lifecycleListeners =
Collections.newSetFromMap(new WeakHashMap<LifecycleListener, Boolean>());
private boolean isStarted;
private boolean isDestroyed;
/**
* Adds the given listener to the list of listeners to be notified on each lifecycle event.
*
* <p> The latest lifecycle event will be called on the given listener synchronously in this
* method. If the activity or fragment is stopped, {@link LifecycleListener#onStop()}} will be
* called, and same for onStart and onDestroy. </p>
*
* <p> Note - {@link com.bumptech.glide.manager.LifecycleListener}s that are added more than once
* will have their lifecycle methods called more than once. It is the caller's responsibility to
* avoid adding listeners multiple times. </p>
*/
@Override
public void addListener(@NonNull LifecycleListener listener) {
lifecycleListeners.add(listener);
if (isDestroyed) {
listener.onDestroy();
} else if (isStarted) {
listener.onStart();
} else {
listener.onStop();
}
}
@Override
public void removeListener(@NonNull LifecycleListener listener) {
lifecycleListeners.remove(listener);
}
void onStart() {
isStarted = true;
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onStart();
}
}
void onStop() {
isStarted = false;
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onStop();
}
}
void onDestroy() {
isDestroyed = true;
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onDestroy();
}
}
}
LifecycleListener 接口
这里只对onStart、 onStop、onDestroy这三个生命周期做回调处理吧
package com.bumptech.glide.manager;
/**
* An interface for listener to {@link android.app.Fragment} and {@link android.app.Activity}
* lifecycle events.
*/
public interface LifecycleListener {
/**
* Callback for when {@link android.app.Fragment#onStart()}} or {@link
* android.app.Activity#onStart()} is called.
*/
void onStart();
/**
* Callback for when {@link android.app.Fragment#onStop()}} or {@link
* android.app.Activity#onStop()}} is called.
*/
void onStop();
/**
* Callback for when {@link android.app.Fragment#onDestroy()}} or {@link
* android.app.Activity#onDestroy()} is called.
*/
void onDestroy();
}
RequestManager
我们来验证下上面说的生命周期,来看看这个RequestManager类;
绑定监听了吧 addListener 传入的是this吧?因为自己是实现了这个监听的接口的吧;
然后三个生命周期的回调方法都实现了吧,生命周期回调过来,自己去做处理吧;
public class RequestManager implements LifecycleListener,
ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<Drawable>> {
......
@Synthetic final Lifecycle lifecycle;
......
private final Runnable addSelfToLifecycle = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//绑定生命周期的监听
lifecycle.addListener(RequestManager.this);
}
};
......
RequestManager(
Glide glide,
Lifecycle lifecycle,
RequestManagerTreeNode treeNode,
RequestTracker requestTracker,
ConnectivityMonitorFactory factory,
Context context) {
......
......
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
mainHandler.post(addSelfToLifecycle);
} else {
//绑定生命周期监听
lifecycle.addListener(this);
}
//绑定生命周期监听
lifecycle.addListener(connectivityMonitor);
......
}
//onStart回调 通过在ActivityFragmentLifecycle 类中绑定的监听回调出来的吧
@Override
public synchronized void onStart() {
resumeRequests();
targetTracker.onStart();
}
//onStop回调
@Override
public synchronized void onStop() {
pauseRequests();
targetTracker.onStop();
}
//onDestroy回调
@Override
public synchronized void onDestroy() {
targetTracker.onDestroy();
for (Target<?> target : targetTracker.getAll()) {
clear(target);
}
targetTracker.clear();
requestTracker.clearRequests();
lifecycle.removeListener(this);
lifecycle.removeListener(connectivityMonitor);
mainHandler.removeCallbacks(addSelfToLifecycle);
glide.unregisterRequestManager(this);
}
}
requestTracker.clearRequests()
我们在上面into小结的时候,提了一嘴,在当前界面关闭的时候,会将活动缓存里面的图片资源添加到内存缓存中,我们来看看onDestroy生命周期中调用的clearRequests这个方法
看方法名就是清理请求;
clearRemoveAndMaybeRecycle这里是最终的清理请求和释放;
我们需要跟进Request接口的clear方法去,这是个接口;
public class RequestTracker {
......
public void clearRequests() {
for (Request request : Util.getSnapshot(requests)) {
// It's unsafe to recycle the Request here because we don't know who might else have a
// reference to it.
clearRemoveAndMaybeRecycle(request, /*isSafeToRecycle=*/ false);
}
pendingRequests.clear();
}
......
private boolean clearRemoveAndMaybeRecycle(@Nullable Request request, boolean isSafeToRecycle) {
if (request == null) {
return true;
}
boolean isOwnedByUs = requests.remove(request);
isOwnedByUs = pendingRequests.remove(request) || isOwnedByUs;
if (isOwnedByUs) {
//我们来看这个clear调用
request.clear();
if (isSafeToRecycle) {
request.recycle();
}
}
return isOwnedByUs;
}
}
这个clear的实现了SingleRequest,还记得我们上面说的SingleRequest这个是with的时候创建吧?不记得童鞋回过头上去看看…
SingleRequest类里面releaseResource里面调用了Engine对象的release方法,我们一步步的跟进去;
@Override
public synchronized void clear() {
assertNotCallingCallbacks();
stateVerifier.throwIfRecycled();
if (status == Status.CLEARED) {
return;
}
cancel();
// Resource must be released before canNotifyStatusChanged is called.
if (resource != null) {
releaseResource(resource);
}
if (canNotifyCleared()) {
target.onLoadCleared(getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
status = Status.CLEARED;
}
private void releaseResource(Resource<?> resource) {
engine.release(resource);
this.resource = null;
}
这里是Engine类中的代码
刚刚SingleRequest类里面releaseResource方法中调用了这个release代码吧?
然后这类调用了EngineResource类中的release方法;
onResourceReleased这个方法中,将活动缓存移除掉对应key的图片资源,并将图片资源添加到内存缓存中去了吧?
往下看↓,我们跟进去
public void release(Resource<?> resource) {
if (resource instanceof EngineResource) {
((EngineResource<?>) resource).release();
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot release anything but an EngineResource");
}
}
//接口回调出来,也就是在资源引用计数器等于0的时候回调过来的
@Override
public synchronized void onResourceReleased(Key cacheKey, EngineResource<?> resource) {
activeResources.deactivate(cacheKey);
if (resource.isCacheable()) {
cache.put(cacheKey, resource);
} else {
resourceRecycler.recycle(resource);
}
}
EngineResource类中的代码
这是个图片资源类,开启同步锁,然后计数器已经小于或者等于0的时候,就抛出异常;否则-1后等于0了,就回调这个接口的方法;
onResourceReleased这个方法?那不就是走到了上面这个Engine类中?
void release() {
synchronized (listener) {
synchronized (this) {
if (acquired <= 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot release a recycled or not yet acquired resource");
}
if (--acquired == 0) {
listener.onResourceReleased(key, this);
}
}
}
}
小结
这里就是上面说的当前界面退出时,将活动缓存中的图片资源又添加到了内存缓存中
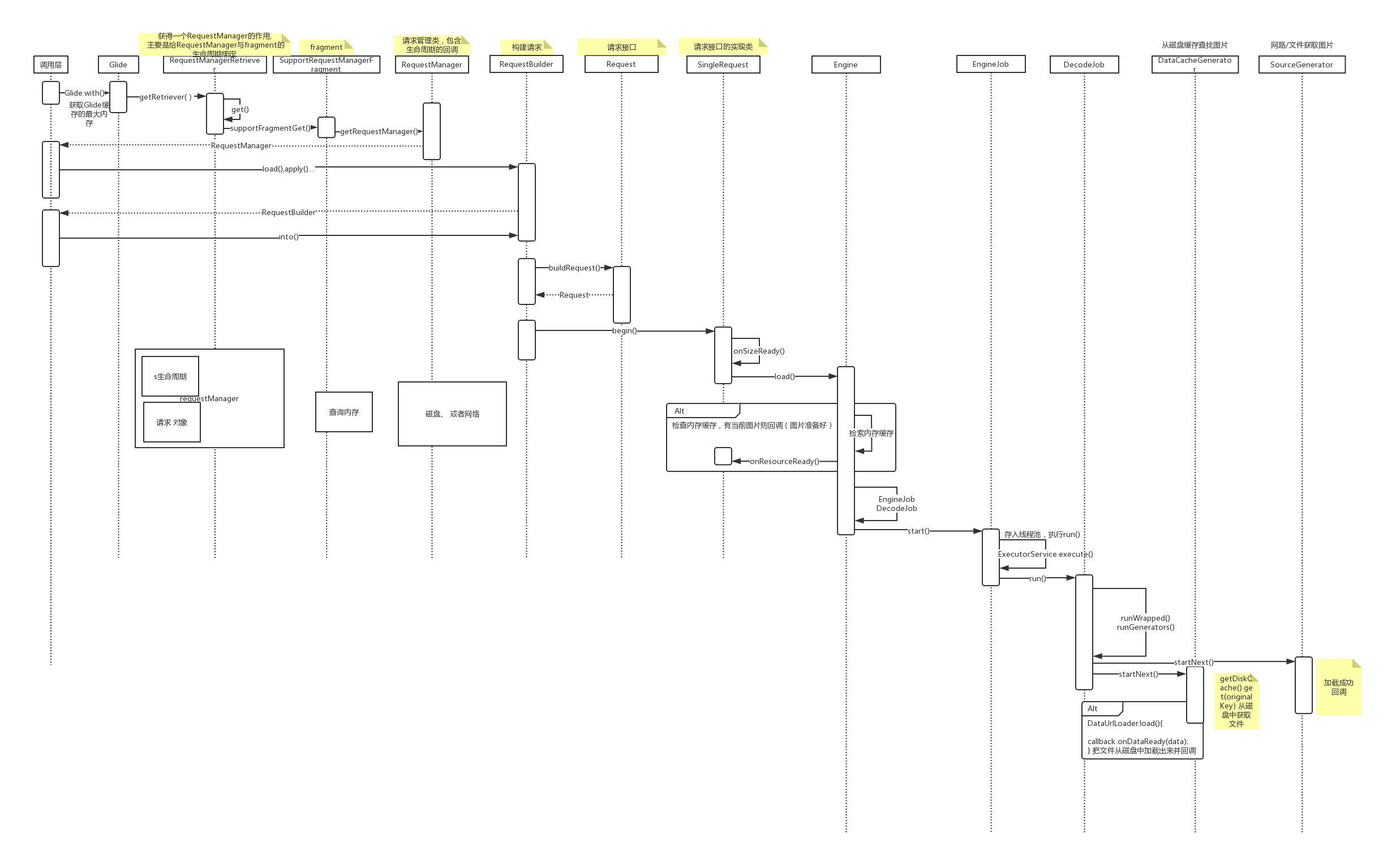
流程图
Glide加载的大致流程方向
Glide生命周期绑定类图
辛苦各位童鞋观看到最后,如果博客中有不对的地方望指出,大神勿喷,谢谢~~
最后
以上就是懦弱银耳汤最近收集整理的关于Android-图片加载GildeAndroid-图片加载Gilde的全部内容,更多相关Android-图片加载GildeAndroid-图片加载Gilde内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复